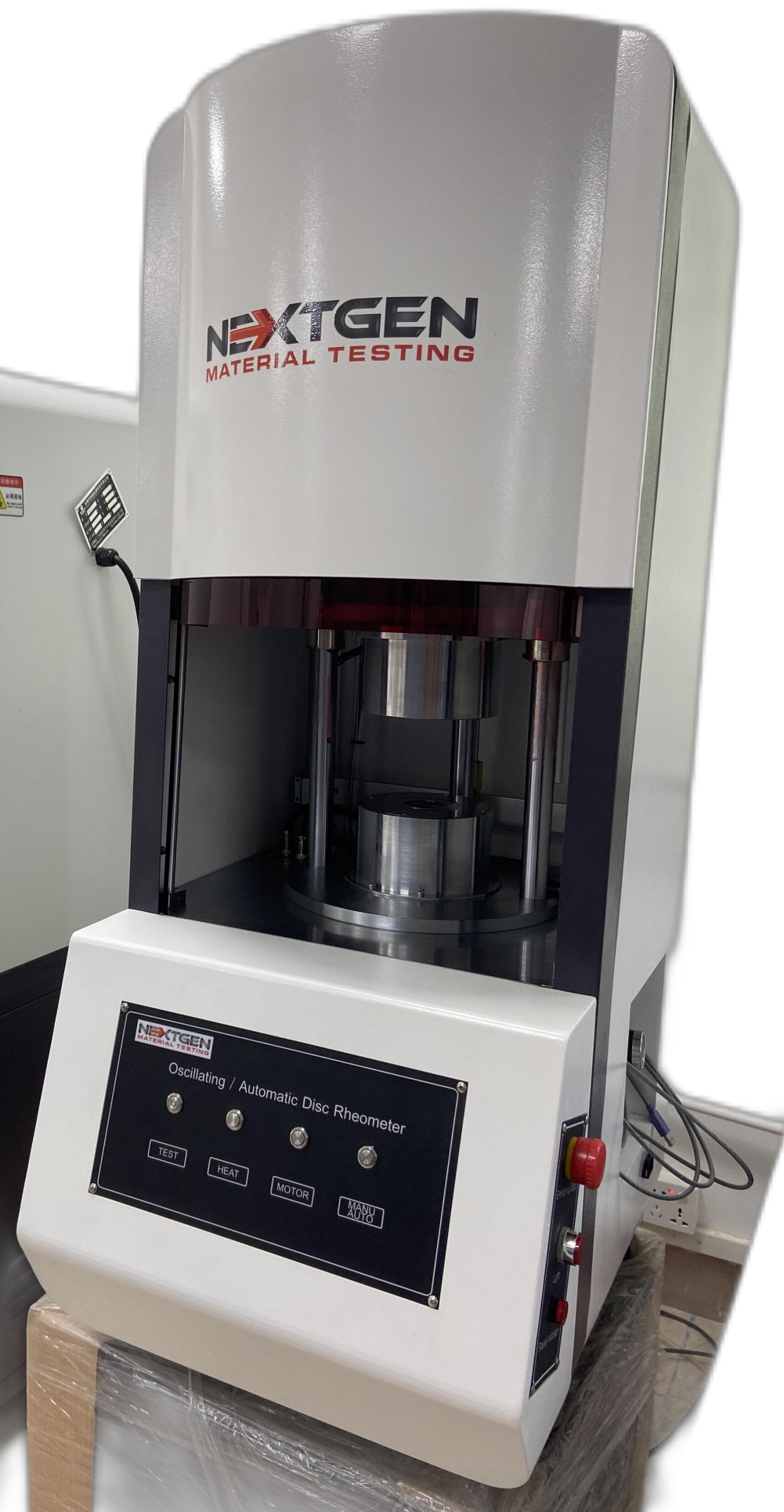

Rubber Testing Equipment

Standards
ASTM D2084, ASTM D5289, ISO 6502






Description
This machine is designed to get the characteristic curve and characteristic parameters of rubber vulcanization by measuring the applied moment of rubber to the oscillating dye body. NG-ODR rotor-free vulcameter has an excellent stability of results. The data and diagrams can be used as a reference for development, research and production quality.
NG-ODR describes precisely and quickly the curing and processing characteristics of vulcanized rubber compounds. It works on a very simple principle. A test piece of rubber compound is contained in a sealed test cavity under positive pressure and maintained at a specified elevated temperature. A Rotor (oscillating disc) is embedded in the test piece and is oscillated through a small specified rotary amplitude. This action exerts a shear strain on the test piece and the torque (force) required to oscillate the disc depending on stiffness (shear modulus) of the rubber compound.
Functionality
- Database functionality can store your curves, drawings and results for printing at any time.
- Allows you to export your testing results in Excel format.
- It has multiple analysis functions like statistics, deviation setting, standard curve setting, and CPK statistical calculations
- Interface allows for local zoom and curve comparison
- It has such functions as selection of any vulcanization time, range selection and screen capture.
- It can reanalyze your previous test data, and increase or modify the reports according to the users requirements
- Multiple data sequences provide convenient ways for data retrieval
Testing Curve and Results
- ML - Minimum torque (dNm) - Measures value of the vulcanization characteristic (viscosity) of the unvulcanised test sample
- MH - Maximum torque (dNm) - Measures value of the shear modulus or rigidity of the fully vulcanized test sample. This includes the maximum torque of the flat curve and titration curve as well as the maximum torque when the flat and titration curves don't appear within the given time.
- Ts1 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 1dNm when the swing angle is 0.5° or 1°
- Ts2 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 2dNm when the swing angle is 3°
- Ts10 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 10(MH-ML)/100dNm
- Ts30 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 30(MH-ML)/100dNm
- Ts60 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 60(MH-ML)/100dNm
- Ts90 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 90(MH-ML)/100dNm, reflecting the optimum vulcanization of your testing specimen
Standard Configurations
Sealing rings: 10pcs
Heating plate: 2pcs
High temperature paper: 3 copies
Desktop (PC): 1 set
Printer: 1 set
Hexagonal wrench: 1 set
Technical Specifications
| Temperature Range | Room Temperature to 22°C - 200°C |
| Temperature Accuracy | Within ±0.3°C |
| Temperature Display Resolution | 0.01°C |
| Oscillation Frequency | 1.6Hz, (100r/min) |
| Heating Rate | 120 °C / min |
| Torque Range | 0 - 20nm |
| Minimum Torque Reading | 0.001nm |
| # of Swing Angles | ± 0.5°C ± 1°C ± 2°C (standard matching angle 1 degree) |
| Swing Angle | 100r / min (1.66hz) |
| Control | Computer Controlled |
| Communication Mode | COM Port |
| Air Pressure | 65psi (4.6 bar) - Not including air compressor |
| Specimen Dimensions | 5cm |
| Display | NextGen Software |
| Dimension (W x D x H) | 51.5x22x24.4" 131x56x62cm |
| Weight | 498lbs / 226kg |
| Power | 110V/60Hz or 220V/50Hz 1000 W |
FAQs
While maintaining or even increasing the elastic qualities of rubber, vulcanization reduces its plasticity. In the past, the term "vulcanization" was primarily used to describe the reaction between sulphur and rubber, but it is now typically used to describe any process that modifies a material's characteristics, whether it be caused by sulphur or another substance.
Practical vulcanization techniques rely on the transfer of heat from the exterior to the inside of the object being cured. Since compounding adjustments cannot significantly alter the heat conductivity of realistic rubber compounds, increasing temperature is a frequent way to hasten the vulcanization process. The most recent curing or moulding techniques, like injection moulding, the liquid curing medium (LCM) method, and microwave curing, employ higher curing temperatures.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR weights 498lbs / 226kg, has the following dimensions: 51.5x22x24.4" / 131x56x62cm, and power: 110V/60Hz or 220V/50Hz 1000 W
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
If the vulcanization temperature is raised when silicone rubber products are being moulded, both the vulcanization time and efficiency can be effectively increased. As a result, many vulcanization moulding experts will begin their processes as soon as the temperature rises in order to speed up the moulding of custom silicone rubber keypads. Sometimes it does shorten the cure period, but other times it is counterproductive and causes a lot of numbness and rupture rather than enhancing productivity.
Natural rubber (NR) vulcanization temperature recommendations: the most suitable range is 140 to 150 °C, with a maximum temperature of 160 °C.
Butadiene rubber (BR), isoprene rubber (IR), and neoprene rubber (CR) should be vulcanized at temperatures between 150 and 160 °C, with the peak temperature not surpassing 170 °C.
The suggested vulcanization temperature for SBR and NBR is over 150°C, with the peak temperature not exceeding 190°C.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) temperature display resolution is 0.01°C.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
By monitoring the applied moment of rubber to the oscillating dye body, this machine is intended to obtain the characteristic curve and characteristic parameters of rubber vulcanization. The results are quite stable when using the NG-ODR rotor-free vulcameter. The information and diagrams can be consulted for development, research, and product quality.
NG-ODR precisely and promptly describes the curing and processing characteristics of rubber compounds that have been vulcanised. It operates on a very basic idea. Under positive pressure and while being kept at a predetermined high temperature, a test piece of rubber compound is kept inside a sealed test cavity. A Rotor (oscillating disc) that is placed in the test component oscillates via a limited rotary amplitude that is determined. The test piece experiences a shear strain as a result of this motion. Depending on the stiffness (shear modulus) of the rubber compound a torque is required to oscillate the disc.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) is computer controlled.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
Rubber undergoes physical modification during vulcanization as a result of being forced to retract. Of course, mechanical techniques can also make rubber retract using force. But vulcanization is different since the rubber's natural shape is preserved. Rubber shrinks during the vulcanization process while maintaining its original shape. The process of vulcanization essentially shrinks rubber without distorting or changing its shape.
Vulcanization not only modifies rubber's size while maintaining its shape but also guards against further deformation. Rubber hardens and becomes less prone to distortion as it contracts. Vulcanized rubber won't deform as easily as regular, non-vulcanized rubber, but it may still distort if subjected to significant stress.
When rubber is vulcanized, it also becomes harder, increasing its tensile strength and lowering the possibility of physical harm.
The swing angle parameter for NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) is 100r / min (1.66hz).
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
Depending on where it comes from, rubber can be divided into natural rubber and synthetic rubber.
Latex, a milky-white liquid produced by the rubber tree (Hevea Brasiliensis) or other plants, is the source of natural rubber.
Conversely, synthetic rubber is a man-made polymer made from petroleum waste. Rubber is now thermoplastic, squishy, and sticky and has low tensile strength and elasticity.
The qualities of both natural and synthetic rubber can be enhanced by vulcanization, turning them into a strong, hard, non-thermoplastic substance with increased tensile strength.
The vulcanization process involves three stages:
The crosslinking process begins at a temperature between 180 °F (82 °C) and 230 °F (110 °C) during the flow duration of the induction step.
Permanent crosslinks are created during the curing stage, which is ultimately influenced by the rubber's composition, activity level, reaction time, temperature, and curing stage conditions.
All of the qualities in the rubber compound are generated as the curing process progresses to the point where it reaches its elastic behaviour in the final stage, also known as the optimum condition of cure.
The specimen dimensions for NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) are 5 centimetres.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
The rheometer measures the vulcanization strength required for the test specimen's deformation. The term "rheometer curve" refers to the strength's shift over time. These curves aid in assessing the rubber compound's quality.
These are the testing curves and results for NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR):
- ML - Minimum torque (dNm) - Measures value of the vulcanization characteristic (viscosity) of the unvulcanised test sample
- MH - Maximum torque (dNm) - Measures value of the shear modulus or rigidity of the fully vulcanized test sample. This includes the maximum torque of the flat curve and titration curve as well as the maximum torque when the flat and titration curves don't appear within the given time.
- Ts1 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 1dNm when the swing angle is 0.5° or 1°
- Ts2 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 2dNm when the swing angle is 3°
- Ts10 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 10(MH-ML)/100dNm
- Ts30 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 30(MH-ML)/100dNm
- Ts60 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 60(MH-ML)/100dNm
- Ts90 (Minimum) - Time in which the torque is increased to ML + 90(MH-ML)/100dNm, reflecting the optimum vulcanization of your testing specimen
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
An elastomer that has been strengthened by the biochemical process of vulcanization is known as vulcanized rubber. A curing agent, typically sulphur, is mixed with the milky latex from the rubber tree and heated under pressure.
Rubber and sulphur are chemically combined during vulcanization. The sulphur atoms join lengthy chains of rubber molecules when under high pressure and heat. This lessens the stickiness of the rubber while increasing its strength and durability. Additionally, it enables the rubber to maintain its flexibility across a much larger temperature range, making vulcanized rubber significantly more beneficial for a variety of applications.
Rubber becomes more durable, resilient, and heat resistant by vulcanization, making it more useful for industrial applications and some products. Vulcan, the Roman deity of fire and metalworking, is the source of the word "vulcanized."
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) is designed to get the characteristic curve and characteristic parameters of rubber vulcanization by measuring the applied moment of rubber to the oscillating dye body.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
Rubber and a functional group undergo vulcanization, a chemical process that is typically triggered by heat. As a result, the product is more durable, elastic, resilient, and resistant to solvent action and temperature fluctuations than the original polymer was.
Chemical vulcanization involves heating rubber at 140–160 °C with sulphur, an accelerator, and an activator. Longer rubber molecules are cross-linked during the process to improve elasticity, resilience, tensile strength, viscosity, hardness, and weather resistance.
Rubber is reduced in size by vulcanization without changing or deforming its shape. Additionally, it keeps its shape, guarding against further deformation of the rubber.
Using the most common vulcanizing agent to vulcanize the rubber Rubber that is not saturated begins to cross-link when sulphur is added. Sulphur, as a vulcanizing agent, does not, however, work quickly. Chemical reactions involving rubber and hydrocarbons frequently include double bonds or C==C, and each cross-linking requires 40–55 sulphur atoms without an accelerator.
The torque range of NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) is 0 - 20nm
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
Rubber that has been vulcanized is substantially stronger than regular rubber. Since it can handle more strain and stress, many manufacturing companies choose it.
Rubber that has been vulcanized is also more elastic than unvulcanized rubber. Many individuals believe that flexibility and strength are related. However, just because something is sturdy doesn't automatically rule out the possibility of it being elastic. Rubber that has been vulcanized is durable and stretchy. It may be stretched further without permanently deforming, thanks to its improved flexibility.
Traditional rubber is often less resistant to abrasion than vulcanized rubber. Damage from scraping is what is meant by abrasion. Rubber that has been vulcanized is stronger and harder than unvulcanized rubber, which makes abrasion damage less likely.
When the rubber reaches a temperature of between 300 and 400 degrees Fahrenheit, it is taken out of the heating chamber and left to cool.
The temperature range of NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) is Room Temperature to 22°C - 200°C.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing
Any sort of rubber that has been made harder by using heat and sulphur is vulcanized rubber. It is created by a curing process in which heat and sulphur cause the rubber's elastomers to harden. New cross-links are formed in the rubber as a result of exposure to heat and sulphur, making it stronger and more elastic overall.
A multi-step vulcanization method is used to create vulcanized rubber. The rubber is first immersed in a sulphur and additive-filled solution. Sulphur is the main component that promotes vulcanization. However, it is combined with additional chemicals. Both colour-enhancing pigments and a process accelerator may be included in the bath.
The rubber is then shaped in the manner desired. Moulding vulcanized rubber is difficult. Instead, because of its strength and flexibility, it is challenging to mould. As a result, the rubber is moulded after being immersed in a sulphur and additive bath.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) temperature accuracy is within ±0.3°C.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
The curing and processing characteristics of vulcanized rubber compounds are precisely and promptly described by NG-ODR. It operates on a fairly straightforward idea. A test piece of rubber compound is kept at a predetermined elevated temperature and enclosed in a sealed test cavity under positive pressure. The test item contains an embedded Rotor (oscillating disc) that oscillates through a narrow range of rotary amplitudes. The test piece experiences a shear strain as a result of this action, and the torque (force) necessary to cause the disc to oscillate depends on the stiffness (shear modulus) of the rubber compound.
Rubber is created through a series of activities that entail the addition of value-adding material through chemical reactivity, irreversible physical feature modification, and flow. Extrusion, calendaring, vulcanization, and breaking down the polymer through mastication on a mill are the processes that are crucially important during chemical modification in tyre production.
The lead time for NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) is 2-5 Months Depending on when the PO is placed.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
This device is intended to measure the applied moment of rubber to the oscillating dye body in order to obtain the characteristic curve and characteristic parameters of rubber vulcanization. The results from the NG-ODR rotor-free vulcameter are highly stable. The information and illustrations can be used as a guide for development, investigation, and product quality.
Sulphur is necessary for the majority of vulcanizing techniques. Sulphur does not vulcanize synthetic polyolefins since it is a sluggish vulcanizing agent. Various substances that alter the kinetics of crosslinking are used to accelerate vulcanization; this mixture is frequently referred to as a cure package. Most street-legal car tyres are made of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), which is the primary polymer exposed to sulphur vulcanization. For the substrate and application, the cure package is customized.
Here is the list of standard accessories of NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR):
- Sealing rings - 10
- Heating plate - 2
- High temperature paper – 3
- Desktop computer – 1
- Hexagonal wrench – 1
- Printer – 1
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
A number of procedures are used for vulcanizing rubbers. The most popular method of treating natural rubber with sulphur was the only one to which the phrase originally applied. It has expanded to now include several methods for hardening other (synthetic) rubbers. Examples include the room-temperature vulcanization of silicone rubber and the use of metal oxides to vulcanize chloroprene rubber (neoprene).
The term "vulcanization" and "curing" are occasionally used synonymously in this context. Vulcanization is the process of curing elastomers. It functions by creating cross-links between polymer chain segments, increasing the material's rigidity and endurance, as well as altering its mechanical and electrical properties. Similar to the curing of other thermosetting polymers, vulcanization is typically irreversible.
Rubber hoses, shoe bottoms, toys, erasers, conveyor belts, vibration mounts/dampers, insulating materials, tyres, and bowling balls are just a few examples of the many applications for vulcanized materials. Most rubber products are vulcanized, which greatly increases their strength, durability, and longevity.
The air pressure of NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) is 65psi (4.6 bar) - Not including air compressor
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
The recurrent or periodic change of a quantity around a central value (often an equilibrium point) or between two or more different states is known as oscillation. An alternating current and a swinging pendulum are two common examples of oscillation. In physics, oscillations can be used to simulate complex interactions like those between atoms.
The beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator-prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, the vibration of strings in guitars and other string instruments, the periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy are just a few examples of dynamic systems that oscillate outside of mechanical systems.
When it comes to processing control and control theory (as in sliding mode control), where the goal is the convergence to a stable state, oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesired feature. It is referred to as chattering or flapping in these situations, such as valve chatter and route flapping.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) oscillation frequency is 1.6Hz, (100r/min).
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
Here are the technical specifications of NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR):
|
Temperature Range |
Room Temperature to 22°C - 200°C |
|
Temperature Accuracy |
Within ±0.3°C |
|
Temperature Display Resolution |
0.01°C |
|
Oscillation Frequency |
1.6Hz, (100r/min) |
|
Heating Rate |
120 °C / min |
|
Torque Range |
0 - 20nm |
|
Minimum Torque Reading |
0.001nm |
|
# of Swing Angles |
± 0.5°C ± 1°C ± 2°C (standard matching angle 1 degree) |
|
Swing Angle |
100r / min (1.66hz) |
|
Control |
Computer Controlled |
|
Communication Mode |
COM Port |
|
Air Pressure |
65psi (4.6 bar) - Not including air compressor |
|
Specimen Dimensions |
5cm |
|
Display |
NextGen Software |
|
Dimension (W x D x H) |
51.5x22x24.4" |
|
Weight |
498lbs / 226kg |
|
Power |
110V/60Hz or 220V/50Hz |
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
List of features of NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR):
- Alpha closed mold cavity structure;
- Body surface treatment: American DuPont powder and electrostatic painting process are adopted. It is cured at 200 ℃ to ensure long-term color fastness;
- The alpha force sensor technology is adopted;
- The control accuracy of the heating plate at the inlet of the upper and lower mold cavities shall be within ± 0.15 ℃;
- The result report can be printed directly to check the change of vulcanization curve;
- LED lighting observation is set in the box;
- Software control can independently correct PID parameter values;
- Oil water separator with secondary pass rate self-locking;
- The machine is equipped with self-seat platform, storage box cabinet and • convenient mobile platform;
- The mechanical parts are composed of non-corrosive structural aluminum and stainless steel materials;
- Metal led button, waterproof, safe and durable, soft vision;
- Color LCD touch screen controls and displays, human-computer interaction interface, simple operation, convenient maintenance, stability and reliability;
- One button automatic test, simple and convenient operation
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) has the following functionality:
- Your curves, drawings, and results can be stored in a database for printing at any time.
- Provides the option to export test results in Excel format.
- Numerous analytical features are available, including statistics, deviation setting, standard curve setup, and CPK statistical computations.
- Curve comparison and local zoom are features of the interface.
- It includes options for choosing any vulcanization time, choosing a range, and screen capture.
- Your earlier test data can be reanalyzed, and the reports can be expanded or changed to meet the needs of the user.
- Data retrieval is made simple by the existence of several data sequences.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
When a rubber compound is vulcanized, its properties change, and the vulcanization characteristics can be discovered by observing how the qualities vary with temperature and time. The tools known as curemeters are used to apply cyclic stress or strain to a test piece and measure the resulting strain or force in order to identify the features of vulcanization. The test is typically conducted at a predetermined constant temperature, with the stiffness measurement being continually recorded as a function of time.
The rubber becomes more rigid as the vulcanization process continues. When the observed stiffness reaches a plateau or a maximum and then starts to fall, vulcanization is complete. The loss of stiffness in the latter instance is brought on by reversion. When the observed stiffness keeps increasing (marching-modulus cure), vulcanization is regarded as complete after a certain time.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) complies with ISO 6502 standard.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
ASTM D5289 test method describes how to use sealed and unsealed torsion shear cure metres to measure certain vulcanization properties of rubber compounds. The outcomes from the two different types of instruments could differ.
NOTE: Test Approach ASTM D2084 provides an alternate method for determining vulcanization characteristics.
The values given in SI units should be taken as the norm. Parenthetical values are provided only for informational purposes.
This standard does not claim to resolve all, or even some, safety issues connected to its use. The user of this standard shall adopt adequate safety, health, and environmental practices and shall before use, determine the application of any regulatory constraints.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) complies with ASTM D5289 standard.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
In the cure metre test cavity, a test sample of vulcanizable rubber compound is placed, and after a closure action, it is enclosed in a sealed cavity under positive pressure. The cavity is kept at a higher-than-normal vulcanization temperature. After the dies are closed, a biconical disc is completely encased in rubber. The test specimen experiences a shear strain as a result of the disc oscillating via a short rotating amplitude (1° or 3°). As a function of time, the force needed to rotate or oscillate the disc at its greatest amplitude is continually recorded, with force being proportional to the shear modulus (stiffness) of the test specimen at the test temperature.
The test is considered to be finished when the recorded torque reaches its equilibrium or maximum value or when the allotted amount of time has passed.
NextGen’s Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR) complies with ASTM D2084 Standard.
Click here to obtain a personalized quote from NextGen Material Testing.
For Torque characteristics, the MI (Initial torque), ML (Minimum Torque) and MH (Maximum Torque) can be ready from the Cure Curve. Time values are indicated as ts2 (Induction time), ts5 (scorch time), tc50 (optimum cure time) and tc90 (optimum cure time). Finally, the derived values consist of the curing rate "CR", the Thermoplasticity (Tp=MI-ML) as well as the Reversion time "RT".
The Cure Curve is the measure of Torque Vs Cure Time and is a clear indication of all the rubbers vulcanization characteristics. The Cure Curve, or Rheograph, is separated into three phases. Phase 1 provides a good indication of the processing behavior of the compound. Phase 2 provides the technician with information on the curing characteristics. Phase 3 supplies information on the physical traits and properties of the rubber compound.
A test specimen of a rubber compound is contained in a sealed test cavity which is held under a positive pressure and maintained at a specified elevated temperature dictated within the ASTM or ISO standard. A rotor (biconical disc) is embedded in the test specimen and is oscillated through a specific rotary amplitude. The rotor exerts a shear strain on the specimen and the torque required to oscillate the rotor depends on the toughness of the compound.
The vulcanization of rubber is defined as the curing of elastomers – in other words, it is the analysis of the processes involved with the hardening of rubbers. Knowing the characteristics of the vulcanization process can help determine the rubbers rigidity and durability, as well as other mechanical and electrical properties of the material.
The Rheometer is used to evaluate test batches and ensure consistency. Since materials are mixed in batches, there can be variations which need to be controller and limited to ensure a consistent product being produced. By testing material from different batches, production environments can set acceptable upper and lower control limits, ranges, the mean and standard deviation with reference to Rheological parameters. With this information, future batches can then be tested and easily fit within set Pass/Fail criteria.
The Rheometer allows for the curing characteristics of the Rubber Compound to be evaluated while also monitoring the processing characteristics and the physical properties of the test specimen. The "Cure Curve" provided after the test is the diagnostic of the compounds vulcanization and processing character.
The testing results of the Oscillating Disk Rheometer can be used for quality control in rubber manufacturing plants, for research and development on raw rubber compounded in an evaluation formulation and for analyzing raw materials in the preparation of rubber compounds.
Related Products

NG-EML Series A – Single Column Bench Top Universal Testing Machine (50 N – 5 kN)
The NG-EML Series A – Single Column Bench Top UTM (50 N–5 kN) is a precision electromechanical system designed for tension, compression, and flexural testing of low-force specimens. Featuring GenTest™ software, a high-speed servo drive, Class 0.5 accuracy, and USB/Ethernet control, this compact tabletop unit supports ASTM, ISO, and EN standards. Ideal for testing plastics, rubber, foams, films, composites, and thin metals.

ICI / Mace Snag Tester
Discover the Fabric Textile ICI / Mace Snag Tester, a reliable tool for assessing fabric snagging under normal wear conditions.

Moving Die Rheometer (MDR)
Introducing the NG-MDR Moving Die Rheometer, your solution for accurately assessing the curing and processing characteristics of vulcanized rubber compounds. Designed for precision, this state-of-the-art rheometer captures the characteristic curve and parameters of rubber vulcanization by measuring the torque applied to the oscillating die.

Aging Oven – High-Temperature Chamber – NG-AGOV-ADV
The NG-AGOV-ADV Aging Oven is designed for high-temperature testing of rubber, plastics, and insulating materials. It features programmable PID control, uniform airflow, and forced convection for stable and repeatable aging cycles. This system supports global testing standards including ISO 188, ASTM D573, and IEC 60216-4-1. With its durable stainless-steel chamber and user-friendly interface, it’s ideal for R&D, quality control, and certification labs.
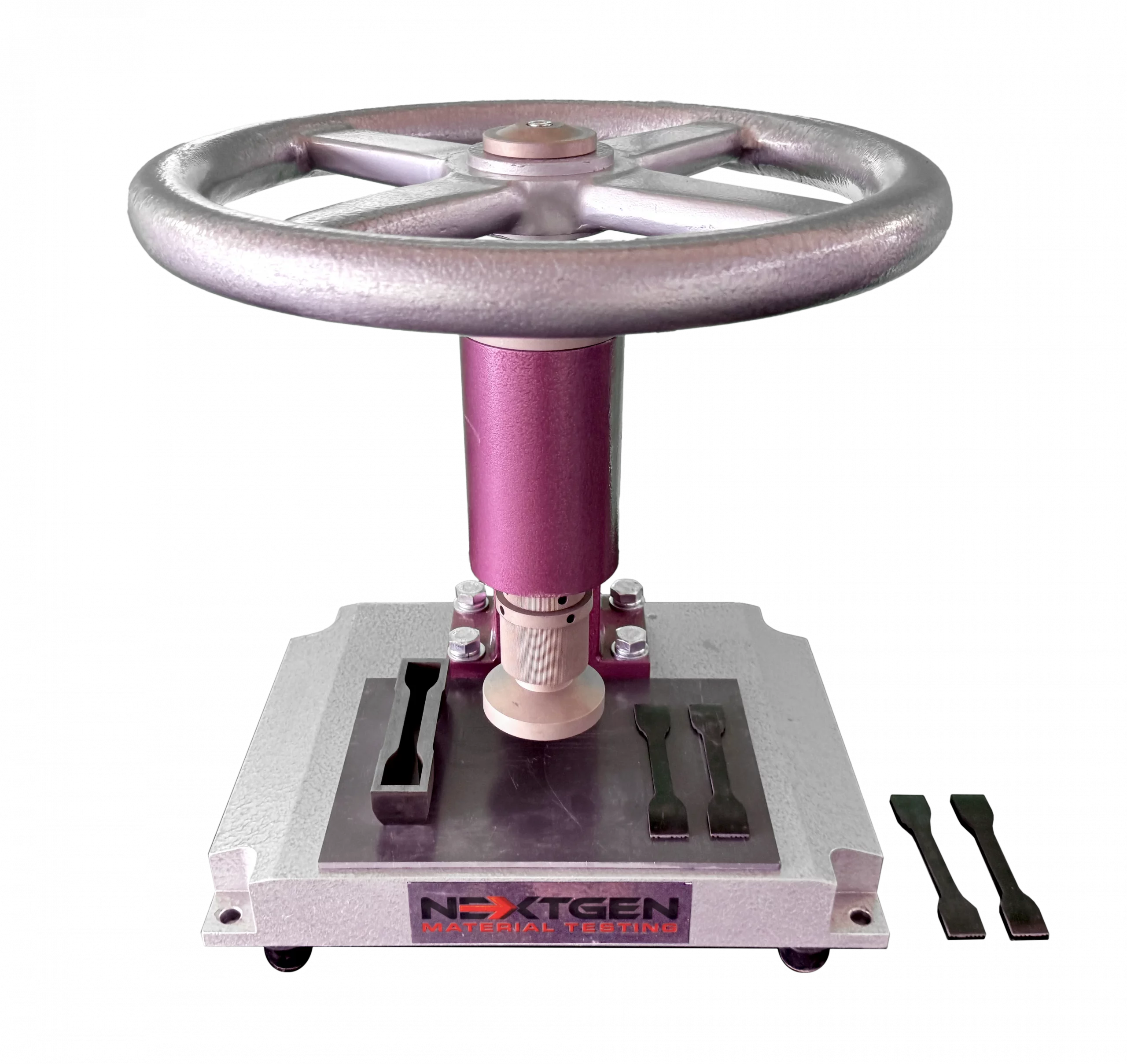
NG-T-Press M Series - Manual Cutting Press System for Rubber Tensile Specimens
Our newest manual cutting press system is suitable for laboratories to create specimens from rubber, tape, and special materials.
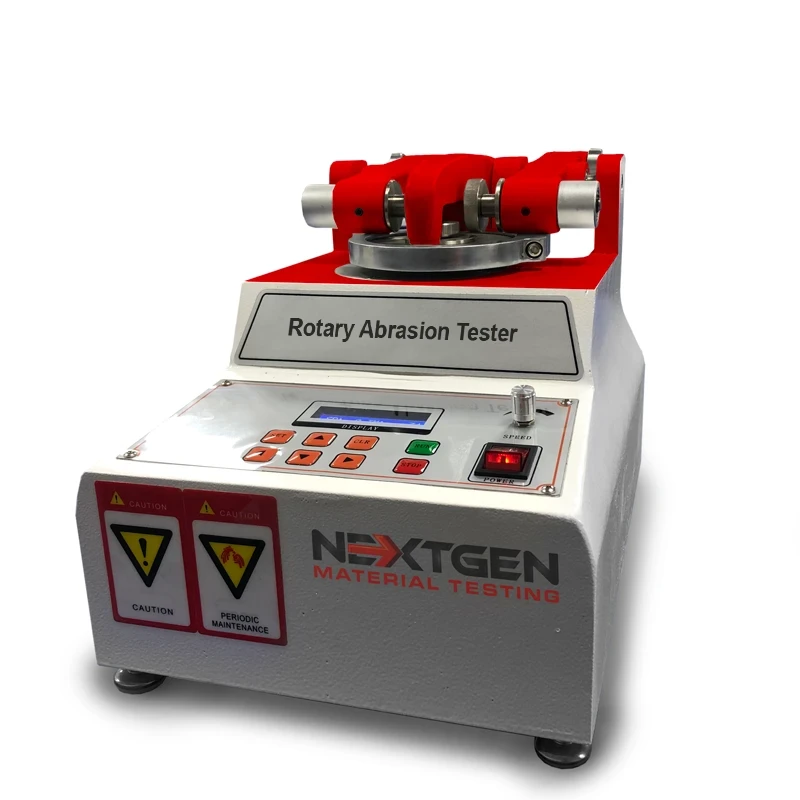

Rotary Abrasion Tester Single & Dual Wheel
GenRotary used evaluate abrasion resistance. It can conduct tests on a wide range of materials such as: cloth, paper, paint, plywood, leather, tile, glass, rubber etc. It tests the specimen by rotating it while in contact with the grinding wheel and applying the required pressure. The Joss of weight reflects on the change in weight of the specimen. The unit also has an intelligent power failure recovery function.
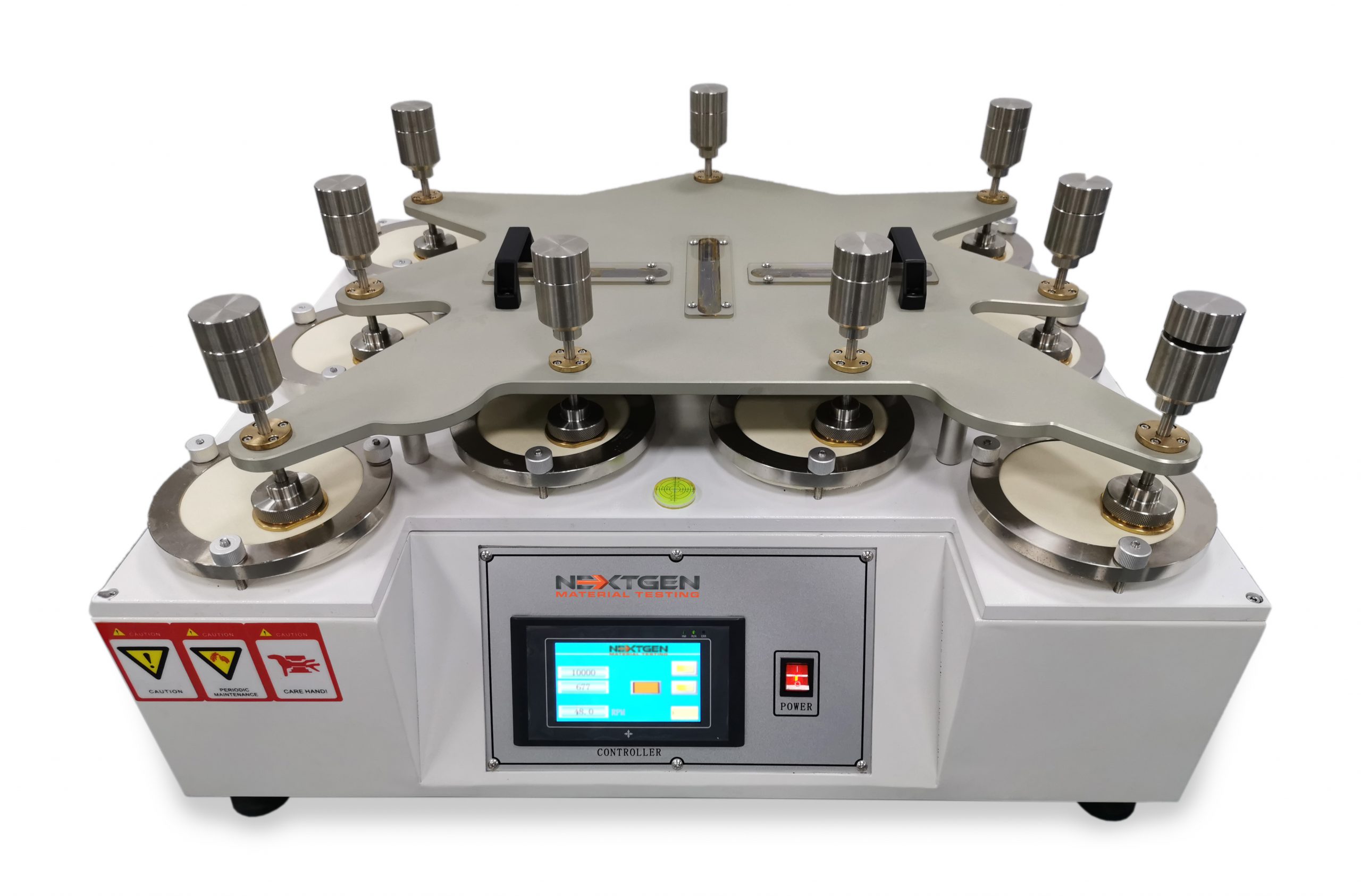

9-Station Martindale Abrasion Tester
The GenDale - Martindale Abrasion Tester is mainly used to test shoe fabric, shoe lining, and many other types of shoe related materials.
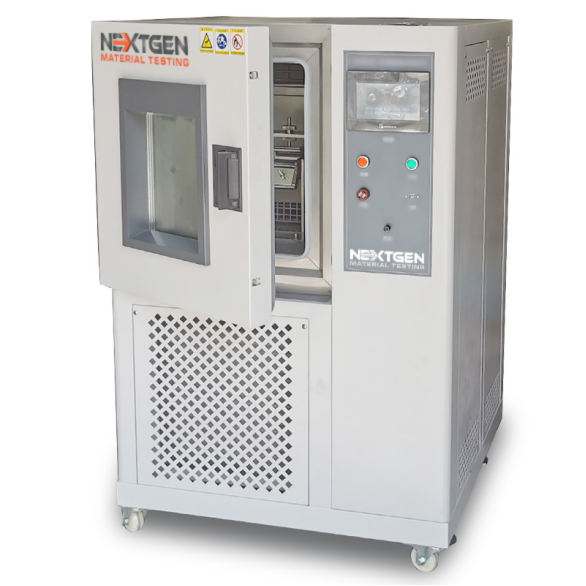

GenRoss-CH - Ross Flex Tester with Low Temperature Chamber
GenRoss-CH is an advanced Ross Flex Tester designed for assessing the cold resistance of materials in low temperature environments.
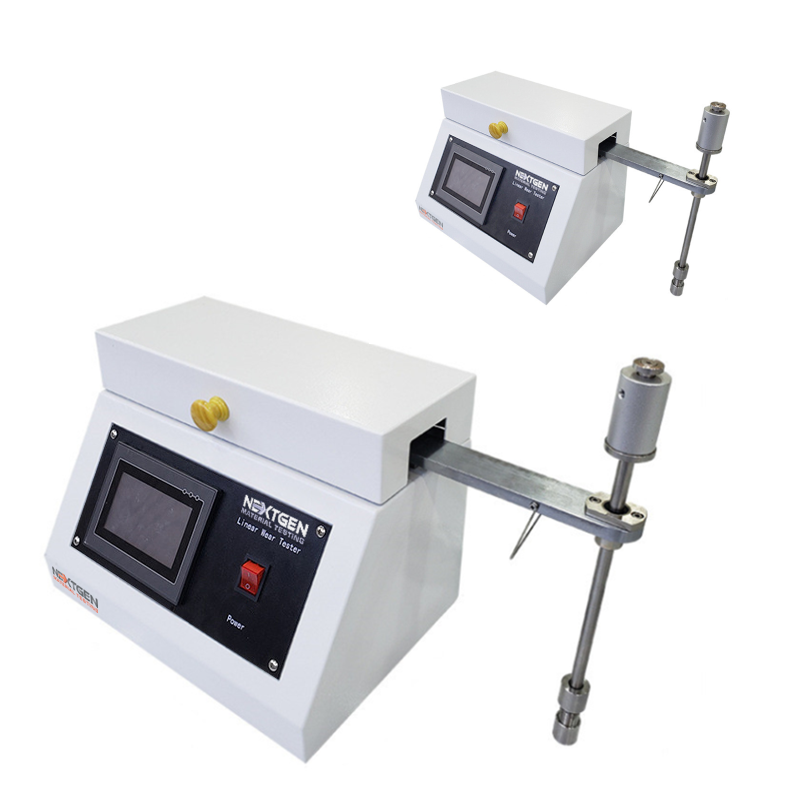

Linear Abrasion Tester
NextGen's linear abrasion meters evaluate the abrasion and scratch resistance of products, along with color transmission.

NextGen Environmental Chambers NG-EC 100,150,225,408,1000
The temperature and humidity NextGen Environmental Chambers features a sturdy cabinet made of cold-rolled steel and stainless steel.

digiChamber - Temperature Controlled Hardness Testing
Discover digiChamber from NextGen Material Testing, the advanced temperature-controlled hardness tester developed by Bareiss.

HDA 120 - Hardness and Density Automation Test System
The HDA 120 test system is a versatile solution for semi-automatic detection of sample hardness and density.

RPA Ultra - Advanced Rubber Process Analyzer Rheometer
RPA Ultra is an advanced rubber process analyzer rheometer that measures the dynamic and static characteristics of raw rubber compounds

NG-EML Series B – Dual Column Bench Top Universal Testing Machine (100 N – 10 kN)
The NG-EML Series B is a high-precision dual-column benchtop universal testing machine engineered for tensile, compression, and flexural testing in the 0.1 kN to 10 kN range. It features Class 0.5 accuracy, a rigid FEM-optimized frame, and a direct-drive servo system with advanced closed-loop control, making it ideal for testing rubber, plastics, metals, composites, and high-performance polymers in both R&D and quality assurance settings.
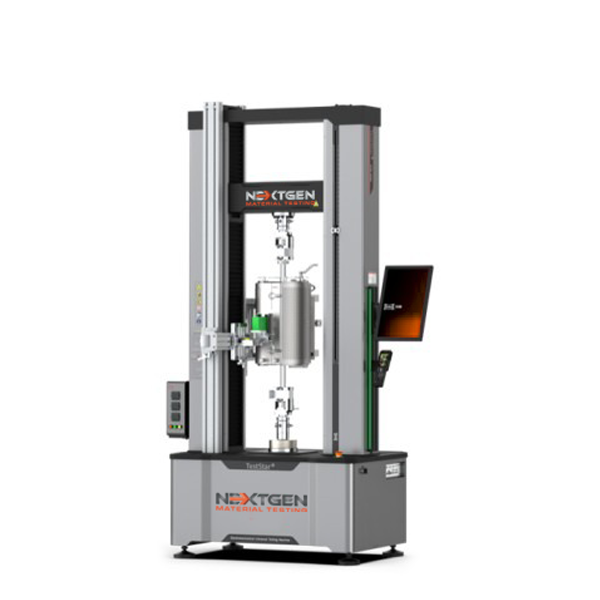

NG-EML Series C – Dual Column Bench Top and Floor Standing Universal Testing Machine (5 kN – 50 kN)
The NG-EML Series C is a precision-engineered dual-column universal testing machine for tension, compression, and flexural testing of metals, composites, rubbers, and polymers. Available in both bench-top and floor-standing formats, with force capacities from 5 kN to 50 kN and Class 0.5 accuracy.
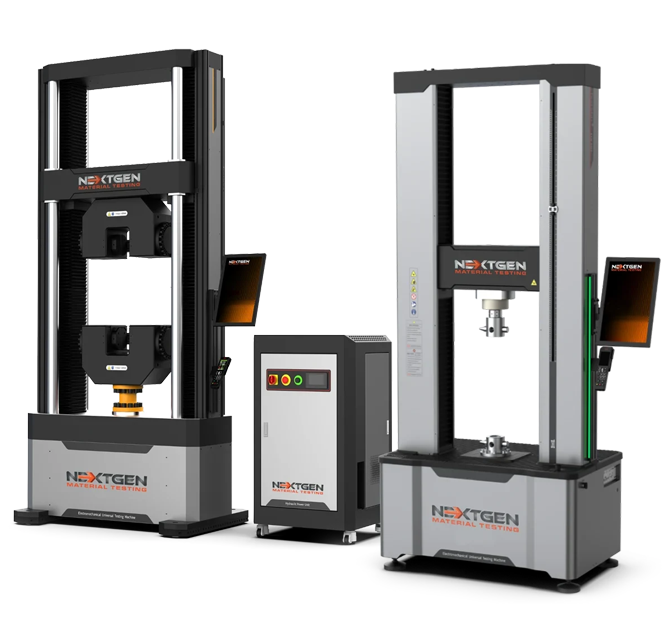

NG-EML Series D – Floor Standing Universal Testing Machine (50 kN – 1000 kN)
The NG-EML Series D – Floor Standing Universal Testing Machine (50 kN–1000 kN) is a dual-column system for tensile, compression, flexural, shear, and cyclic testing of high-strength metals, composites, polymers, and advanced materials. Available in single-space and dual-space configurations, it meets ASTM E8, ISO 6892-1, ISO 527, and GB/T 228 standards. With closed-loop control, 1200 Hz sampling, ultra-low speeds (0.00005 mm/min), and waveform generation, it is ideal for aerospace, automotive, construction, and research labs.

GenTest – Advanced UTM Testing Software
GenTest Software provides test control and data acquisition for universal testing machine workflows used in quality control and materials testing. It combines method templates, step-based sequencing, live curve monitoring, and built-in calculations in one environment. The software supports standards-based testing programs aligned with ASTM, ISO, DIN, EN, and BS. Results and reports remain linked to the method and specimen inputs for consistent review, auditing, and customer documentation.
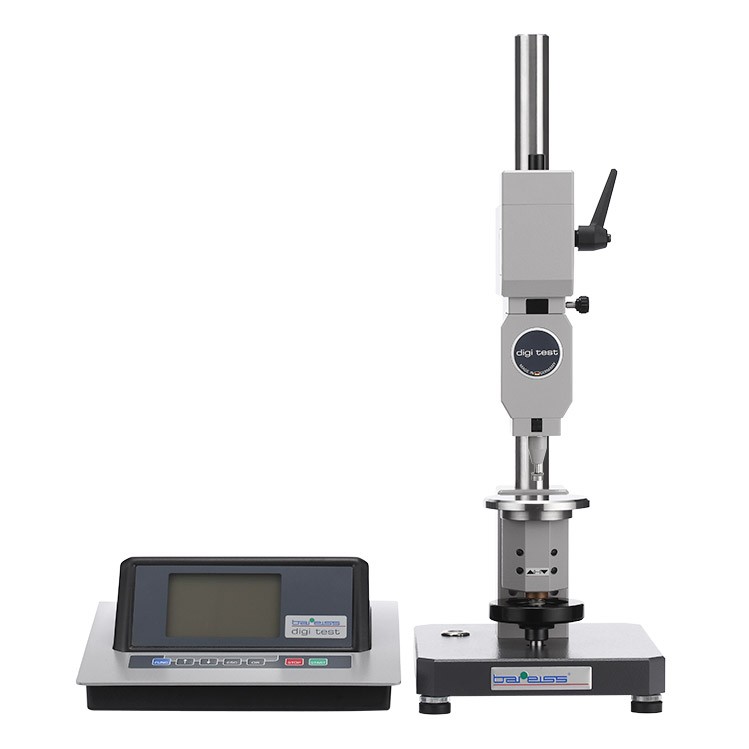

Automatic Shore, IRHD and VLRH Hardness Testing System
NextGen is proud to present our German line of fully-automatic Shore, IRHD and VLRH hardness testing system for plastic materials, plastic and foam compounds for the ultimate precision, accuracy and repeatability, exceptional ease-of-use and maintenance. Experience the industry leader for specimen testing including rubbers, plastics, foams, composites, o-rings, and more.
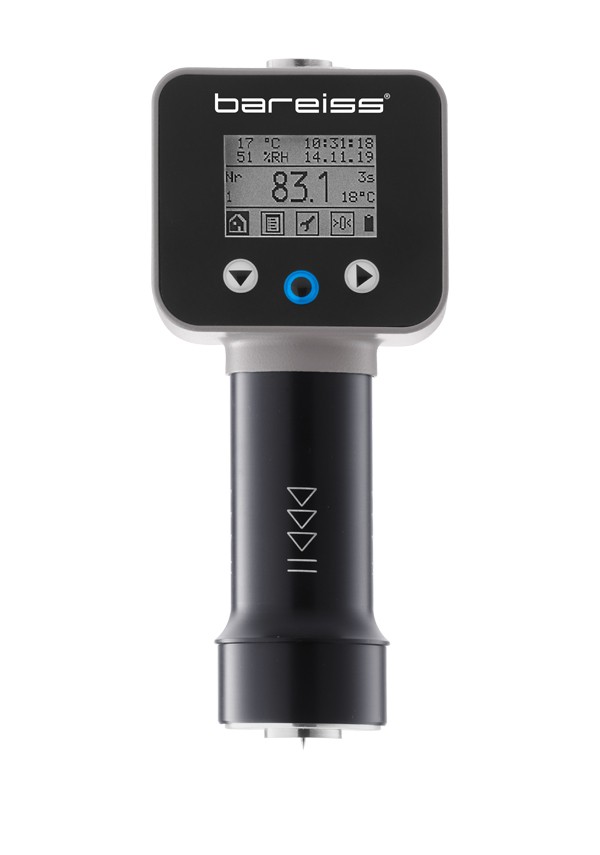

Advanced Portable Shore Durometer System with Test Stand Options
HPEIII is NextGen's advanced German line of equipment that is the new generation of HPE systems ideal for various plastic and plastic compound testing. The new system enhancements offer advantages including temperature sensor, reading values of ambient temperature and humidity, historical hardness value display, larger LCD display, standard USB connection and much more. These advanced portable systems can be paired up with either manual or automatic motorized test stands to help eliminate the human error factor and maximize accuracy and repeatability between test when switching from one operator to the next.

Classic Analogue Shore Durometer with Test Stand Options
This German-manufactured system has been the global benchmark of Shore hardness testing systems since 1954. With ever enhanced ergonomic design, the HP Shore Hardness Tester is both visually appealing and precise rubber and plastic testing system as it has been for nearly 50 years.

Akron Abrasion Tester
GenKron is used together with a special balance for testing the abrasive consumption of materials. The measurements are done through volumetric loss of a rotating specimen exposed to the action of a standard grinding wheel. It is especially suited for testing harder materials such as shoe soles, tires and other rubber materials.

Burst Strength Tester for Fabric
GenBurst is the Burst Strength Tester designed to test anti-rupture strength of variety of materials such as leather, paper and fabric.
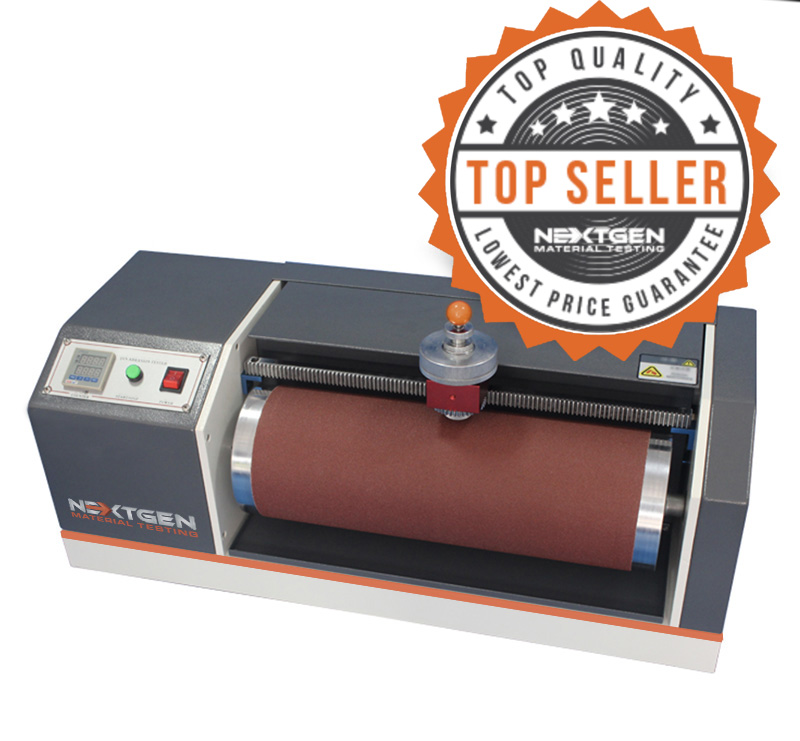

DIN Abrasion Tester
GenDin, is designed to conform to the ASTM D5963 and IS0 4649 standards. This top quality and highly popular abrasion tester will allow you to measure the abrasion resistance of rubbers (vulcanized thermo set rubbers and thermoplastic elastomers) that are subject to abrasive/frictional wear on their actual service. Since wear is always a result of abrasion, different test methods have been developed for the simulation of long term wear.
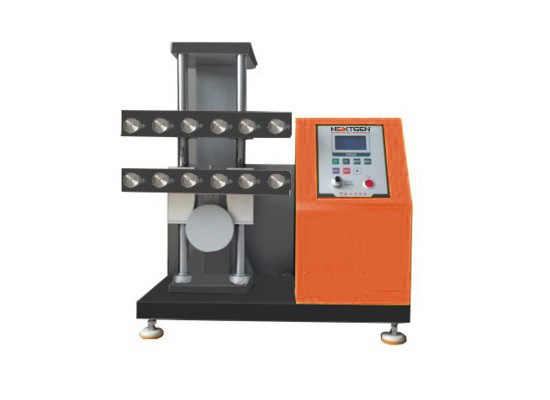

Demattia Flex Cracking Tester
GenFlex tests the ability of rubber products to withstand repeated flexing without developing cracks is of prime importance where such products are used in conditions undergoing repeated flexing. Flexing endurance of rubber products is determined by simulating in laboratory the action of flexing repeatedly under standard conditions of speed, mode, and degree of flexing.

Discoloration Meter
The machine is used to simulate an environment of sunlight radiation on a specimen to identify the resistance of fabric to discoloration.
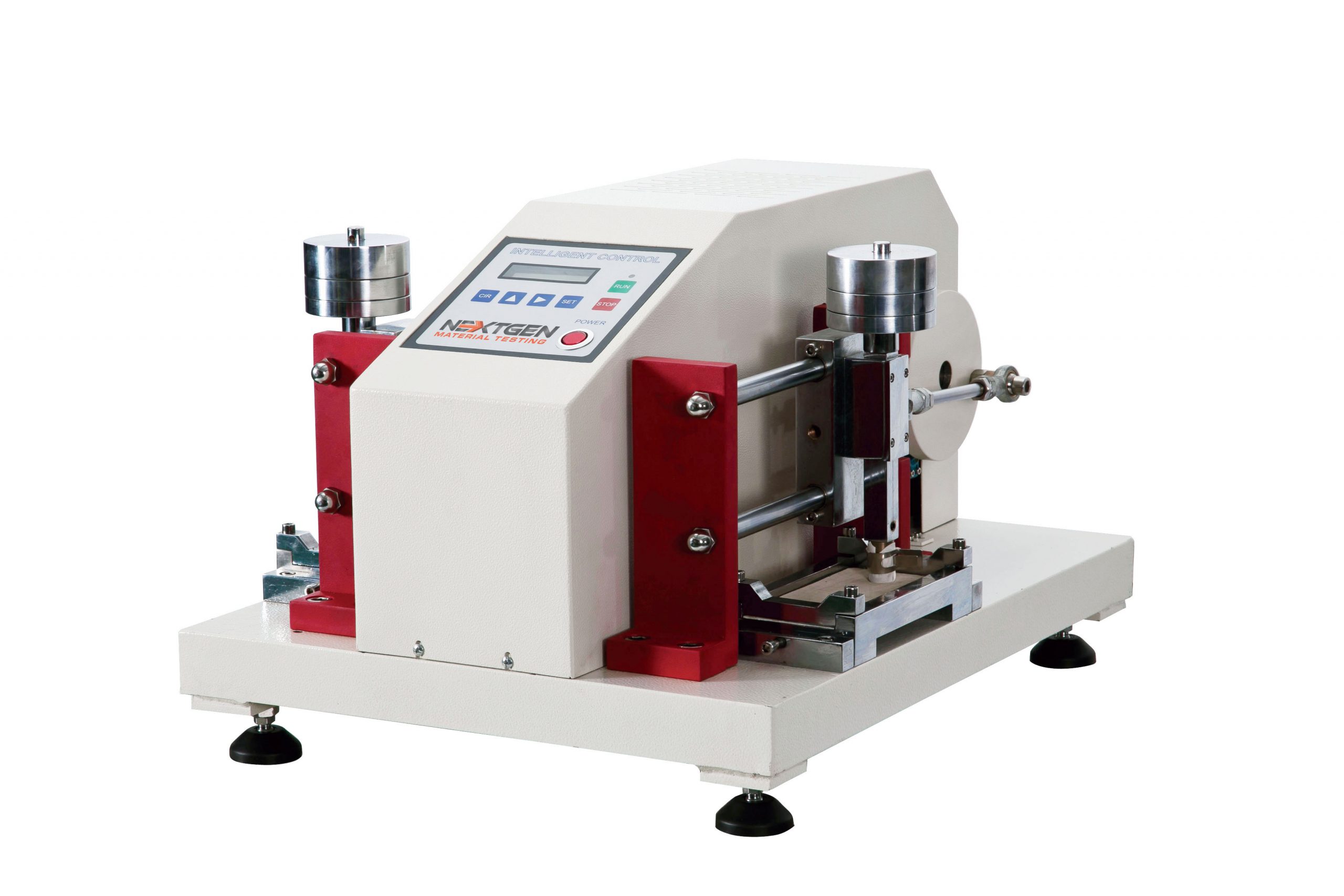

Electric Crocking Tester - GenCrock
The machine is used to test the dyeing of the fabric, and the fade degree of the leather after dry or wet rubbing. The test method involves the specimen to be fastened to the base of the crocking meter and rubbed with an abrasive hammer attached to a wet or a dry cloth under controlled conditions. The transfer of colour is then measured using a scale to evaluate the rating of the specimen's dyeing grade.

Freezing Tester - GenFreeze
GenFreeze is specially designed to test the characteristics of various materials in a cold environment to ensure suitability for use in a cold climate. Based on the testing demand, adjust the beater and flexing grip, then load to the desired position. It can be used to test rubbers, leather, and plastics, PU leather etc. The unit can be adjusted to meet different requirements.
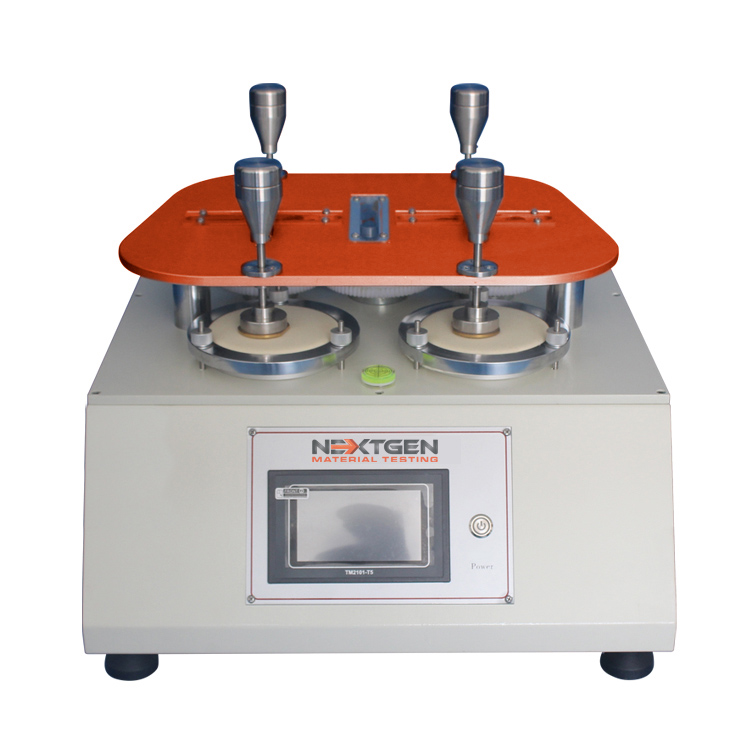

Martindale Abrasion Tester - GenDale
GenDale is mainly used to test shoe fabric, shoe lining, and many other types of shoe related materials. The unit can test up to four specimens at the same time for abrasion. The fabric specimen is measured by having rubbing applied on it via a complex direction of back and forth motion. The accuracy of abrasion strength is determined by the specific number of cycles conducted until a hole appears in the test area of the fabric specimen.

Mooney Viscosity Testing Machine - GenMooney
GenMooney is a viscosity testing machine is applied to measure the viscosity of the unmixed or mixed unvulcanized natural rubber, synthetic rubber and regenerated rubber .This tester has many functions such as fast warming, maintaining temperature, data stability, etc. It is equipped with an automated calibration feature for a simple data calibration of each experiment.

NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester - GenNBS
GenNBS is used to test the abrasion resistance of vulcanized rubber or other rubber compounds. It is commonly used for the soles and heels of footwear. It has an intelligent power failure recovery system. The unit conducts measurements through volumetric loss of specimens exposed to the action of a normalized abrasive medium secured to a rotations cylinder.
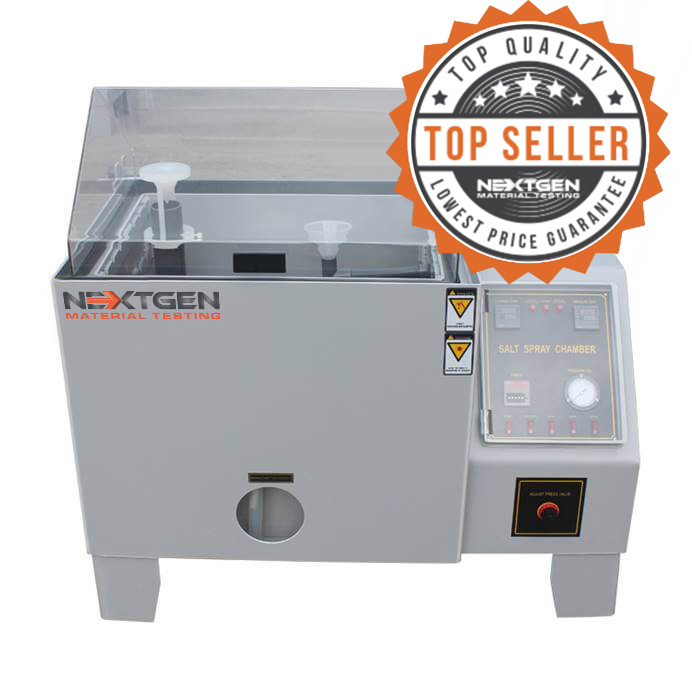

Salt Spray Tester - GenSalt
GenSalt is designed to test the surface of different materials for resistance to corrosion. The unit is commonly used to test coated materials of a metallic nature in a controlled corrosive environment. The test can be used on rust-proof painting, anodizing, electroplating and rust-proof of grease. The machine imitates expedited corrosion process via salt spraying on a given test sample to identify the corrosion (oxides) resistance. Test results are based on the longevity of time a material can resist visible corrosion on the test sample.
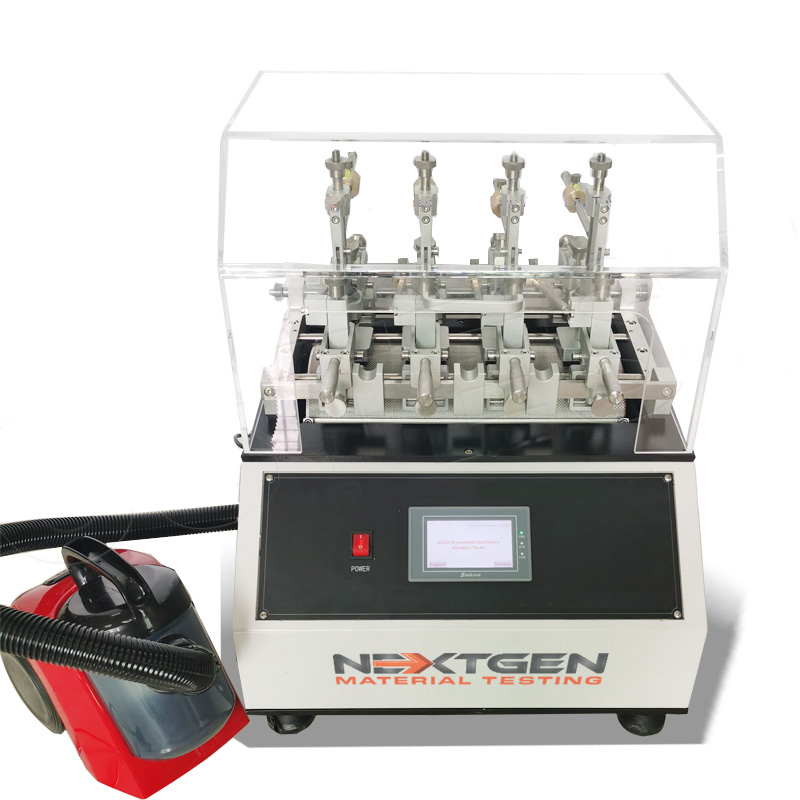

Wyzenbeek Abrasion Tester - GenWyze
The machine is designed to test the abrasion resistance of fabrics and metals. The abrasion of fabrics is tested when the specimen is pulled over the frame and rubbed against an abradant over a curved surface. The number of cycles, also known as double rubs, conducted on the specimen before the fabric shows visible wear is used to determine the rating of abrasion.
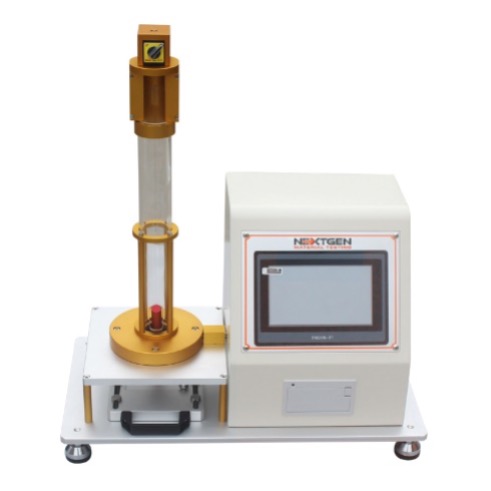

Vertical Rebound Resilience Tester - GenRebound
GenRebound tests the resilience of rubber compounds. The machine must be adjusted in a horizontal position and the plunger raised at a specific height. The plunger is then released onto the specimen for a given number of impacts. The measurements are based on the 4th, 5th, and 6th impacts. The average of the three (3) measurements is then calculated for the test result. The machine is highly useful in production of compounds designed to absorb vibration or shock according to the ASTM standards.

Digital Densimeter Systems
Description The NG-DM-A Series offers high-accuracy digital Densimeters designed for a wide variety of material testing needs. These elegant and compact densimeter systems offer capacity ranges from 150g to 3000g with accuracy of 0.001g/cm3 down to 0.0002g/cm3. Advanced Densimeter System […]
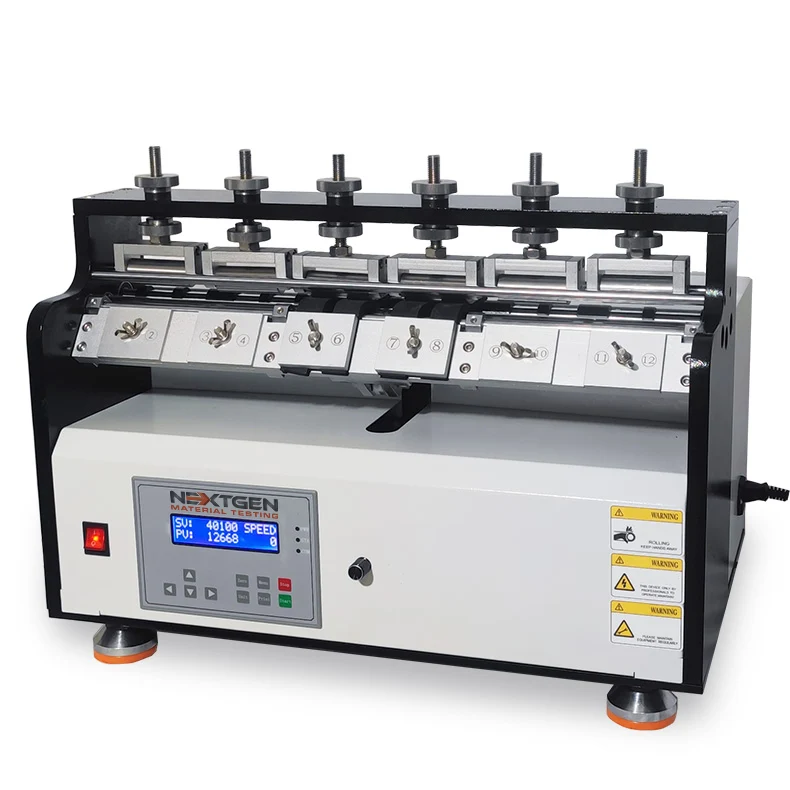

Ross Flex Tester
Ross Flex Tester is designed to determine the resistance of vulcanized or synthetic elastomers to cut growth. The system does so under continuously bend flexing in 90°.