
Rubber Testing Equipment

Standards






GenNBS is NextGen's NBS Abrasion Tester used to test the abrasion resistance of vulcanized rubber or other rubber compounds. It is commonly used for the soles and heels of footwear. It has an intelligent power failure recovery system. The unit conducts measurements through volumetric loss of specimens exposed to the action of a normalized abrasive medium secured to a rotations cylinder. Learn all you need to know about NBS Abrasion Testing Systems.
Specifications
| Specimen | 3 sets, 25.4 x 25.4 x 6.35 mm |
| Load | 2265g, 3 sets |
| Counter | LCD 0 - 999.999 |
| Rotation Speed | 45&#plusmn;5 rpm |
| Suction | 2kg/cm2 |
| Spare Parts | Standard Rubber (5pc) North American #40 Grit (1pc) |
| Dimension (W x D x H) | 21.65 x 11.80 x 19.70-inches 55 x 30 x 50 cm |
| Weight | 154 lbs / 70 kg |
| Power | 110V/60Hz or 220V/50Hz |
FAQs
One of the many important physical characteristics to take into account while developing polyurethanes is hardness. Polyurethanes, unlike metals, rubbers, and plastics, can be specially designed to provide a wide range of hardness with different features. In this article, we'll examine what hardness is and how it affects the performance of your product.
Hardness is a gauge of a material's resistance to force and is frequently measured on a Shore durometer scale. The surface of the material will be more easily deformed or indented, and this will result in a softer durometer reading. To accurately gauge a material's hardness, a variety of durometer scales are utilized. However, polyurethanes often employ just three scales: A, D, or 00. Softer materials are measured by Shore A and Shore 00, while stiffer materials are measured by Shore D.
For comparison, an inline speed skating wheel is approximately 80 Shore A, a gummy bear is approximately 10 Shore 00, and a hard hat is approximately 70 Shore D. Anything harder than a 90 shore D will fall within a Rockwell hardness scale, typically used to measure the hardness of metals. A Rockwell hardness scale, which is commonly used to gauge the hardness of metals, classifies anything that is harder than a 90-shore D.
If you are searching for a rubber abrasion tester, look no more. NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester is all you need!
Click here to obtain your personalized quote
Localized friction forces that cause sliding can put a lot of energy into the rubber. When the rubber cannot endure these forces, abrasion and wear occur.
Particle impingement happens in systems like chutes, rebound plates, and sandblast hoses. Elastomers are flexible and can disperse pressures brought on by particle impact. According to a sandblast test, soft, resilient rubber is more resistant to abrasion than steel or cast iron at a 90-degree impingement angle. But not any elastomer can be applied. A hard tyre tread will degrade more quickly than a soft elastomer under the same circumstances. Which material to be utilized depends significantly on the angle of particle impact. Which material to be utilized depends significantly on the angle of particle impact. The advantage of elastomers over metals diminishes and eventually vanishes as the angle decreases below 90 degrees.
For sliding abrasion, NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester is your go to choice on the market!
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
Abrasion comes in two flavours: sliding and impingement. The passing of an adjacent surface across the rubber surface is known as sliding. Sand grains striking the surface are an example of impingement, which is the wearing down of rubber. In actual service, sliding and impingement together cause the majority of the wear.
Localized friction forces that cause sliding can put a lot of energy into the rubber. When the rubber cannot endure these forces, abrasion and wear occur.
There are at least 25 laboratory abrasion test devices, which suggests that it is challenging to relate the results of this kind of test to service performance. The National Bureau of Standards Abrader, a slinging type abrader, is the most well-known testing apparatus in the rubber sector. The NBS Abrader operates at a steady speed with a fixed load and an established abrasive grit.
It does not provide information on a compound's performance across a wide range of conditions or regarding cut resistance, chunking, or flat spots.
NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester is your go to tester on the market!
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
The variations in how well the urethane vulcanizates perform have a reason. The NBS testing simulates an extremely demanding service condition. The toughest of the vulcanizates are able to withstand the most pressure in this particular situation.
The Taber test, on the other hand, is a far less severe kind of test. Because they have more resilience and "give" while under load, the softer compounds outperformed the tougher ones.
For the NBS tests, the sliding abrasion resistance rises as the hardness does. The NBS Index of the 75A durometer vulcanizate was extremely high. This is most likely due to the plasticizer used in the compound lubricating the abrasive wheels.
It is without a doubt challenging to derive useful values from laboratory abrasion tests. Urethane is nevertheless regarded as having better sliding abrasion resistance, despite this. In many applications where wear is a concern, it performed quite well. Urethane routinely outlasted traditional rubber and plastic materials in the tests, often by a ratio of up to 8 to 1.
NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester – GenNBS can generate Suction at 2kg/cm².
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
The abrasion resistance of vulcanized rubber or other rubber compounds is tested using GenNBS. It is frequently used for shoe heels and soles. It has a sophisticated power failure recovery system. The instrument performs measurements through the volumetric loss of samples subjected to the action of a standardized abrasive media secured to a rotating cylinder.
There are at least 25 lab abrasion test equipment options. This is a blatant sign that it is difficult to connect this kind of testing to service performance. The National Bureau of Standards (NBS) Abrader is the most extensively used testing tool in the rubber industry. It is an abrader of the slinging variety. The NBS abrader operates at a steady velocity while applying a predetermined abrasive grit to a fixed load.
It won't demonstrate how a certain molecule will function in highly variable circumstances. It won't reveal anything about the material's ability to resist cuts, flat spots, or chunking either.
NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester – GenNBS uses America #40 grinding paper
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
The NBS abrasion tester, also known as the NBS abrasion testing machine, is a professional tool used to evaluate the vulcanized rubber or other rubber materials used in shoe soles and heels for their resistance to abrasion. Particularly for materials with a thickness exceeding 2.5 mm.
It is well acknowledged that when comparing various rubber materials, service performance may not always directly correspond to the outcomes of the predictive test. The abrasion resistance of materials whose compositions significantly deviate from the reference compound standard cannot be measured using the test procedure.
When contrasting polyurethane compositions with the reference compound standard, for example, the findings could be deceptive.
Correlating laboratory-based abrasion studies with end-use scenarios might be challenging. The choice of materials will benefit from the measurement of attributes. However, it is not advised to compare to the rates in actual service because the differences in temperatures and speeds may be thousands of times greater.
The rotation speed of NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester – GenNBS is 45±5 rpm.
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
There are generally two forms of abrasion. Sliding and impingement are these. When the surrounding surface slides across the rubber surface, sliding abrasion occurs. Impingement abrasion, on the other hand, is characterized by sand particles that strike the surface as the rubber wears away. In actual service, the two types of abrasion combine to cause the majority of the wear.
When sliding on rubber, localized or constrained friction forces can cause significant energy damage. Abrasion and wear occur when the rubber is unable to endure such forces.
Particle impingement occurs in a variety of applications, including chutes, sandblast hoses, and rebound plates. Elastomers are easily yieldable, which allows them to disperse the tension caused by particle impingement. There will be a 90-degree impingement angle during a sandblast test. Compared to steel or cast iron, rubber is resilient and supple and has greater abrasion resistance.
NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester – GenNBS can load 3 specimen load sets.
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
Correlating laboratory-based abrasion studies with end-use scenarios might be challenging. The choice of materials will benefit from the measurement of attributes. However, it is not advised to compare to the rates in actual service because the differences in temperatures and speeds may be thousands of times greater.
Here are the technical specifications of NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester – GenNBS
|
Specimen |
3 sets, 25.4 x 25.4 x 6.35 mm |
|
Load |
2265g, 3 sets |
|
Counter |
LCD 0 – 999.999 |
|
Rotation speed |
45±5 rpm |
|
Suction |
2kg/cm² |
|
Grinding paper |
America #40 |
|
Dimensions |
21.65 x 11.80 x 19.70-inches 55 x 30 x 50 cm |
|
Weight |
154 lbs / 70 kg |
|
Power |
110V/60Hz or 220V/50Hz |
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
Correlating laboratory-based abrasion studies with end-use scenarios might be challenging. The choice of materials will benefit from the measurement of attributes. However, it is not advised to compare to the rates in actual service because the differences in temperatures and speeds may be thousands of times greater.
Vulcanized rubber and other rubber compounds with similar compositions are tested for their degrees of abrasion resistance using the NBS abrasion tester. Most frequently, the system complies with ASTM D1630 and D394 standards. The heels and bottoms of shoes are frequent locations for these materials. A clever system for power outage recovery is included in most models. When exposed to movements from an abrasive material that has been normalized and is attached to a rotating cylinder, it accomplishes the measurements through the volumetric specimen loss.
To sum up, NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester – GenNBS comply with ASTM D394 standard.
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
The GenNBS NBS Abrasion Tester from NextGen is used to evaluate the vulcanized rubber or other rubber compounds' resistance to abrasion. It is frequently utilized for shoe heels and soles. It has a sophisticated system for recovering from power outages. The device measures the volumetric loss in samples that have been subjected to the action of a normalized abrasive media that is secured to a rotating cylinder.
The rubber materials used for shoe bottoms and heels are tested for their ability to resist abrasion. For materials that are less than 2.5mm thick, this test is not advised.
Testing techniques are frequently used to assess:
Other rubber materials that are comparable to the standard reference compound, such as vulcanized rubber
To answer your question, yes, NextGen’s NBS Rubber Abrasion Tester – GenNBS comply with ASTM D1630standard
Click here to obtain your personalized quote.
During testing, technicians follow the ASTM D1630 abrasion standard guidelines.
First, the technician unlocks a bridge holding the gauges. The bridge is then lifted to allow the arms to swing backwards for mounting of the specimen. Each compound is then mounted and secured in the slots.
The operator lowers the arms to the metallic drums. The bridge is lowered and locked in place, with a calibration weight on every arm. The technician likewise calibrates the gauges, then sets the test's number of revolutions. Finally, the operator presses the button to start the abrasion testing.
Prior to the actual testing, the equipment is given a break in run to allow the conditioning of the new abrasive paper. Garnet paper with #40 grit is used for the test. It can be used for 18 runs.
The abrader makes 500 revolutions employing break in compounds. It makes a second run of another 500 revolutions. Standard reference compounds are used for the second run. The compounds are discarded after the runs.
In the actual run, the new reference compound is used together with the previous three compounds. The four compounds then undergo four passes. Each pass tests three compounds.
The first pass if for testing the three previous reference compounds. The second pass is for the first two reference compounds along with the new compound. The third pass is for the third, together with the new compound as well as the first compound. The final pass is for testing the new compound, and the second and third reference compounds.
The operator runs the NBS tester until the compounds’ surface matches the drum’s shape. The gauges and revolution counter is set to zero. The operator then restarts the tester.
The tester runs until it 0.1 inch is scraped off from the compounds. The gauges indicate the amount of the material scraped off. The technician logs the readings and number of revolutions from each gauge. He then computes the number of revolutions required to abrade 0.1 inch from all compounds.
The tester needs another run, this time with new standard reference compounds. The reference compounds are then removed and a new compound is mounted on the arms.
The machine will stop from running when it has abraded 0.1 inch off the fresh set of specimens. The operator gets the values from the initial two runs in the latest computation.
Although the NBS abrasion test machine applies the same principle as other rubber abrasion testing machines, the NBS method is designed specifically to test materials that fall under a thickness level not lower than 2.5 mm.
The NBS testing machine employs a test specimen that is abraded against a rotating drum that is covered in abrasive materials. A weight is put in place to pull the specimen towards the drum with the use of a consistent force. The testing machine operator gauges the strength of the material by assessing the remaining volume after a test cycle.
There must be three reference compounds as well as a new reference compound used for testing. The original reference compound standard must be 8 inches long and 1 inch wide. Laboratories cut the material to the standard size specifically for rubber abrasion testing.
The standard reference compound size should measure 1 x 1 x 0.25 inch. The specimen must be of this size in order to fit into the NBS abrasion testing machine's arm slot.
If a specimen is over the standard thickness, it will require buffing until it is reduced to the appropriate size. On the other hand, thinner specimens should be stacked or piled in layers until the required thickness is achieved.
The new reference compound must have been stored during the past six months prior to the scheduled testing. A compound that has been stored for more than six months is not qualified to be used as specimen for the test.
Also, the reference compound must undergo a curing process before the test. This is necessary to make sure that the material will get an even abrasion. The compound reference is cured at a pre-determined temperature.
There is likewise a breach in the compound used for conditioning the new abrasive paper. This break has similar dimensions to the standard reference compound.
The most common test materials for the NBS abrasion testing method are vulcanized rubbers that are a fixture in the footwear industry. To be specific, these materials are used for heels and soles of shoes and other footwear.
The NBS testing machine is ideally used for testing thicker materials. A more abrasive sheet attached to the rotating drum is used to expose the rubber material to more intense revolutions. As a result, the evaluation of wear is achieved faster compared to the results obtained from testing using a DIN abrasion testing machine.
Not all rubber materials can be tested using the NBS abrasion tester. For one, the machine is not suitable for use for thin polyurethane materials. When the material is exposed to the NBS tester's higher abrasion levels, it will result to wearing through after only a small number of short revolutions. The known benchmark for materials appropriate for use with the NBS abrasion testing machine is vulcanized rubber's hardness.
The NBS tester is not suitable for any thin polyurethane materials. Exposing this material to the higher levels of abrasion on the NBS tester will cause them to wear through within only a few short revolutions. The hardness of vulcanized rubber is the benchmark for materials suitable for NBS abrasion testing.
Because the NBS tester is typically used with thicker materials, it uses a more abrasive sheet affixed to the rotating drum to expose the rubber sample to more intense revolutions. This allows for an evaluation of wear at a faster rate than that of a DIN abrasion tester.
Vulcanized rubbers are most common with NBS abrasion test method - typically found in the footwear industry.
The NBS tester uses a test specimen to abrade against a rotating drum covered in abrasive material. A weight pulls the specimen into the drum at a consistent force and the operator can gauge the materials strength by evaluating the volume remaining after the test cycle.
While the principle of the NBS abrasion tester is similar to other rubber abrasion testers, the NBS procedure is specifically designed for testing materials with a thickness of at least 2.5mm.
Related Products
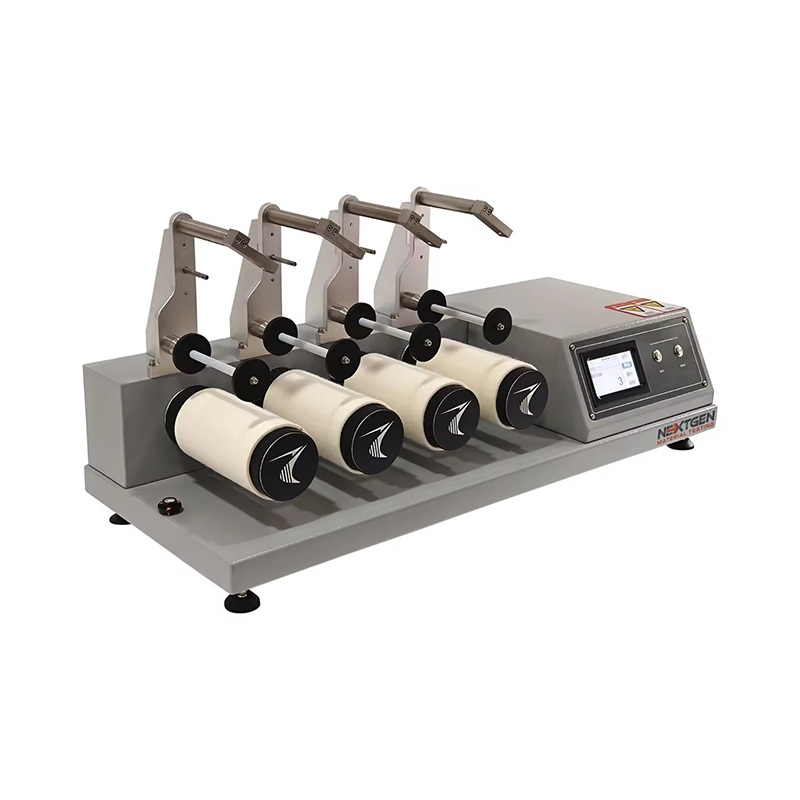

ICI / Mace Snag Tester
Discover the Fabric Textile ICI / Mace Snag Tester, a reliable tool for assessing fabric snagging under normal wear conditions.

Moving Die Rheometer (MDR)
Introducing the NG-MDR Moving Die Rheometer, your solution for accurately assessing the curing and processing characteristics of vulcanized rubber compounds. Designed for precision, this state-of-the-art rheometer captures the characteristic curve and parameters of rubber vulcanization by measuring the torque applied to the oscillating die.
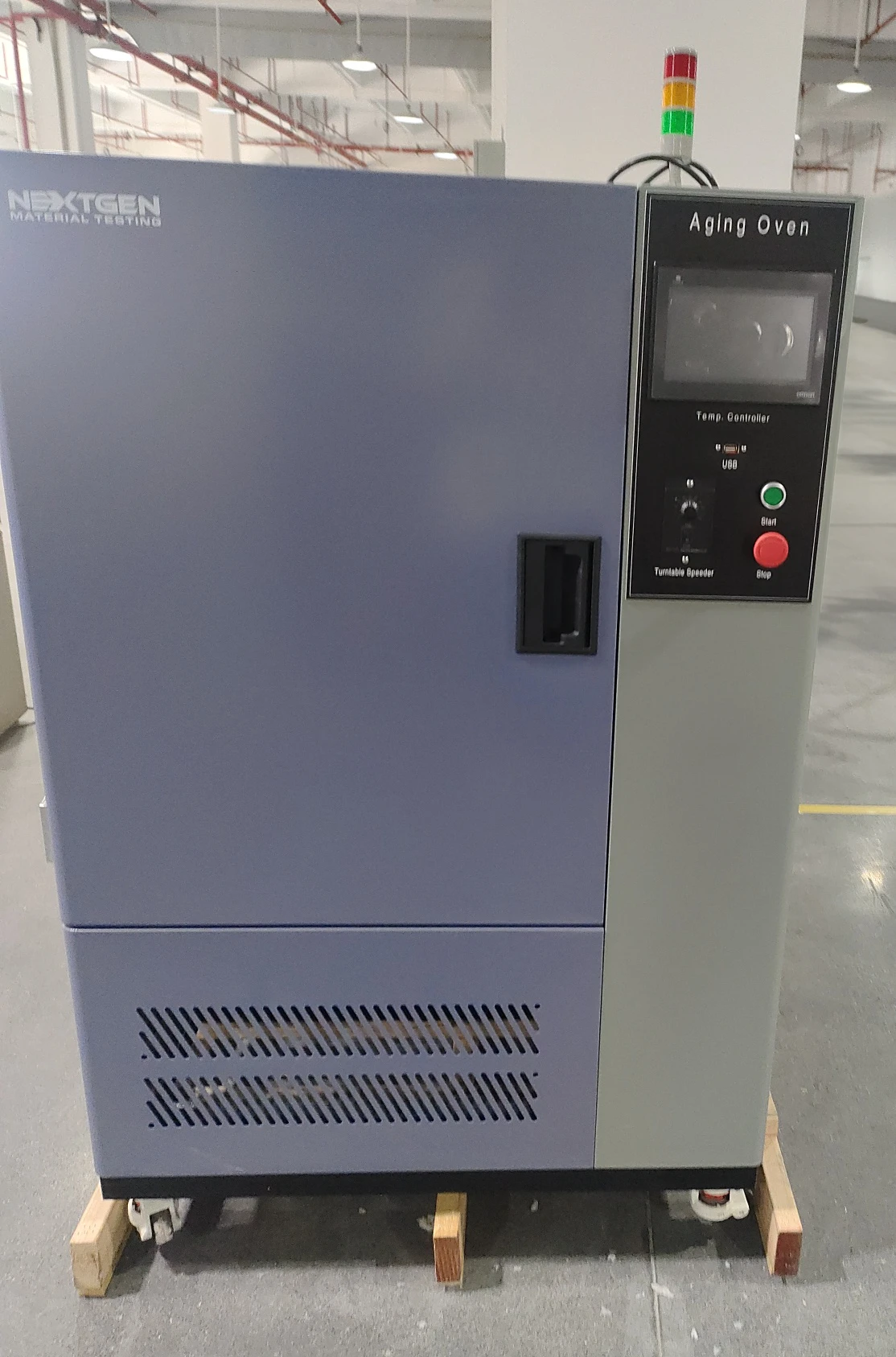

Aging Oven
Our aging oven is well-suited for performing drying, baking, wax melting, and sterilization experiments in industrial and mining enterprises, as well as in laboratories, colleges, and research institutions.
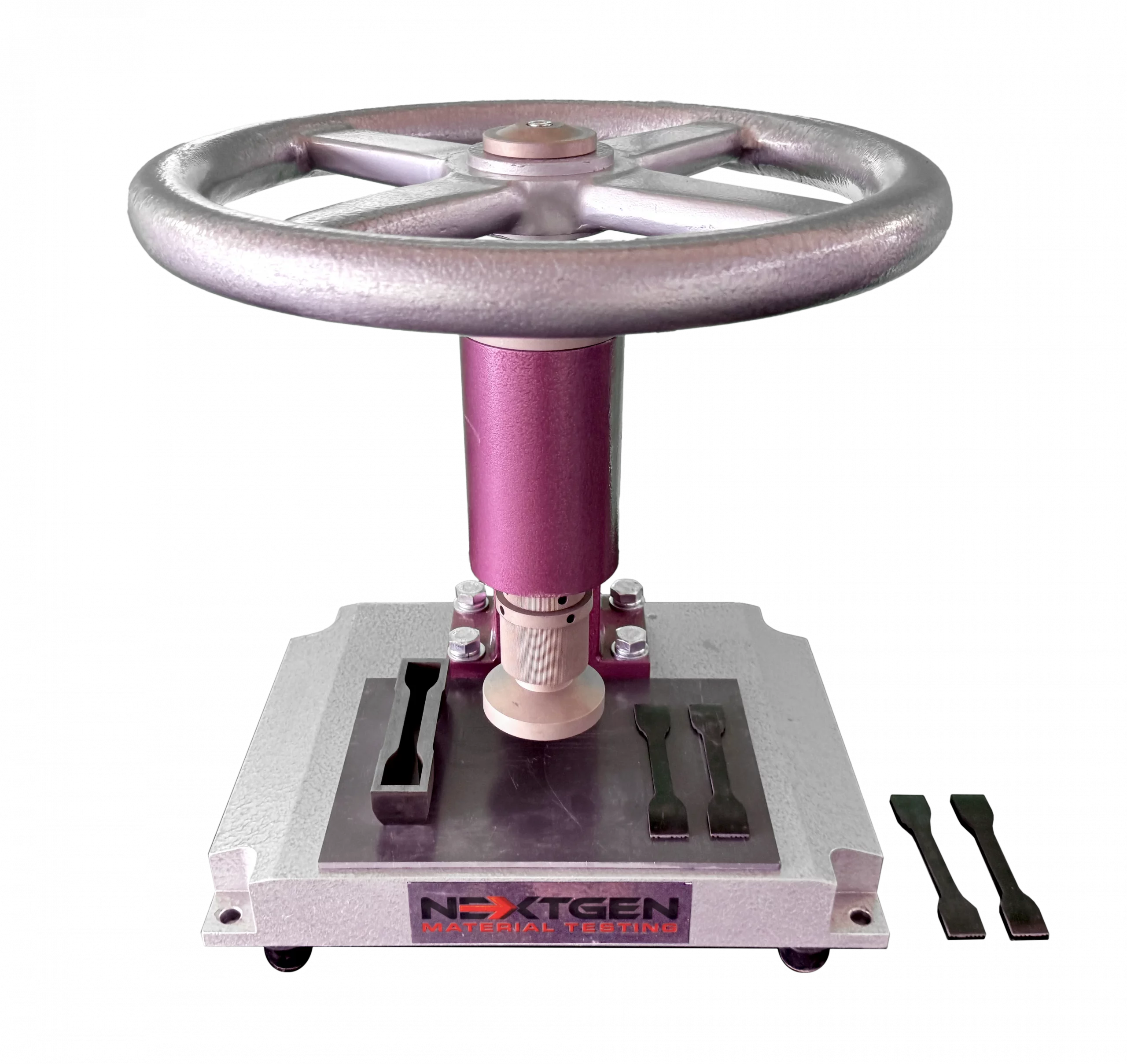
NG-T-Press M Series - Manual Cutting Press System for Rubber Tensile Specimens
Our newest manual cutting press system is suitable for laboratories to create specimens from rubber, tape, and special materials.
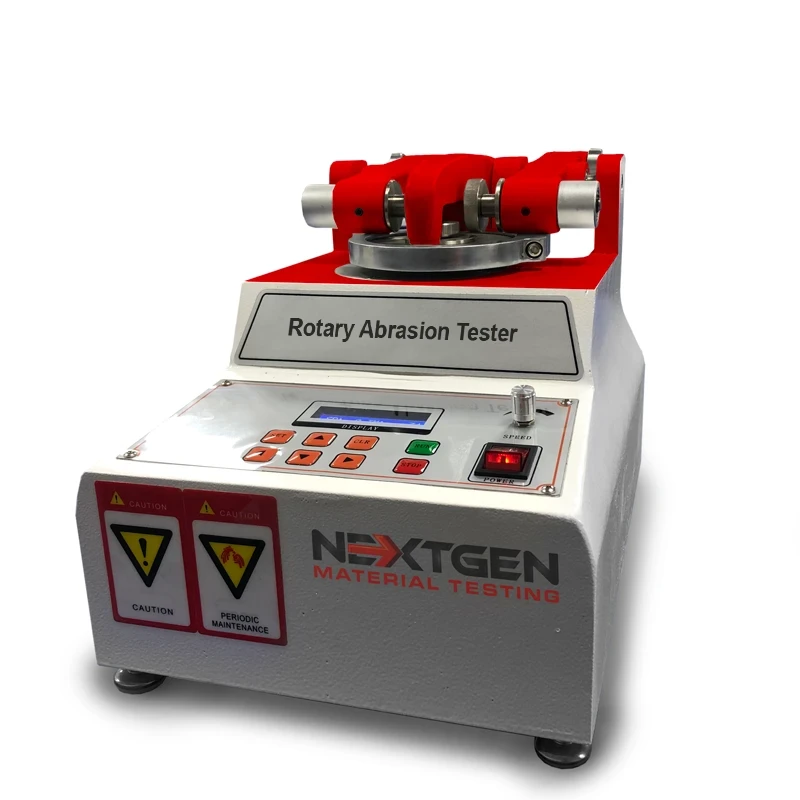

Rotary Abrasion Tester Single & Dual Wheel
GenRotary used evaluate abrasion resistance. It can conduct tests on a wide range of materials such as: cloth, paper, paint, plywood, leather, tile, glass, rubber etc. It tests the specimen by rotating it while in contact with the grinding wheel and applying the required pressure. The Joss of weight reflects on the change in weight of the specimen. The unit also has an intelligent power failure recovery function.
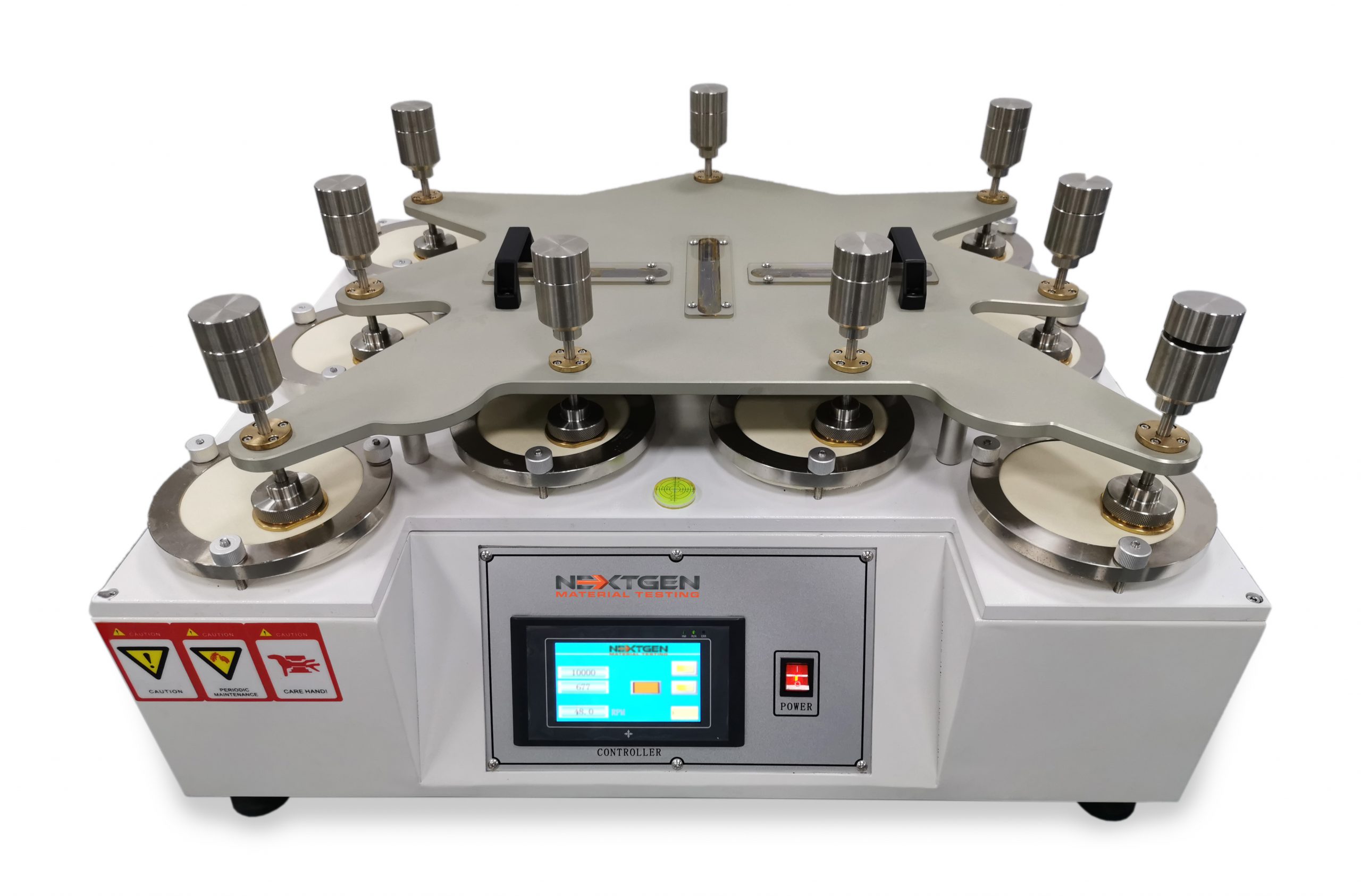

9-Station Martindale Abrasion Tester
The GenDale - Martindale Abrasion Tester is mainly used to test shoe fabric, shoe lining, and many other types of shoe related materials.

GenRoss-CH - Ross Flex Tester with Low Temperature Chamber
GenRoss-CH is an advanced Ross Flex Tester designed for assessing the cold resistance of materials in low temperature environments.

Linear Taber Abrasion Tester
NextGen's linear abrasion meters evaluate the abrasion and scratch resistance of products, along with color transmission.

NextGen Environmental Chambers NG-EC 100,150,225,408,1000
The temperature and humidity NextGen Environmental Chambers features a sturdy cabinet made of cold-rolled steel and stainless steel.

digiChamber - Temperature Controlled Hardness Testing
Discover digiChamber from NextGen Material Testing, the advanced temperature-controlled hardness tester developed by Bareiss.
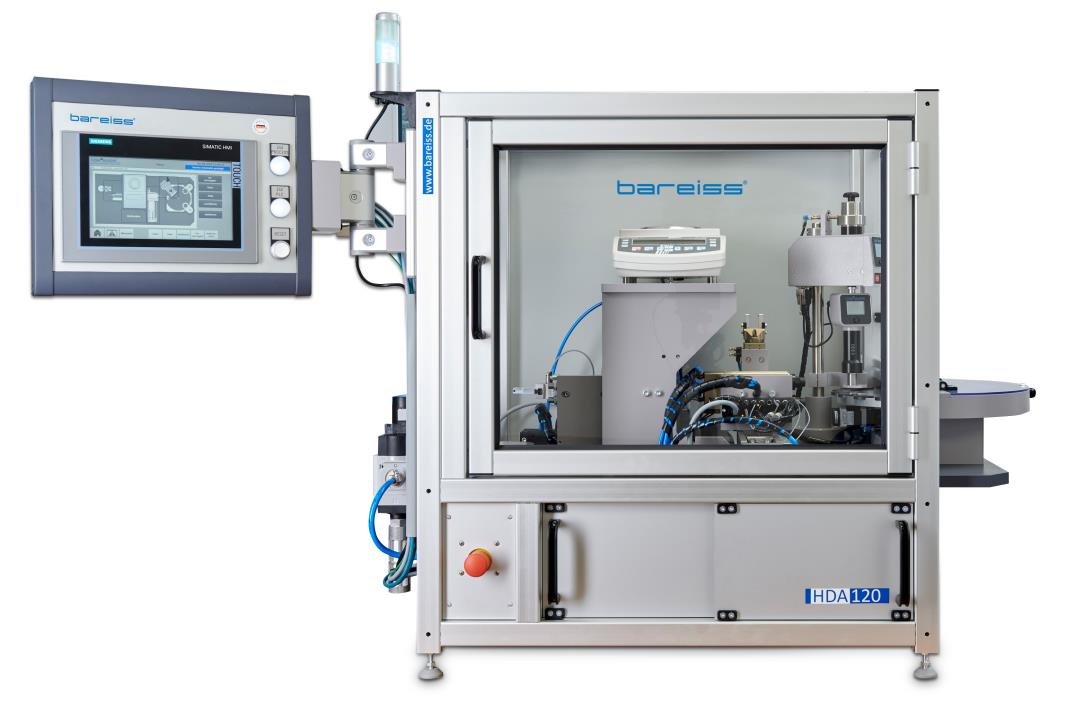

HDA 120 - Hardness and Density Automation Test System
The HDA 120 test system is a versatile solution for semi-automatic detection of sample hardness and density.

RPA Ultra - Advanced Rubber Process Analyzer Rheometer
RPA Ultra is an advanced rubber process analyzer rheometer that measures the dynamic and static characteristics of raw rubber compounds
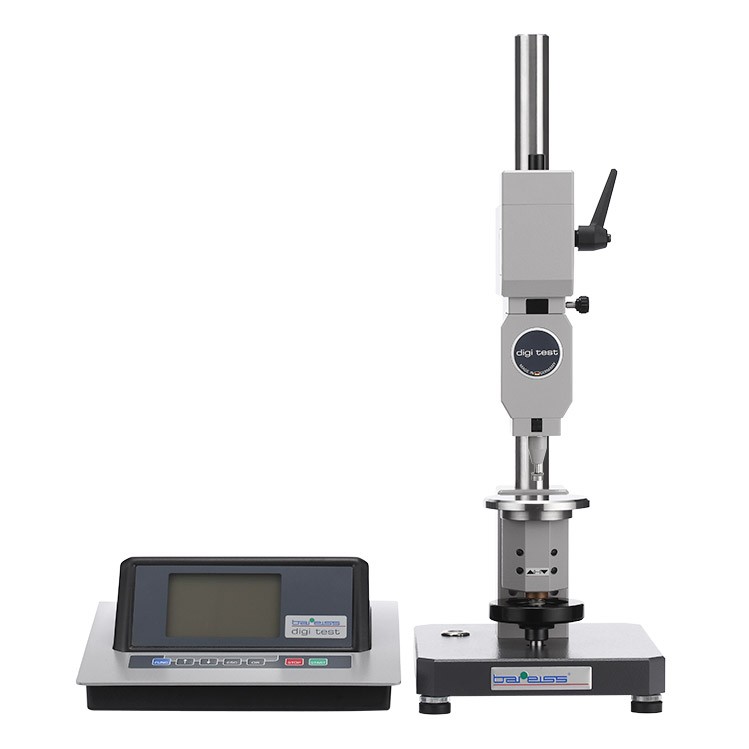

Automatic Shore, IRHD and VLRH Hardness Testing System
NextGen is proud to present our German line of fully-automatic Shore, IRHD and VLRH hardness testing system for plastic materials, plastic and foam compounds for the ultimate precision, accuracy and repeatability, exceptional ease-of-use and maintenance. Experience the industry leader for specimen testing including rubbers, plastics, foams, composites, o-rings, and more.
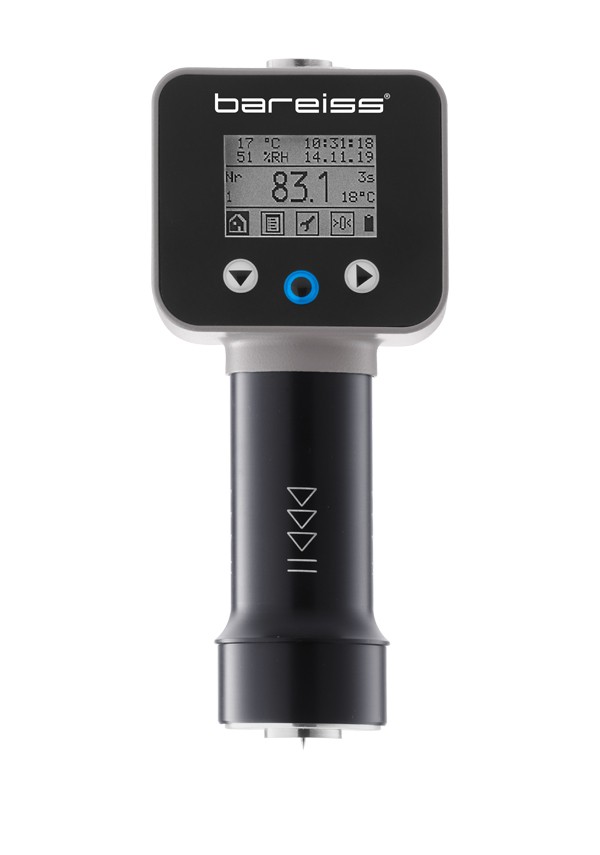

Advanced Portable Shore Durometer System with Test Stand Options
HPEIII is NextGen's advanced German line of equipment that is the new generation of HPE systems ideal for various plastic and plastic compound testing. The new system enhancements offer advantages including temperature sensor, reading values of ambient temperature and humidity, historical hardness value display, larger LCD display, standard USB connection and much more. These advanced portable systems can be paired up with either manual or automatic motorized test stands to help eliminate the human error factor and maximize accuracy and repeatability between test when switching from one operator to the next.

Classic Analogue Shore Durometer with Test Stand Options
This German-manufactured system has been the global benchmark of Shore hardness testing systems since 1954. With ever enhanced ergonomic design, the HP Shore Hardness Tester is both visually appealing and precise rubber and plastic testing system as it has been for nearly 50 years.

Akron Abrasion Tester
GenKron is used together with a special balance for testing the abrasive consumption of materials. The measurements are done through volumetric loss of a rotating specimen exposed to the action of a standard grinding wheel. It is especially suited for testing harder materials such as shoe soles, tires and other rubber materials.

Burst Strength Tester for Fabric
GenBurst is the Burst Strength Tester designed to test anti-rupture strength of variety of materials such as leather, paper and fabric.
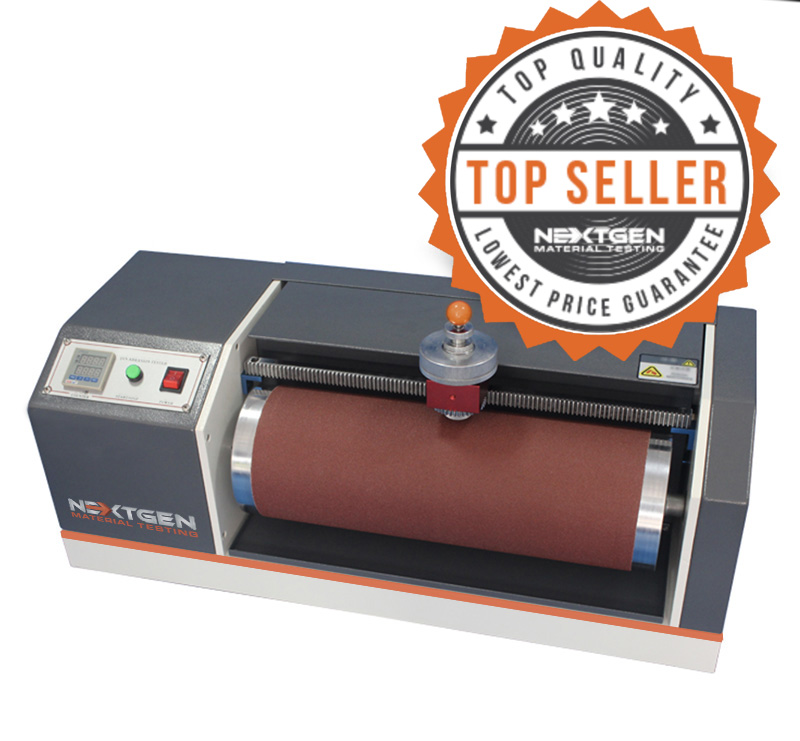

DIN Abrasion Tester
GenDin, is designed to conform to the ASTM D5963 and IS0 4649 standards. This top quality and highly popular abrasion tester will allow you to measure the abrasion resistance of rubbers (vulcanized thermo set rubbers and thermoplastic elastomers) that are subject to abrasive/frictional wear on their actual service. Since wear is always a result of abrasion, different test methods have been developed for the simulation of long term wear.

Demattia Flex Cracking Tester
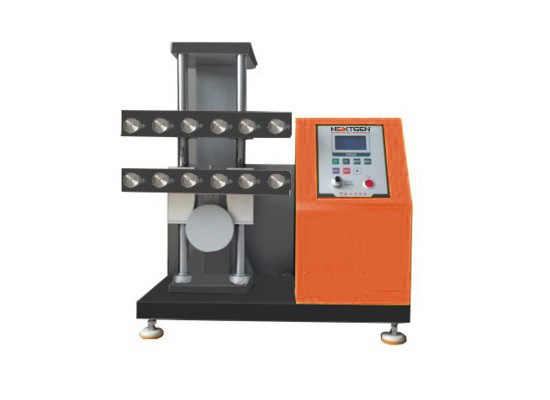
GenFlex tests the ability of rubber products to withstand repeated flexing without developing cracks is of prime importance where such products are used in conditions undergoing repeated flexing. Flexing endurance of rubber products is determined by simulating in laboratory the action of flexing repeatedly under standard conditions of speed, mode, and degree of flexing.

Discoloration Meter
The machine is used to simulate an environment of sunlight radiation on a specimen to identify the resistance of fabric to discoloration.
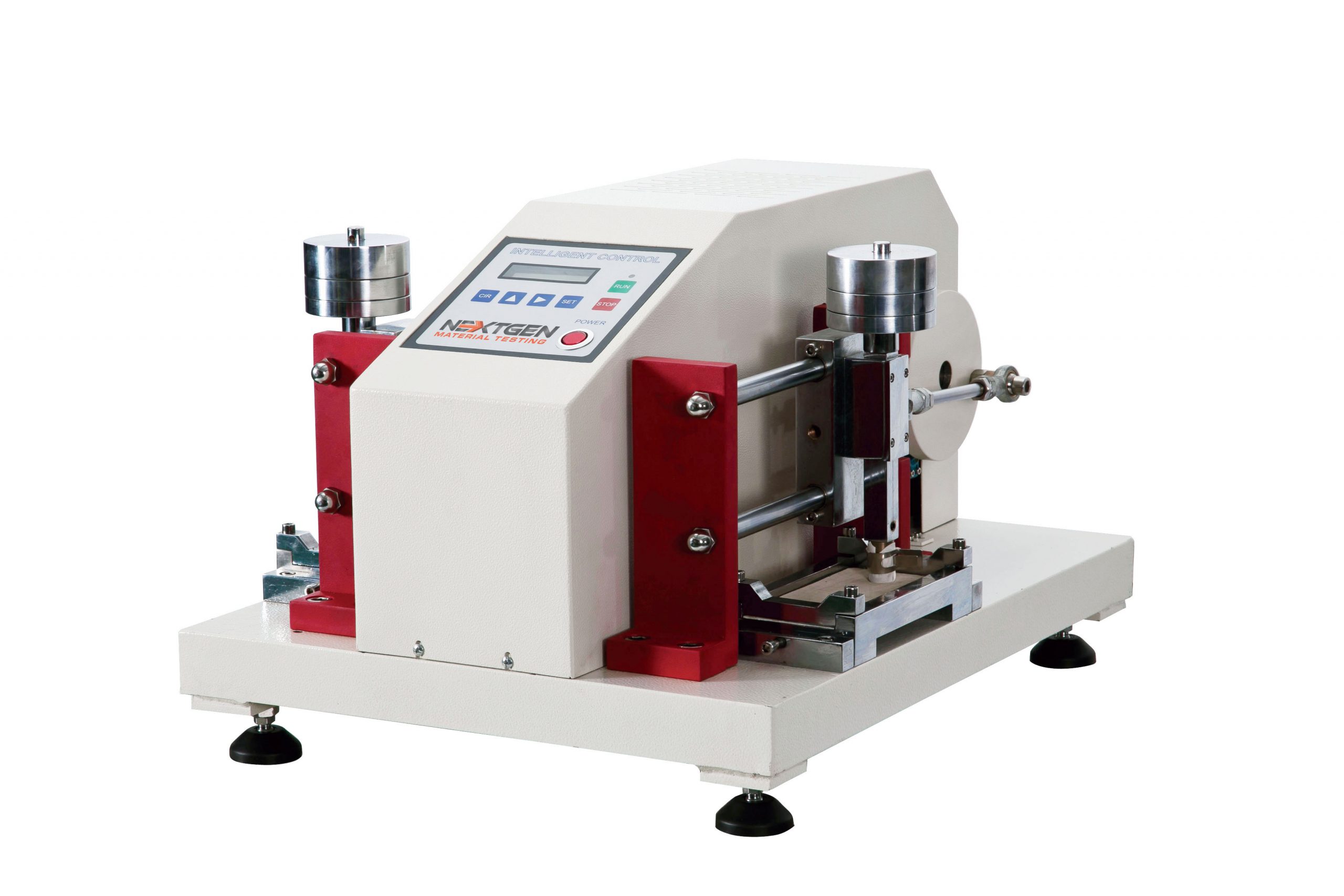

Electric Crocking Tester - GenCrock
The machine is used to test the dyeing of the fabric, and the fade degree of the leather after dry or wet rubbing. The test method involves the specimen to be fastened to the base of the crocking meter and rubbed with an abrasive hammer attached to a wet or a dry cloth under controlled conditions. The transfer of colour is then measured using a scale to evaluate the rating of the specimen's dyeing grade.

Freezing Tester - GenFreeze
GenFreeze is specially designed to test the characteristics of various materials in a cold environment to ensure suitability for use in a cold climate. Based on the testing demand, adjust the beater and flexing grip, then load to the desired position. It can be used to test rubbers, leather, and plastics, PU leather etc. The unit can be adjusted to meet different requirements.
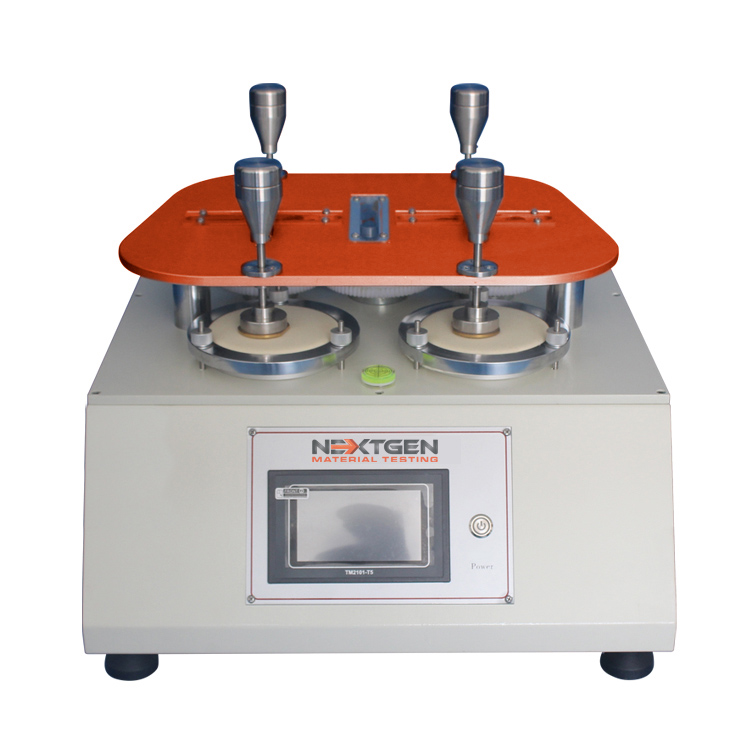

Martindale Abrasion Tester - GenDale
GenDale is mainly used to test shoe fabric, shoe lining, and many other types of shoe related materials. The unit can test up to four specimens at the same time for abrasion. The fabric specimen is measured by having rubbing applied on it via a complex direction of back and forth motion. The accuracy of abrasion strength is determined by the specific number of cycles conducted until a hole appears in the test area of the fabric specimen.

Mooney Viscosity Testing Machine - GenMooney
GenMooney is a viscosity testing machine is applied to measure the viscosity of the unmixed or mixed unvulcanized natural rubber, synthetic rubber and regenerated rubber .This tester has many functions such as fast warming, maintaining temperature, data stability, etc. It is equipped with an automated calibration feature for a simple data calibration of each experiment.
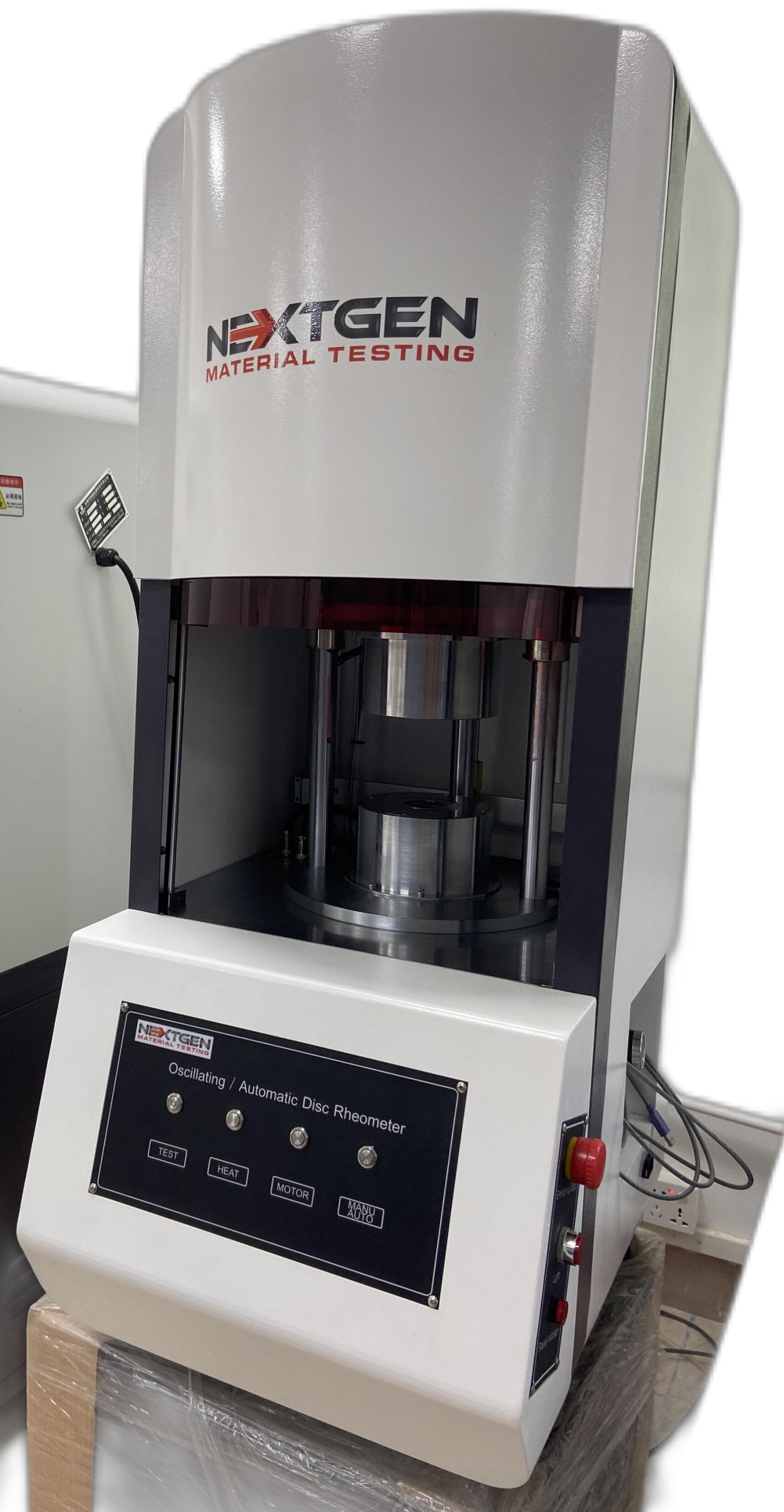

Oscillating / Automatic Disc Rheometer (ODR)
This machine is designed to get the characteristic curve and characteristic parameters of rubber vulcanization by measuring the applied moment of rubber to the oscillating dye body. NG-ODR rotor-free vulcameter has an excellent stability of results. The data and diagrams can be used as a reference for development, research and production quality.
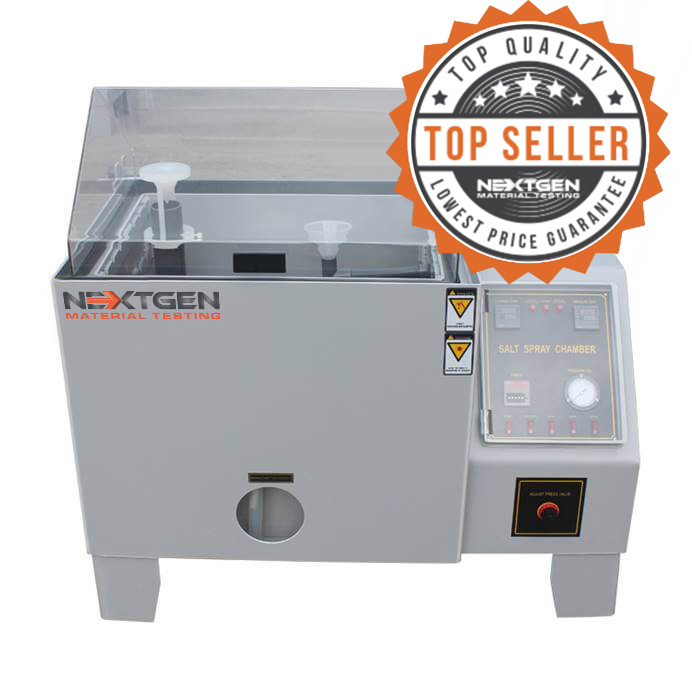

Salt Spray Tester - GenSalt
GenSalt is designed to test the surface of different materials for resistance to corrosion. The unit is commonly used to test coated materials of a metallic nature in a controlled corrosive environment. The test can be used on rust-proof painting, anodizing, electroplating and rust-proof of grease. The machine imitates expedited corrosion process via salt spraying on a given test sample to identify the corrosion (oxides) resistance. Test results are based on the longevity of time a material can resist visible corrosion on the test sample.
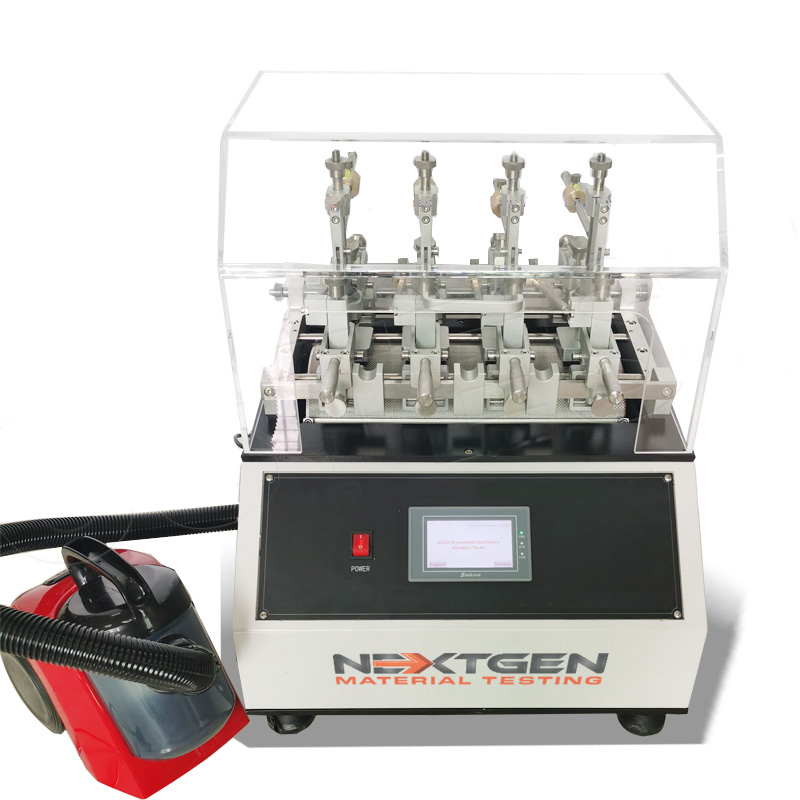

Wyzenbeek Abrasion Tester - GenWyze
The machine is designed to test the abrasion resistance of fabrics and metals. The abrasion of fabrics is tested when the specimen is pulled over the frame and rubbed against an abradant over a curved surface. The number of cycles, also known as double rubs, conducted on the specimen before the fabric shows visible wear is used to determine the rating of abrasion.
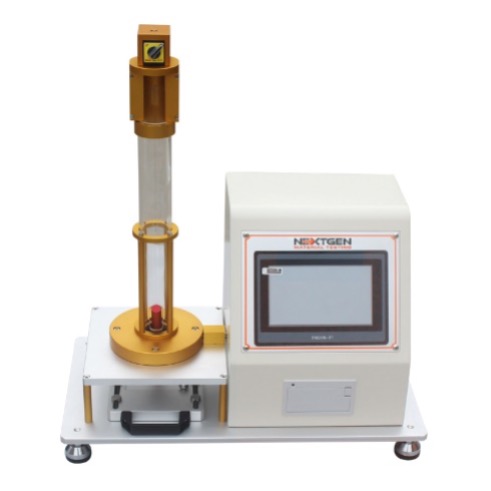

Vertical Rebound Resilience Tester - GenRebound
GenRebound tests the resilience of rubber compounds. The machine must be adjusted in a horizontal position and the plunger raised at a specific height. The plunger is then released onto the specimen for a given number of impacts. The measurements are based on the 4th, 5th, and 6th impacts. The average of the three (3) measurements is then calculated for the test result. The machine is highly useful in production of compounds designed to absorb vibration or shock according to the ASTM standards.

Digital Densimeter Systems
Description The NG-DM-A Series offers high-accuracy digital Densimeters designed for a wide variety of material testing needs. These elegant and compact densimeter systems offer capacity ranges from 150g to 3000g with accuracy of 0.001g/cm3 down to 0.0002g/cm3. Advanced Densimeter System […]
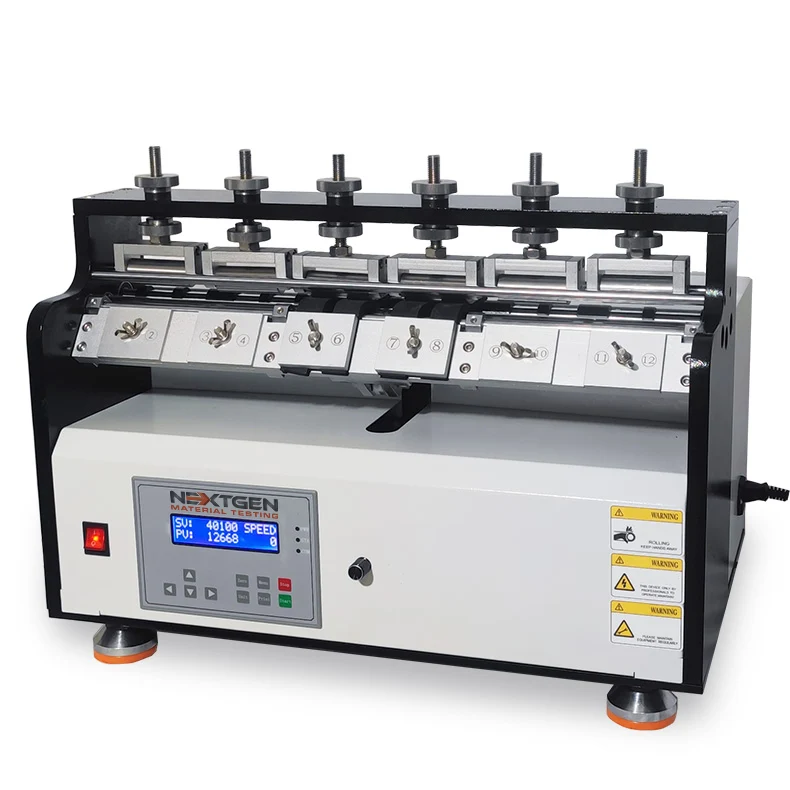

Ross Flex Tester
Ross Flex Tester is designed to determine the resistance of vulcanized or synthetic elastomers to cut growth. The system does so under continuously bend flexing in 90°.