
Rubber Testing Equipment

Standards
ASTM D1646, ISO 289, ISO 667, GB / T 1233






Description
GenMooney is a Mooney viscosity testing machine that is applied to measure the viscosity of unmixed or mixed unvulcanized natural rubber, synthetic rubber, and regenerated rubber. This tester has many functions such as fast warming, maintaining temperature, data stability, etc. It is equipped with an automated calibration feature for a simple data calibration of each experiment.
Mooney Viscosity Testing Machine Features
- Integrated multiple functions: early vulcanization, Mooney viscosity and stress relaxation can be tested in the same machine.
- Accurate temperature measurement and control: strict inspection of temperature calibration process.
- Flexible and accurate torque measurement: includes pressure reduction gear box, high precision sensor and a data acquisition system.
- High data reproducibility and stable electrical properties of the complete machine
- Intelligent software providing the strong data inquiry function, and humidity design, with a user friendly interface
- The test model has the graphs for upper die temperature and lower die temperature viscosity.
Data and Test Results
- Minimum Mooney value within 30s before the finish
- Mooney viscosity value after the MY - (viscosity) time is expired.
- TR80-Required time when the stress relaxation is 80%
- MY-T - Mooney value of the corresponding time
- LM-Min 11m to torque value of minimum Mooney viscosity value in scorch test
- Ml - initial Mooney viscosity
- Me - Mooney viscosity value
- MRe - Mooney stress relaxation test
Mooney Viscosity Testing Machine Technical Specifications
| Temperature range | Room Temperature to 200°C |
| Temperature accuracy | ±0.°C |
| Temperature display resolution | 0.1 "C |
| Rotor frequency | 2 ± 0.02rpm |
| Mooney viscosity range | 0 to 200 Mooney |
| Torque unit | kg-em , 1b-in, N-m Mooney |
| Test time | setting freely when modified in the middle |
| Control | By computer |
| Air pressure | 65psi (4.6bar) Not including air compressor |
| Specimen dimension | 5cm |
| Display | NextGen-Software |
| Dimension (W x D x H) | 12.2 x 22 x 24.40-inches 31 x 56 x 62cm |
| Weight | 770 lbs / 350kg |
| Power | 110V/60Hz or 220V/50Hz |
FAQs
The main difference between silicone and rubber is that most rubber forms have backbones containing carbon-carbon bonds. On the other hand, the backbone of silicone is comprised of silicon and oxygen. Both silicon and rubber are types of elastomer.
The major source of commercial natural rubber latex is the Hevea brasilliensis, more commonly known as the Amazonian rubber tree. It is a member of the Euphorbiaceae from the spurge family. The species is a good option since it can thrive well under cultivation. When properly managed, the tree responds nicely to wounding by providing more latex for many years.
The cure rate is a crucial vulcanization parameter because it defines the time that the compound needs to be cured. This is known as the cure time. The thermo plasticity is taken from the difference between the initial viscosity and the minimum viscosity.
Pre-vulcanized natural rubbers present Mooney viscosity that range between 60 and 90. In tire manufacturing the acceptable range used is anywhere from 75 to 80.
The value of viscosity that the Mooney Viscometer determines only depends on the molecular weight, molecular structure, and non-rubber components present in the rubber specimen. Because the behavior of rubber is that of a non-Newtonian fluid, no direct relationship exists between viscosity and molecular weight.
Stress relaxation is not only an elastic response. It is a viscous response as well. Stress relaxation does not depend on the molecular weight. A slow rate is an indication of a higher elastic portion in the entire specimen. A rapid rate, on the other hand, is an indication of a higher viscous composition. The stress relaxation rate correlates to the data points of the rubber structure such as chain brancing, weight distribution, and gel content.
Yes, absolutely! The increase in viscosity can be detected by the machine. Thus, the test procedure can be employed when measuring the scorch or incipient cure time as well as the cure rate during the initial stages of vulcanization.
An arbitrary unit, a Mooney unit is used for measuring the plasticity of unvulcanized or raw rubber. The plastic expressed in Mooney units is equivalent to the torque, which is measured using an arbitrary scale. It is on a disc inside a vessel containing rubber rotating at two RPM (revolutions per minute, at a temperature setting of 100o C.
It can be defined simply as the shearing torque providing resistance to the rotation of the rotor or cylindrical metal disc that is embedded in a rubber specimen with a cylindrical cavity.
The Mooney viscosity test is among the most prevalent procedures done in the rubber industry at present. It is typically used for measuring raw rubber viscosity as well as to depict the quality of both synthetic and natural rubber.
The Mooney Viscometer confirms to both the ISO 289 industry standards as well as the ASTM D1646 standards.
When the rotor makes an abrupt stop, the stress or torque on the rotor goes down at rate that is promptly measured. The stress relaxation is determined by the type of specimen rubber, as well as the test’s temperature.
The answer is YES. The ASTM standard describes a method to measure the initial vulcanization rate. When testing compounded rubber at a temperature that may possibly result to vulcanization, the reaction generates an increase in torque. This can then be measured using the equipment.
Parts 1 and 2 of the ISO 289 describes the process of Mooney viscosity determination as well as the pre-vulcanization characteristics. The primary difference between the ISO and the ASTM Standard is this: ISO 289 has no provisions for specimen preparation on a mill. The ASTM method, on the other hand, allows the preparation of the milling specimen for a Mooney viscosity test. The use of milling may have an impact on different types of rubber. Thus, the test might produce different results.
After cutting a circular sample from a 6-8mm rubber sheet, the sample is pierced in the middle to form a donut shape. This allows the spindle to pass through the specimen. The temperature begins to rise where the sample reaches thermal equilibrium. The spindle begins to turn and the Mooney value typically remains constant until the temperature reaches higher levels where vulcanization starts and the Mooney value increases.
The Mooney test is frequently used to classify the quality of both natural and synthetic rubber types.
Parts 1 and 2 describe the determination of Mooney Viscosity and the pre-vulcanization characteristics. The main difference from the ISO to the ASTM standard is that ISO 289 does not provide for sample preparation on a mill - while the ASTM method allows milling to prepare the sample for Mooney viscosity testing. Different rubbers may be affected by the use of milling in which cause the results will differ.
Yes, the ASTM standard defines a method for measuring the initial rate of vulcanization. When compounded rubber is tested at a temperature where vulcanization may occur, the reaction produces an increase in torque which can then be measured with the instrument.
When the rotor stops abruptly, the torque or stress on the rotor decreases at a rate which is then measured. The stress relaxation depends on the rubber sample type and the temperature of the test.
The GenMooney Mooney Viscometer follows both the ASTM D1646 standard as well as the ISO 289 industry standard.
It is defined as the shearing torque resisting rotation of a cylindrical metal disc (or rotor) embedded in a rubber sample with a cylindrical cavity.
Absolutely! It can be detected with an increase in viscosity. Because of this, the testing procedure can be used to measure incipient cure (Scorch) time and the rate of cure during the beginning stages of vulcanization.
Stress relaxation is both an elastic and viscous response. Viscosity and stress relaxation do not depend on molecular weight. A slow rate indicates a higher elastic component in the overall sample while a rapid rate indicates a higher viscous component. The rate of stress relaxation correlates with the rubber structure data points such as molecular weight distribution, chain brancing and gel content.
Viscosity values determined by the Mooney Viscometer depend only on molecular structure, molecular weight, and non-rubber constituents that are present in the rubber sample. Seeing as rubber behaves as a non-Newtonian fluid, there is no direct relationship between molecular weight and viscosity.
Related Products
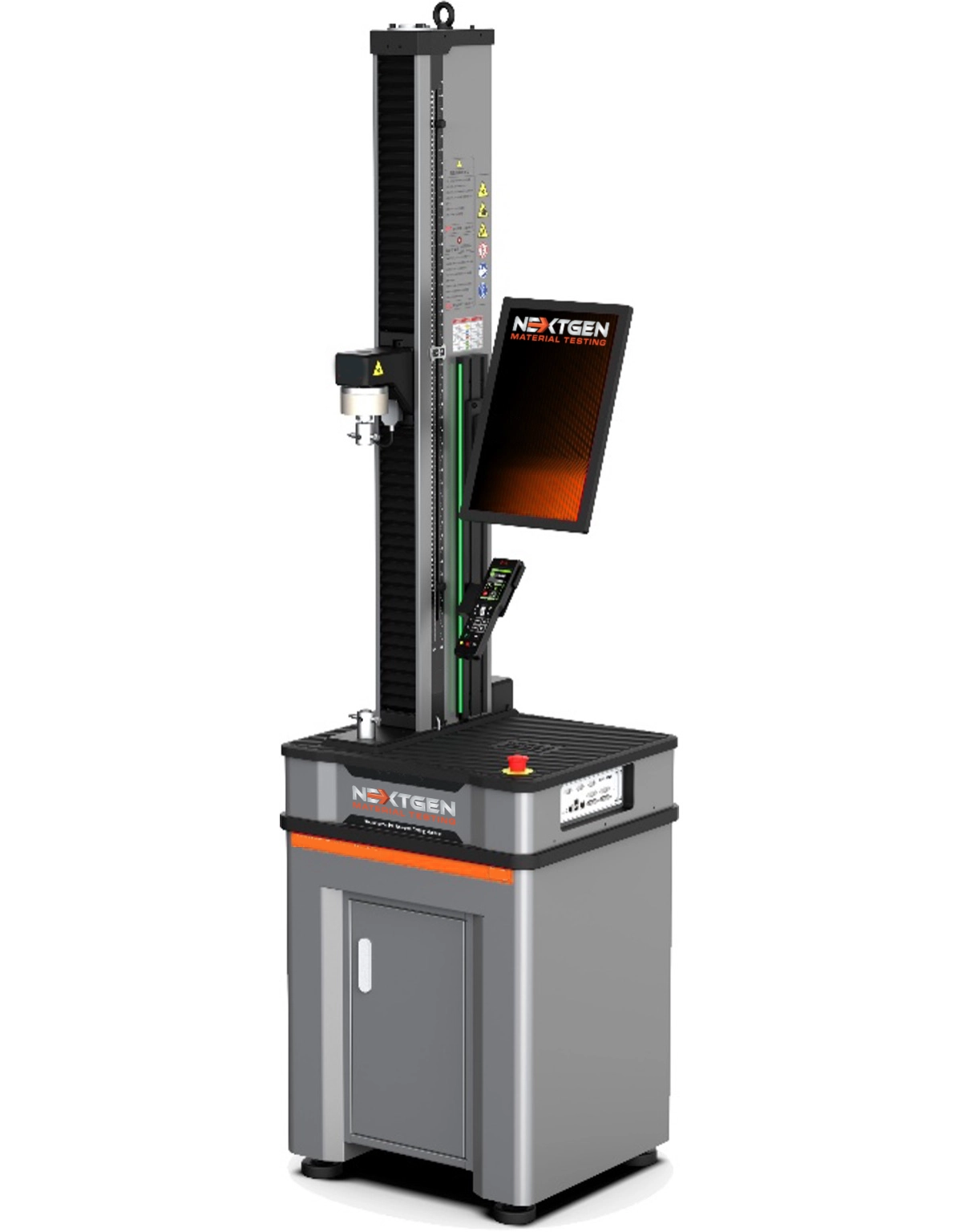

NG-EML Series A – Single Column Bench Top Universal Testing Machine (50 N – 5 kN)
The NG-EML Series A – Single Column Bench Top UTM (50 N–5 kN) is a precision electromechanical system designed for tension, compression, and flexural testing of low-force specimens. Featuring GenTest™ software, a high-speed servo drive, Class 0.5 accuracy, and USB/Ethernet control, this compact tabletop unit supports ASTM, ISO, and EN standards. Ideal for testing plastics, rubber, foams, films, composites, and thin metals.
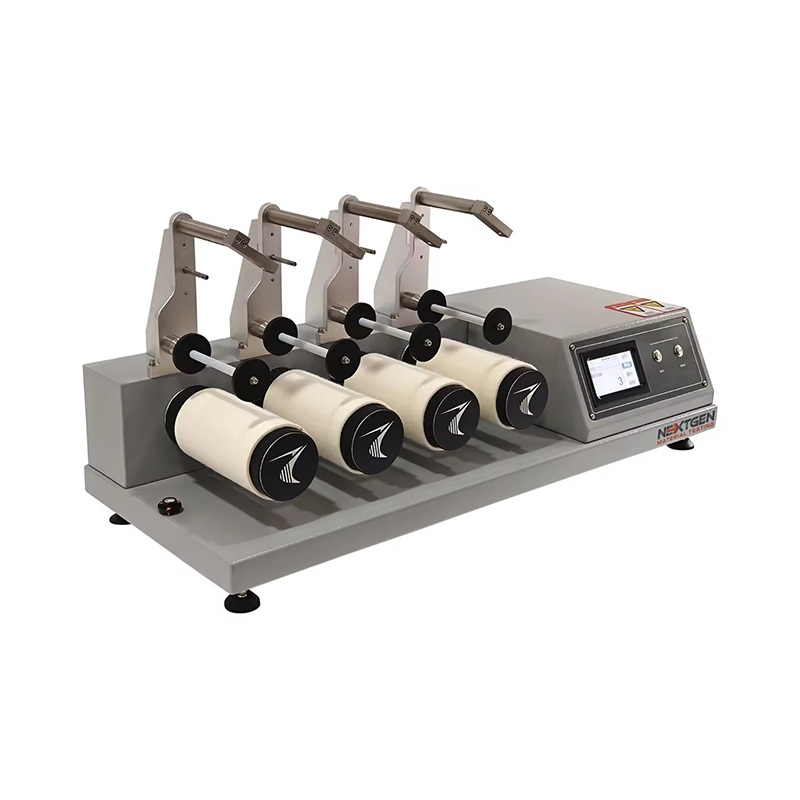

ICI / Mace Snag Tester
Discover the Fabric Textile ICI / Mace Snag Tester, a reliable tool for assessing fabric snagging under normal wear conditions.

Moving Die Rheometer (MDR)
Introducing the NG-MDR Moving Die Rheometer, your solution for accurately assessing the curing and processing characteristics of vulcanized rubber compounds. Designed for precision, this state-of-the-art rheometer captures the characteristic curve and parameters of rubber vulcanization by measuring the torque applied to the oscillating die.
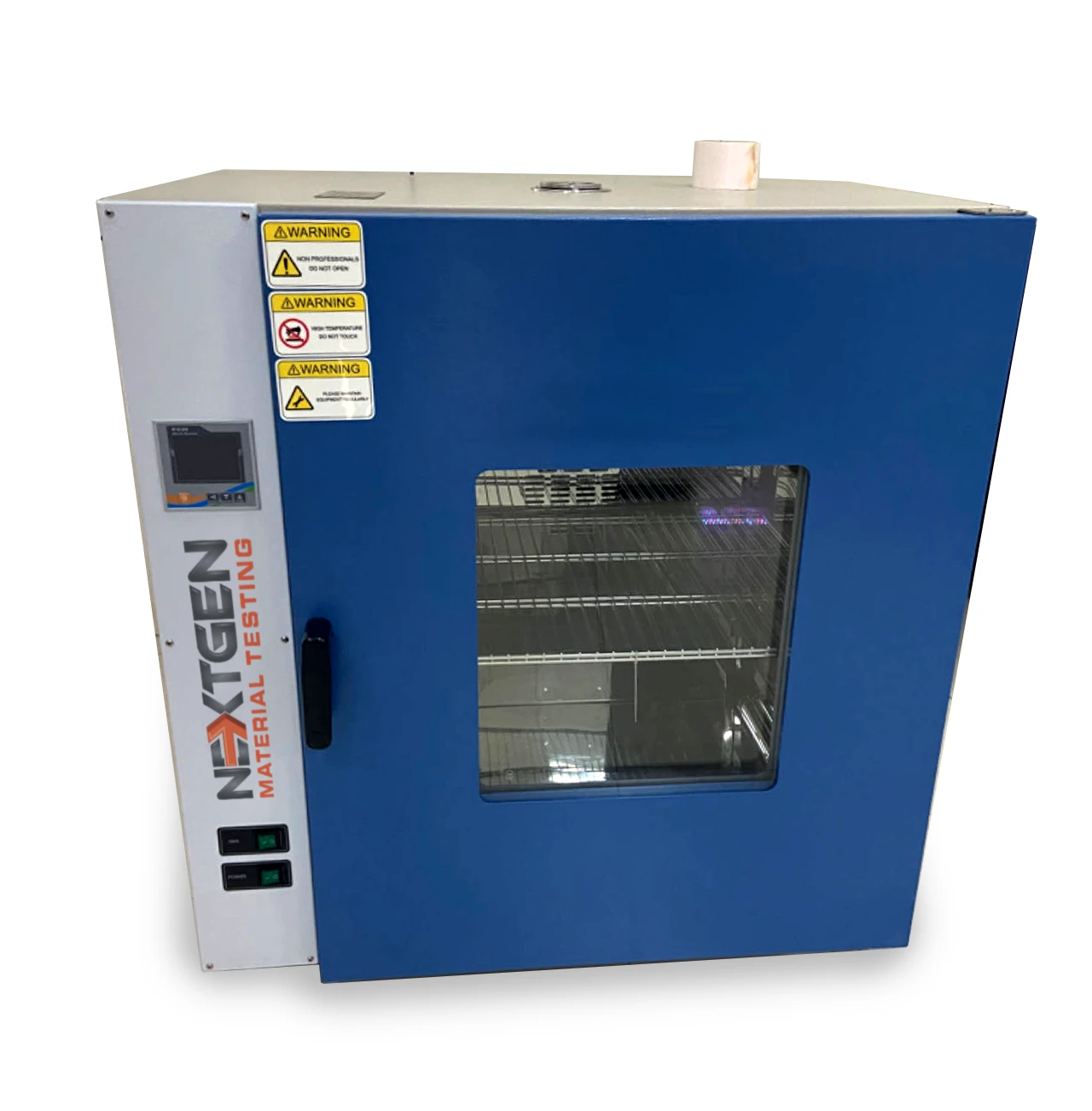

Aging Oven – High-Temperature Chamber – NG-AGOV-ADV
The NG-AGOV-ADV Aging Oven is designed for high-temperature testing of rubber, plastics, and insulating materials. It features programmable PID control, uniform airflow, and forced convection for stable and repeatable aging cycles. This system supports global testing standards including ISO 188, ASTM D573, and IEC 60216-4-1. With its durable stainless-steel chamber and user-friendly interface, it’s ideal for R&D, quality control, and certification labs.
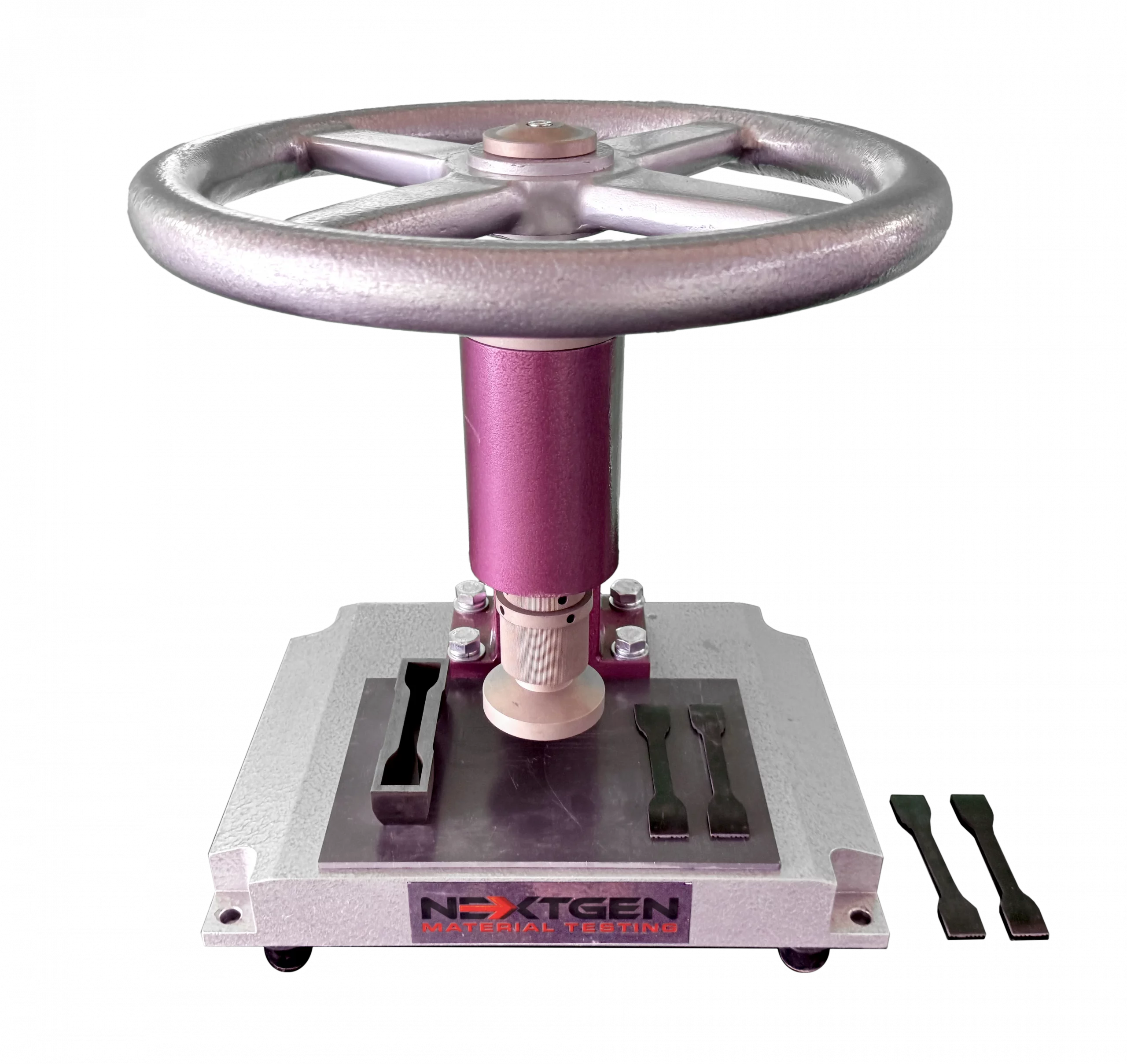
NG-T-Press M Series - Manual Cutting Press System for Rubber Tensile Specimens
Our newest manual cutting press system is suitable for laboratories to create specimens from rubber, tape, and special materials.
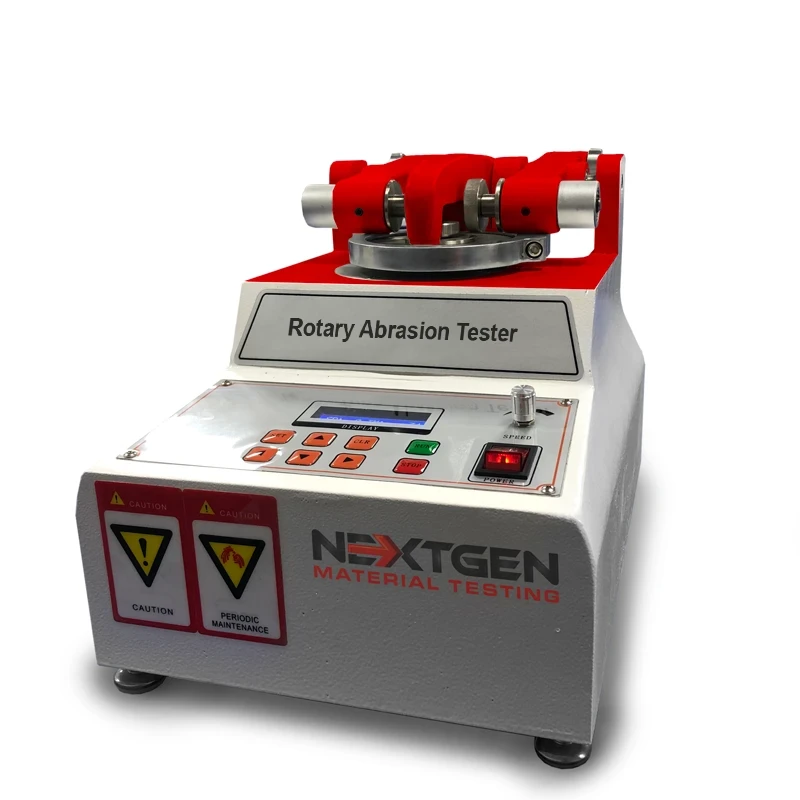

Rotary Abrasion Tester Single & Dual Wheel
GenRotary used evaluate abrasion resistance. It can conduct tests on a wide range of materials such as: cloth, paper, paint, plywood, leather, tile, glass, rubber etc. It tests the specimen by rotating it while in contact with the grinding wheel and applying the required pressure. The Joss of weight reflects on the change in weight of the specimen. The unit also has an intelligent power failure recovery function.
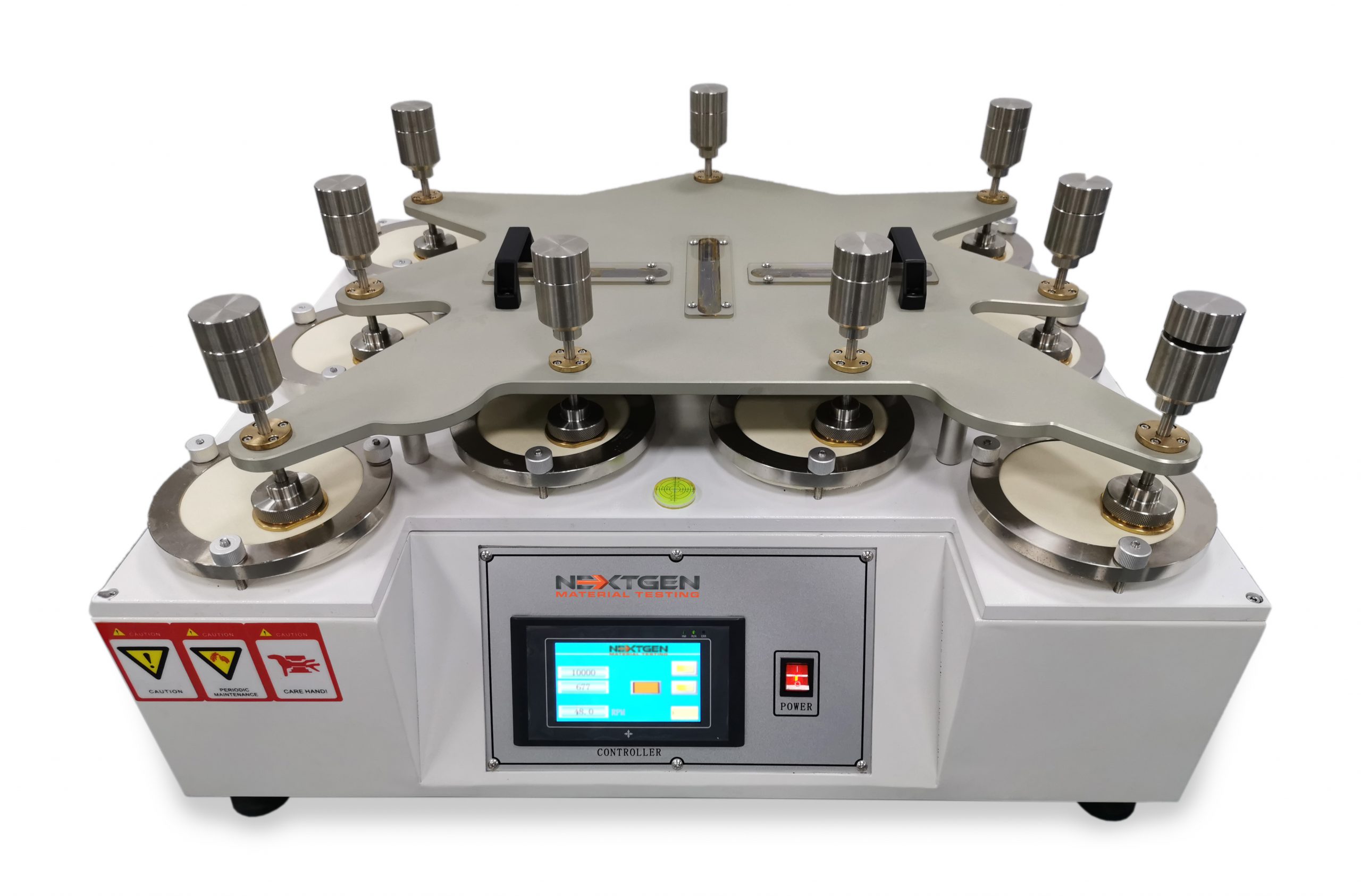

9-Station Martindale Abrasion Tester
The GenDale - Martindale Abrasion Tester is mainly used to test shoe fabric, shoe lining, and many other types of shoe related materials.
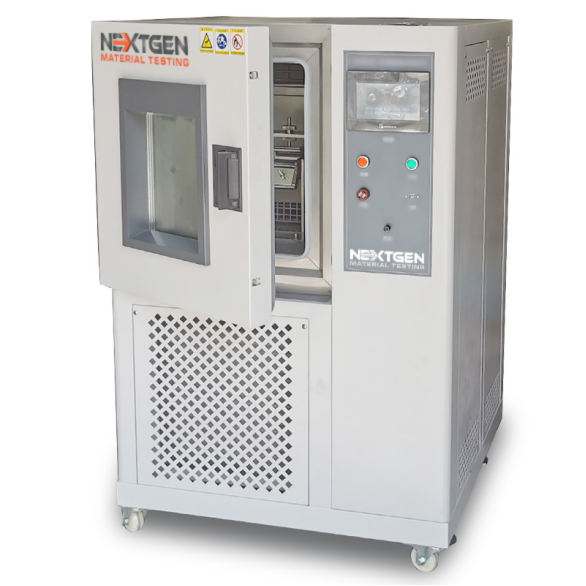

GenRoss-CH - Ross Flex Tester with Low Temperature Chamber
GenRoss-CH is an advanced Ross Flex Tester designed for assessing the cold resistance of materials in low temperature environments.
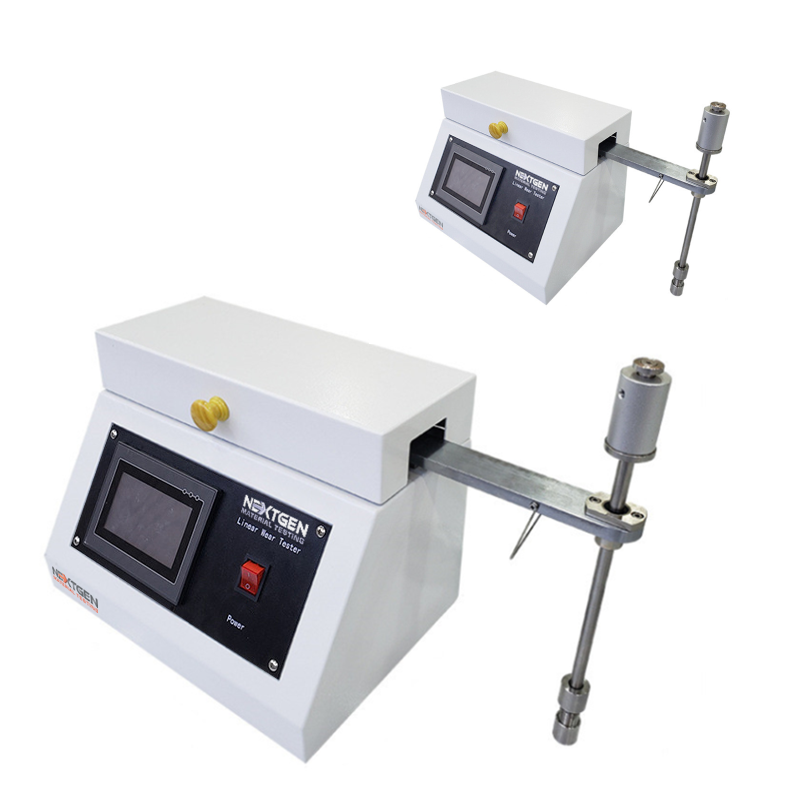

Linear Abrasion Tester
NextGen's linear abrasion meters evaluate the abrasion and scratch resistance of products, along with color transmission.
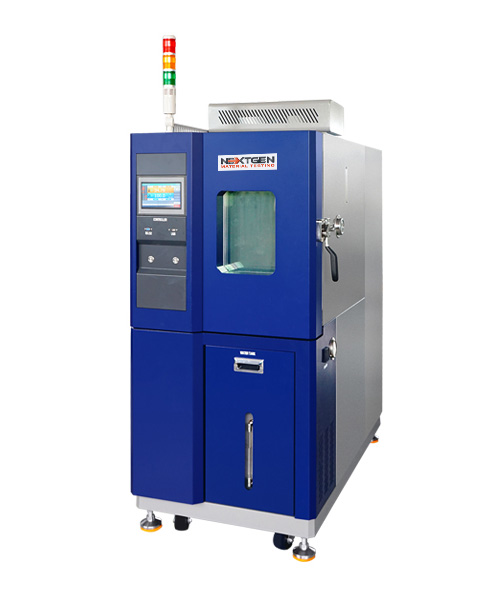

NextGen Environmental Chambers NG-EC 100,150,225,408,1000
The temperature and humidity NextGen Environmental Chambers features a sturdy cabinet made of cold-rolled steel and stainless steel.
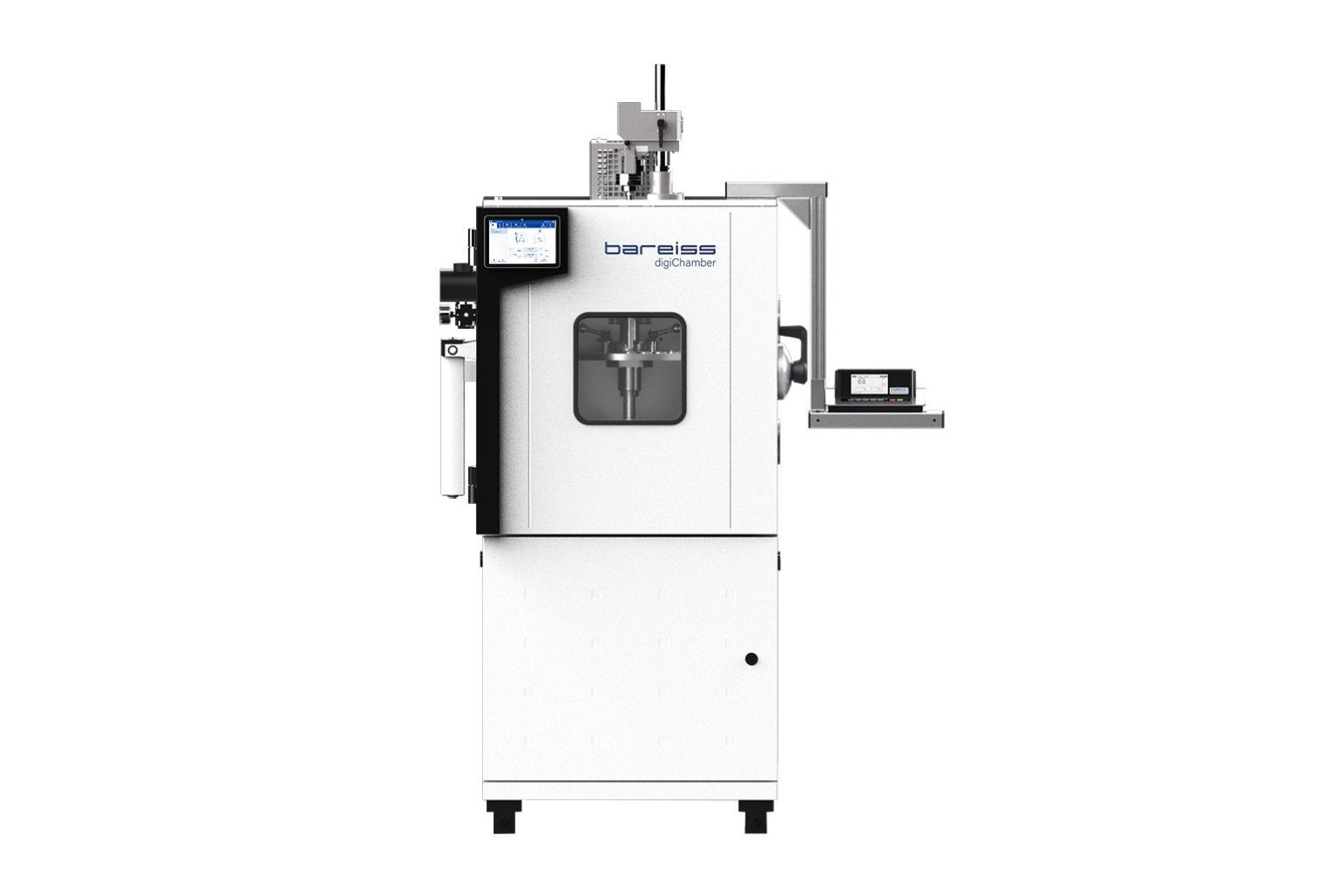

digiChamber - Temperature Controlled Hardness Testing
Discover digiChamber from NextGen Material Testing, the advanced temperature-controlled hardness tester developed by Bareiss.
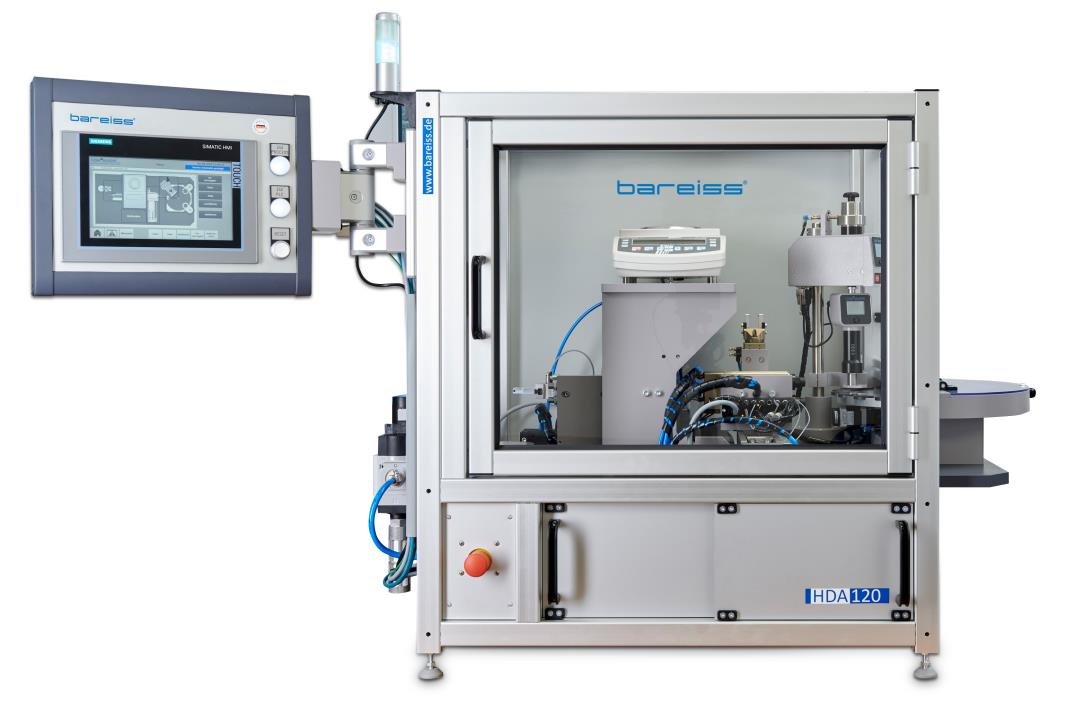

HDA 120 - Hardness and Density Automation Test System
The HDA 120 test system is a versatile solution for semi-automatic detection of sample hardness and density.

RPA Ultra - Advanced Rubber Process Analyzer Rheometer
RPA Ultra is an advanced rubber process analyzer rheometer that measures the dynamic and static characteristics of raw rubber compounds
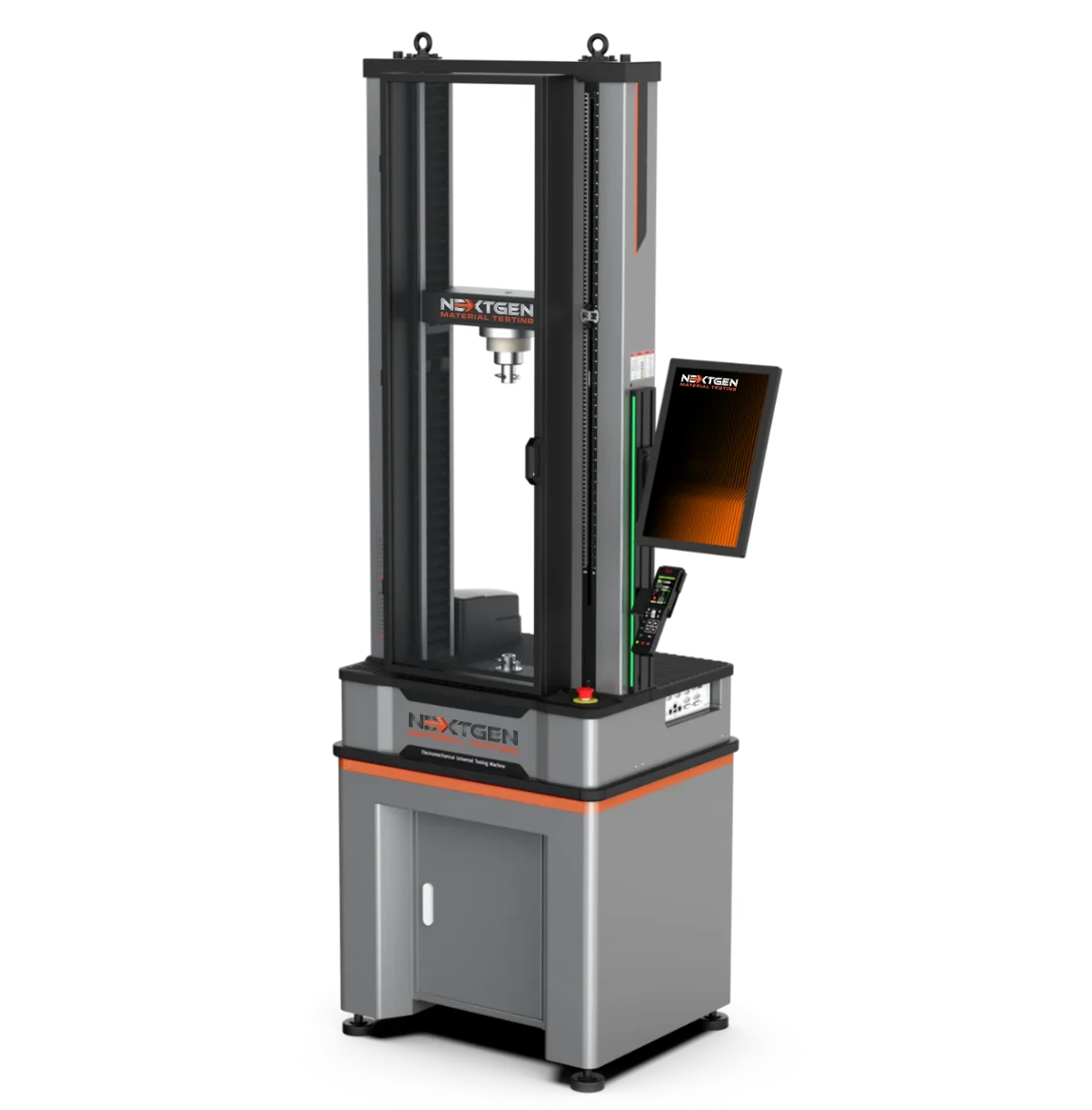

NG-EML Series B – Dual Column Bench Top Universal Testing Machine (100 N – 10 kN)
The NG-EML Series B is a high-precision dual-column benchtop universal testing machine engineered for tensile, compression, and flexural testing in the 0.1 kN to 10 kN range. It features Class 0.5 accuracy, a rigid FEM-optimized frame, and a direct-drive servo system with advanced closed-loop control, making it ideal for testing rubber, plastics, metals, composites, and high-performance polymers in both R&D and quality assurance settings.
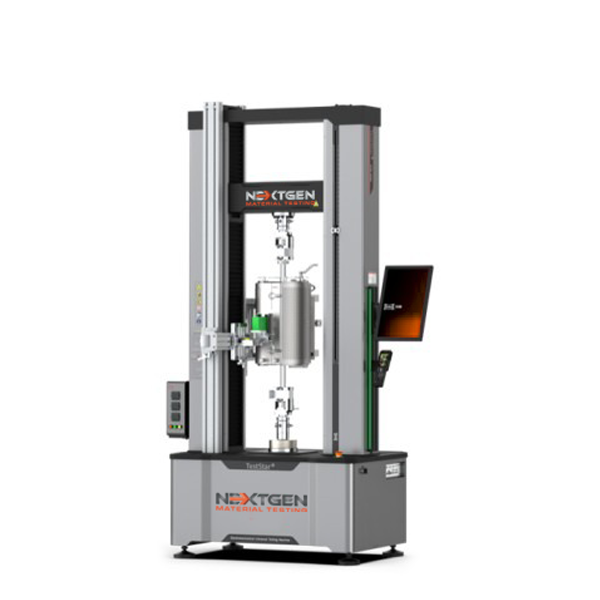

NG-EML Series C – Dual Column Bench Top and Floor Standing Universal Testing Machine (5 kN – 50 kN)
The NG-EML Series C is a precision-engineered dual-column universal testing machine for tension, compression, and flexural testing of metals, composites, rubbers, and polymers. Available in both bench-top and floor-standing formats, with force capacities from 5 kN to 50 kN and Class 0.5 accuracy.
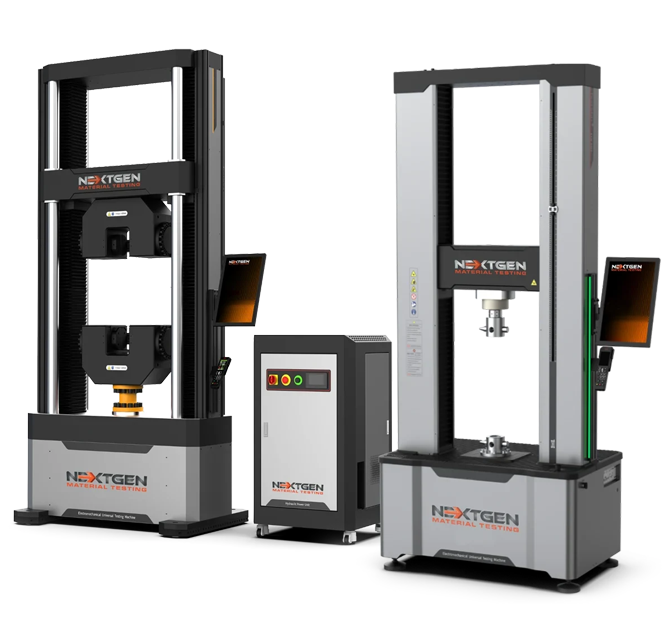

NG-EML Series D – Floor Standing Universal Testing Machine (50 kN – 1000 kN)
The NG-EML Series D – Floor Standing Universal Testing Machine (50 kN–1000 kN) is a dual-column system for tensile, compression, flexural, shear, and cyclic testing of high-strength metals, composites, polymers, and advanced materials. Available in single-space and dual-space configurations, it meets ASTM E8, ISO 6892-1, ISO 527, and GB/T 228 standards. With closed-loop control, 1200 Hz sampling, ultra-low speeds (0.00005 mm/min), and waveform generation, it is ideal for aerospace, automotive, construction, and research labs.

GenTest – Advanced UTM Testing Software
GenTest Software provides test control and data acquisition for universal testing machine workflows used in quality control and materials testing. It combines method templates, step-based sequencing, live curve monitoring, and built-in calculations in one environment. The software supports standards-based testing programs aligned with ASTM, ISO, DIN, EN, and BS. Results and reports remain linked to the method and specimen inputs for consistent review, auditing, and customer documentation.
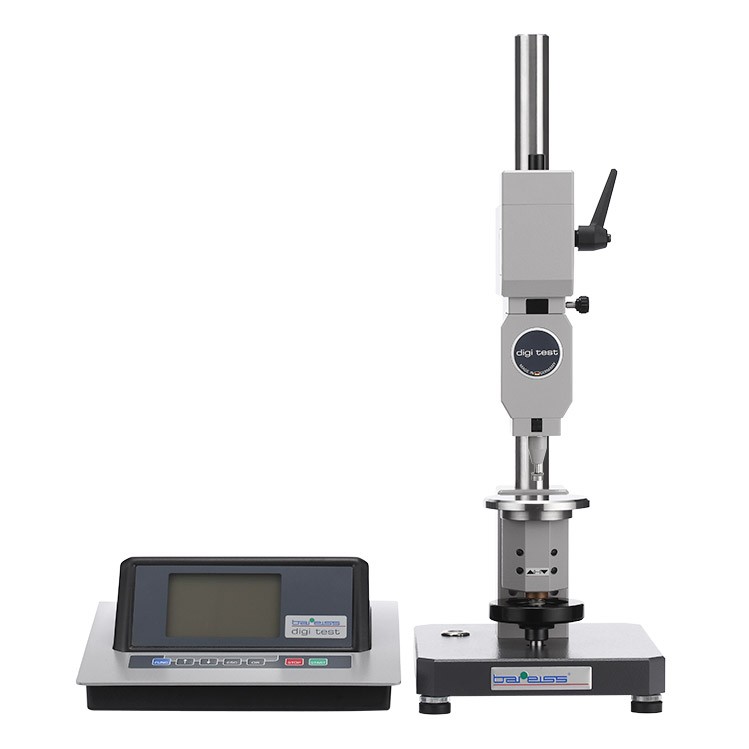

Automatic Shore, IRHD and VLRH Hardness Testing System
NextGen is proud to present our German line of fully-automatic Shore, IRHD and VLRH hardness testing system for plastic materials, plastic and foam compounds for the ultimate precision, accuracy and repeatability, exceptional ease-of-use and maintenance. Experience the industry leader for specimen testing including rubbers, plastics, foams, composites, o-rings, and more.
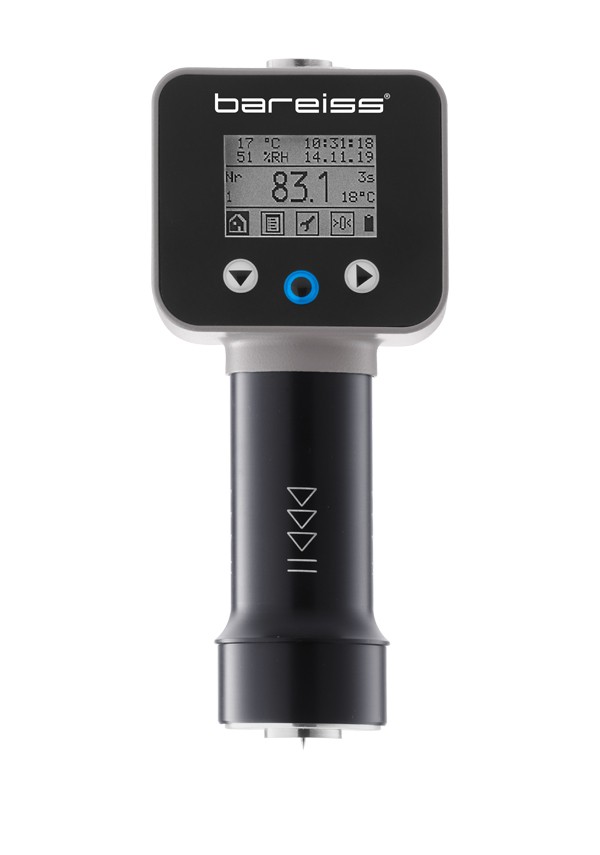

Advanced Portable Shore Durometer System with Test Stand Options
HPEIII is NextGen's advanced German line of equipment that is the new generation of HPE systems ideal for various plastic and plastic compound testing. The new system enhancements offer advantages including temperature sensor, reading values of ambient temperature and humidity, historical hardness value display, larger LCD display, standard USB connection and much more. These advanced portable systems can be paired up with either manual or automatic motorized test stands to help eliminate the human error factor and maximize accuracy and repeatability between test when switching from one operator to the next.

Classic Analogue Shore Durometer with Test Stand Options
This German-manufactured system has been the global benchmark of Shore hardness testing systems since 1954. With ever enhanced ergonomic design, the HP Shore Hardness Tester is both visually appealing and precise rubber and plastic testing system as it has been for nearly 50 years.

Akron Abrasion Tester
GenKron is used together with a special balance for testing the abrasive consumption of materials. The measurements are done through volumetric loss of a rotating specimen exposed to the action of a standard grinding wheel. It is especially suited for testing harder materials such as shoe soles, tires and other rubber materials.

Burst Strength Tester for Fabric
GenBurst is the Burst Strength Tester designed to test anti-rupture strength of variety of materials such as leather, paper and fabric.
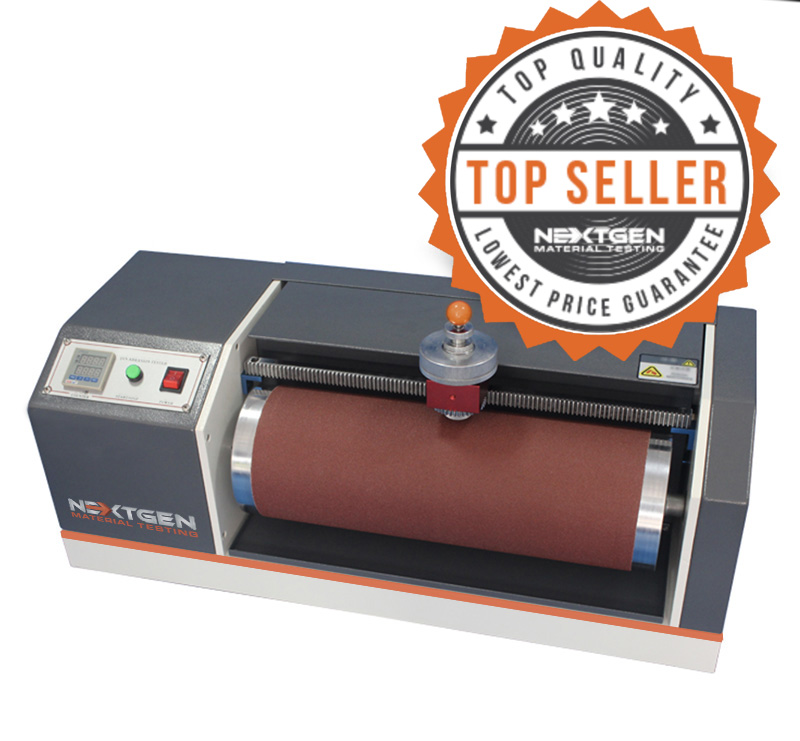

DIN Abrasion Tester
GenDin, is designed to conform to the ASTM D5963 and IS0 4649 standards. This top quality and highly popular abrasion tester will allow you to measure the abrasion resistance of rubbers (vulcanized thermo set rubbers and thermoplastic elastomers) that are subject to abrasive/frictional wear on their actual service. Since wear is always a result of abrasion, different test methods have been developed for the simulation of long term wear.
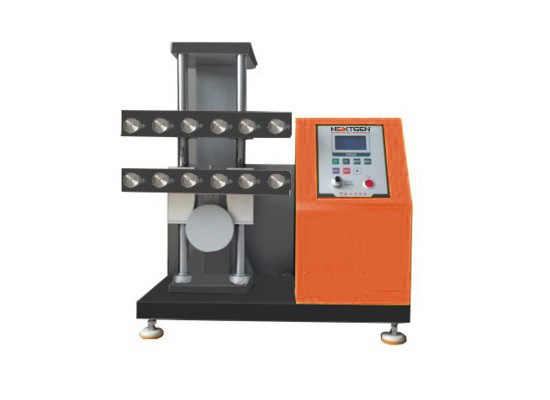

Demattia Flex Cracking Tester
GenFlex tests the ability of rubber products to withstand repeated flexing without developing cracks is of prime importance where such products are used in conditions undergoing repeated flexing. Flexing endurance of rubber products is determined by simulating in laboratory the action of flexing repeatedly under standard conditions of speed, mode, and degree of flexing.

Discoloration Meter
The machine is used to simulate an environment of sunlight radiation on a specimen to identify the resistance of fabric to discoloration.
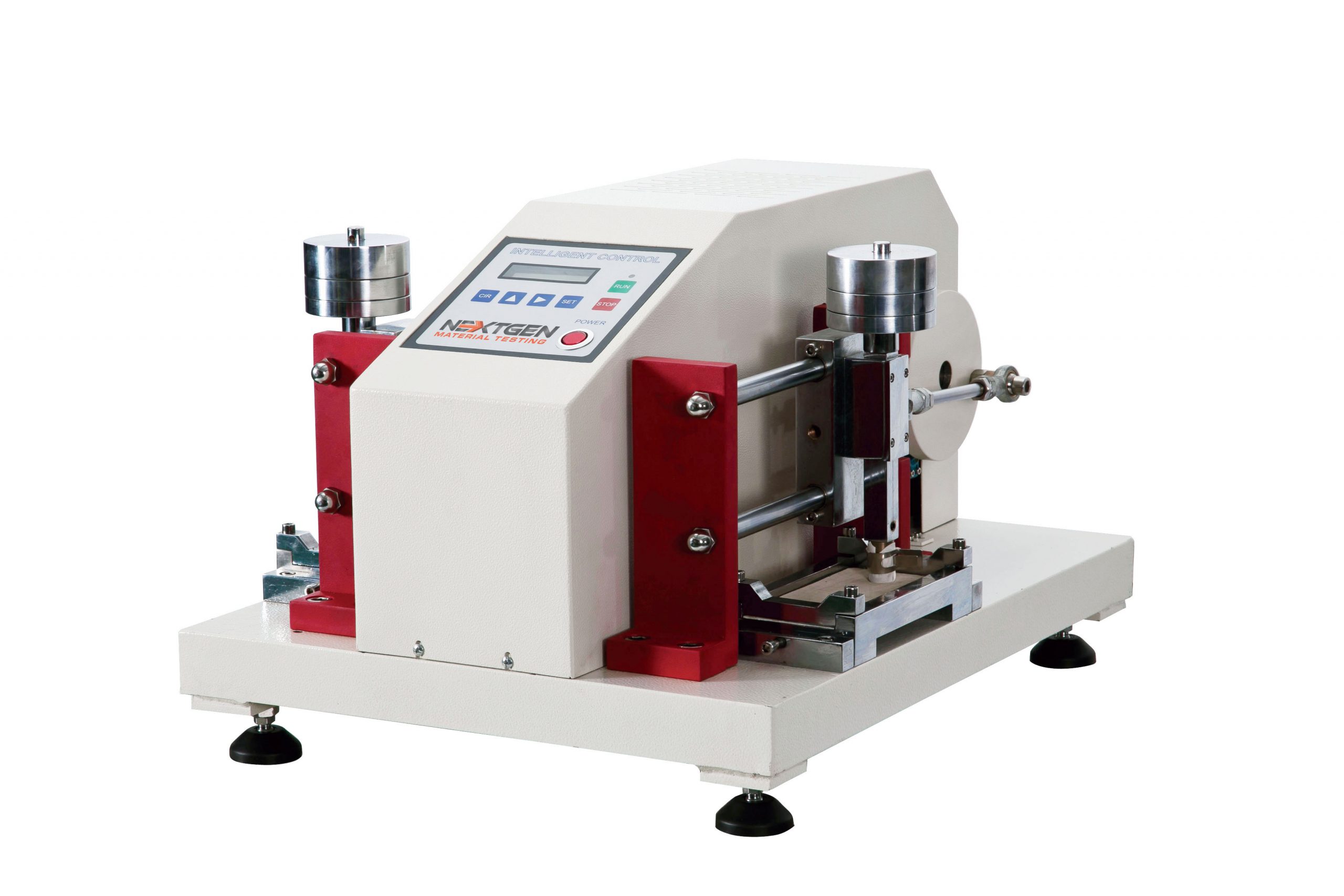

Electric Crocking Tester - GenCrock
The machine is used to test the dyeing of the fabric, and the fade degree of the leather after dry or wet rubbing. The test method involves the specimen to be fastened to the base of the crocking meter and rubbed with an abrasive hammer attached to a wet or a dry cloth under controlled conditions. The transfer of colour is then measured using a scale to evaluate the rating of the specimen's dyeing grade.

Freezing Tester - GenFreeze
GenFreeze is specially designed to test the characteristics of various materials in a cold environment to ensure suitability for use in a cold climate. Based on the testing demand, adjust the beater and flexing grip, then load to the desired position. It can be used to test rubbers, leather, and plastics, PU leather etc. The unit can be adjusted to meet different requirements.
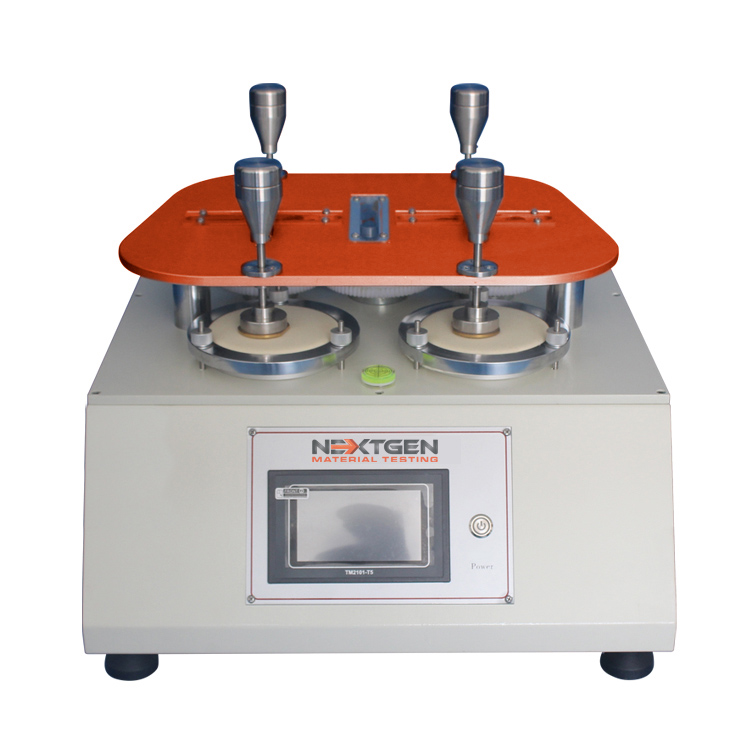

Martindale Abrasion Tester - GenDale
GenDale is mainly used to test shoe fabric, shoe lining, and many other types of shoe related materials. The unit can test up to four specimens at the same time for abrasion. The fabric specimen is measured by having rubbing applied on it via a complex direction of back and forth motion. The accuracy of abrasion strength is determined by the specific number of cycles conducted until a hole appears in the test area of the fabric specimen.

NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester - GenNBS
GenNBS is used to test the abrasion resistance of vulcanized rubber or other rubber compounds. It is commonly used for the soles and heels of footwear. It has an intelligent power failure recovery system. The unit conducts measurements through volumetric loss of specimens exposed to the action of a normalized abrasive medium secured to a rotations cylinder.
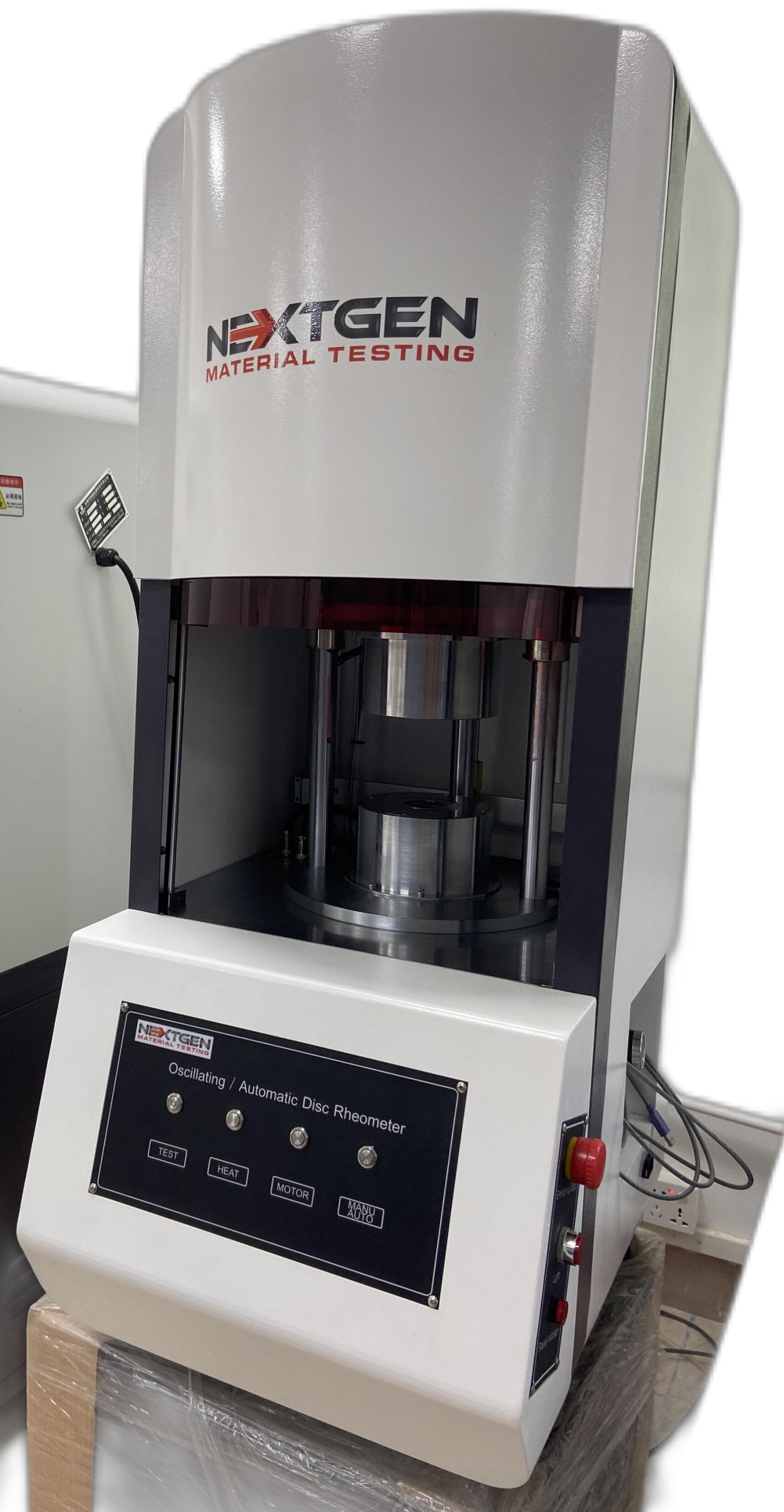

Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR)
This machine is designed to get the characteristic curve and characteristic parameters of rubber vulcanization by measuring the applied moment of rubber to the oscillating dye body. NG-ODR rotor-free vulcameter has an excellent stability of results. The data and diagrams can be used as a reference for development, research and production quality.
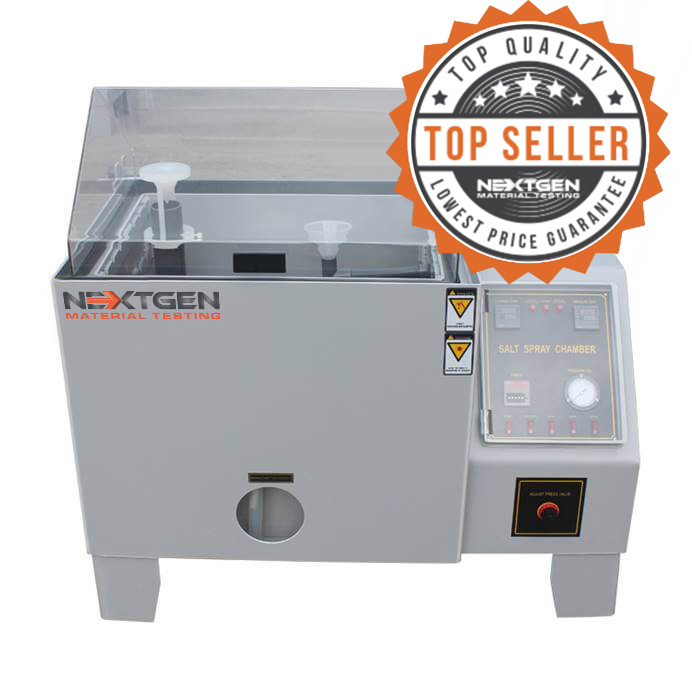

Salt Spray Tester - GenSalt
GenSalt is designed to test the surface of different materials for resistance to corrosion. The unit is commonly used to test coated materials of a metallic nature in a controlled corrosive environment. The test can be used on rust-proof painting, anodizing, electroplating and rust-proof of grease. The machine imitates expedited corrosion process via salt spraying on a given test sample to identify the corrosion (oxides) resistance. Test results are based on the longevity of time a material can resist visible corrosion on the test sample.
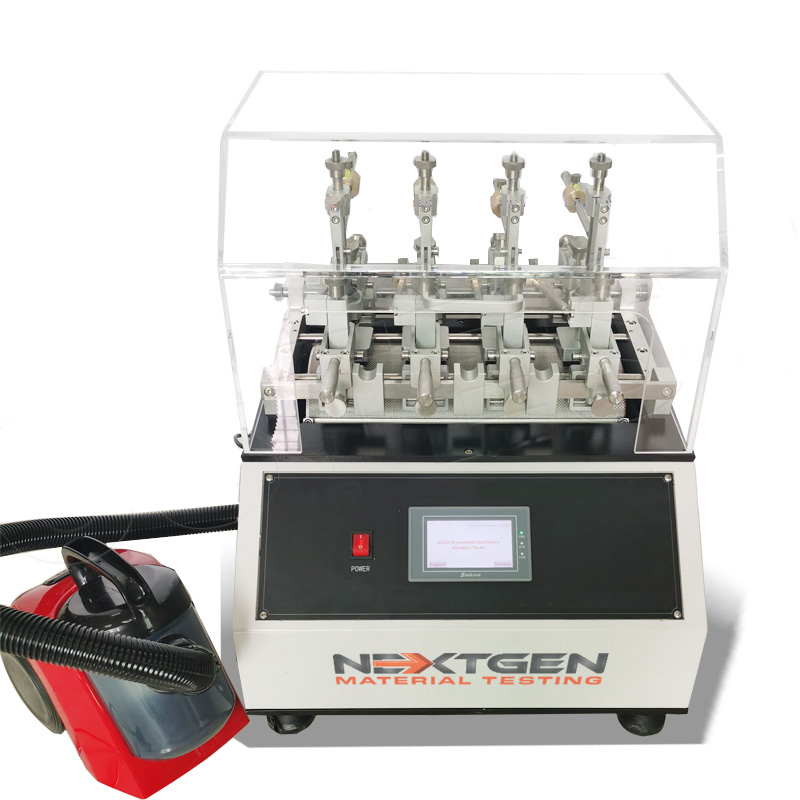

Wyzenbeek Abrasion Tester - GenWyze
The machine is designed to test the abrasion resistance of fabrics and metals. The abrasion of fabrics is tested when the specimen is pulled over the frame and rubbed against an abradant over a curved surface. The number of cycles, also known as double rubs, conducted on the specimen before the fabric shows visible wear is used to determine the rating of abrasion.
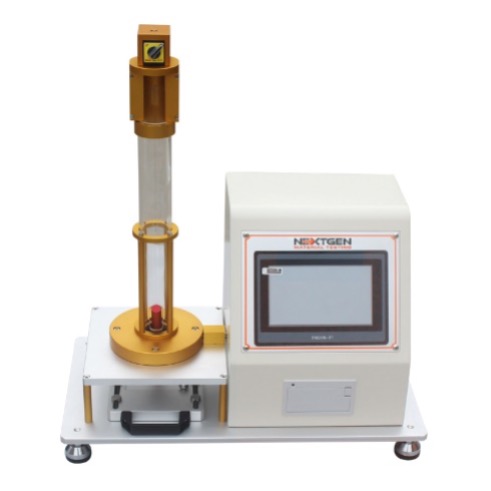

Vertical Rebound Resilience Tester - GenRebound
GenRebound tests the resilience of rubber compounds. The machine must be adjusted in a horizontal position and the plunger raised at a specific height. The plunger is then released onto the specimen for a given number of impacts. The measurements are based on the 4th, 5th, and 6th impacts. The average of the three (3) measurements is then calculated for the test result. The machine is highly useful in production of compounds designed to absorb vibration or shock according to the ASTM standards.

Digital Densimeter Systems
Description The NG-DM-A Series offers high-accuracy digital Densimeters designed for a wide variety of material testing needs. These elegant and compact densimeter systems offer capacity ranges from 150g to 3000g with accuracy of 0.001g/cm3 down to 0.0002g/cm3. Advanced Densimeter System […]
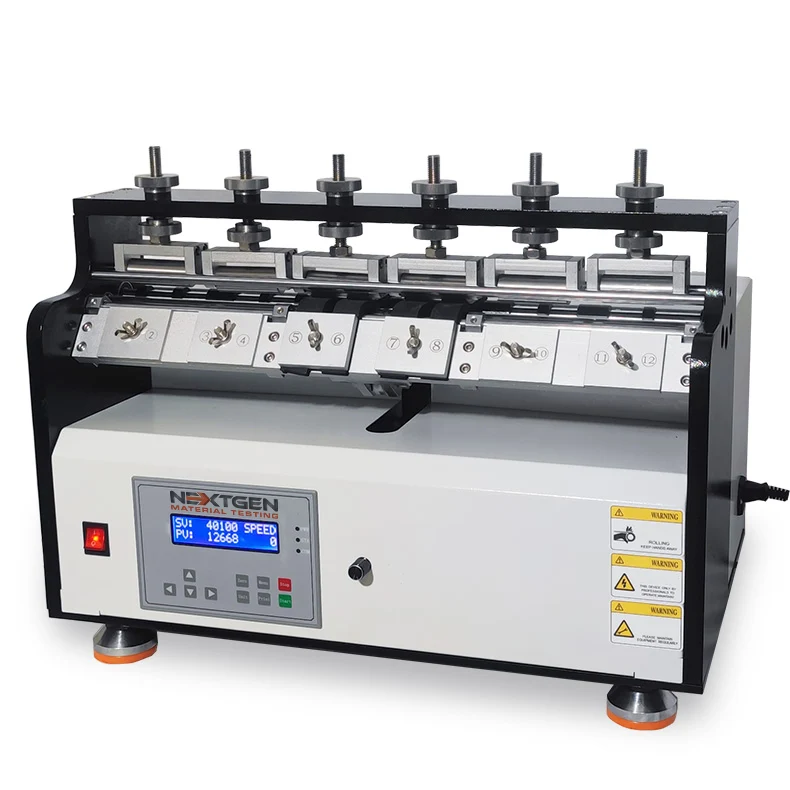

Ross Flex Tester
Ross Flex Tester is designed to determine the resistance of vulcanized or synthetic elastomers to cut growth. The system does so under continuously bend flexing in 90°.