At NextGen, we offer a complete selection of Brinell hardness testing systems, including manual, digital, and fully automatic models. Our BrinGen series is built to deliver stable, repeatable results across a wide range of metals and test forces, from 62.5 kgf to 3000 kgf. With advanced features like closed-loop force control and CCD optical scopes, our testers help streamline testing workflows and reduce operator error.
All models are designed to meet international standards such as ASTM E10 and ISO 6506, making them well-suited for quality control, heat treatment verification, and metallurgical testing.
Understanding the Brinell Hardness Testing Method
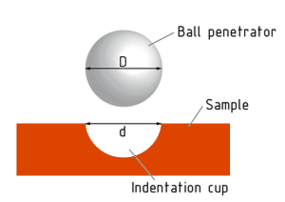
The Brinell hardness test is a well-established method used to determine how resistant a metal is to permanent deformation under load. It works by pressing a tungsten carbide ball—typically 2.5 mm, 5 mm, or 10 mm in diameter—into the surface of the test material using a specified force for a set period of time. Once the load is removed, the diameter of the resulting indentation is measured.
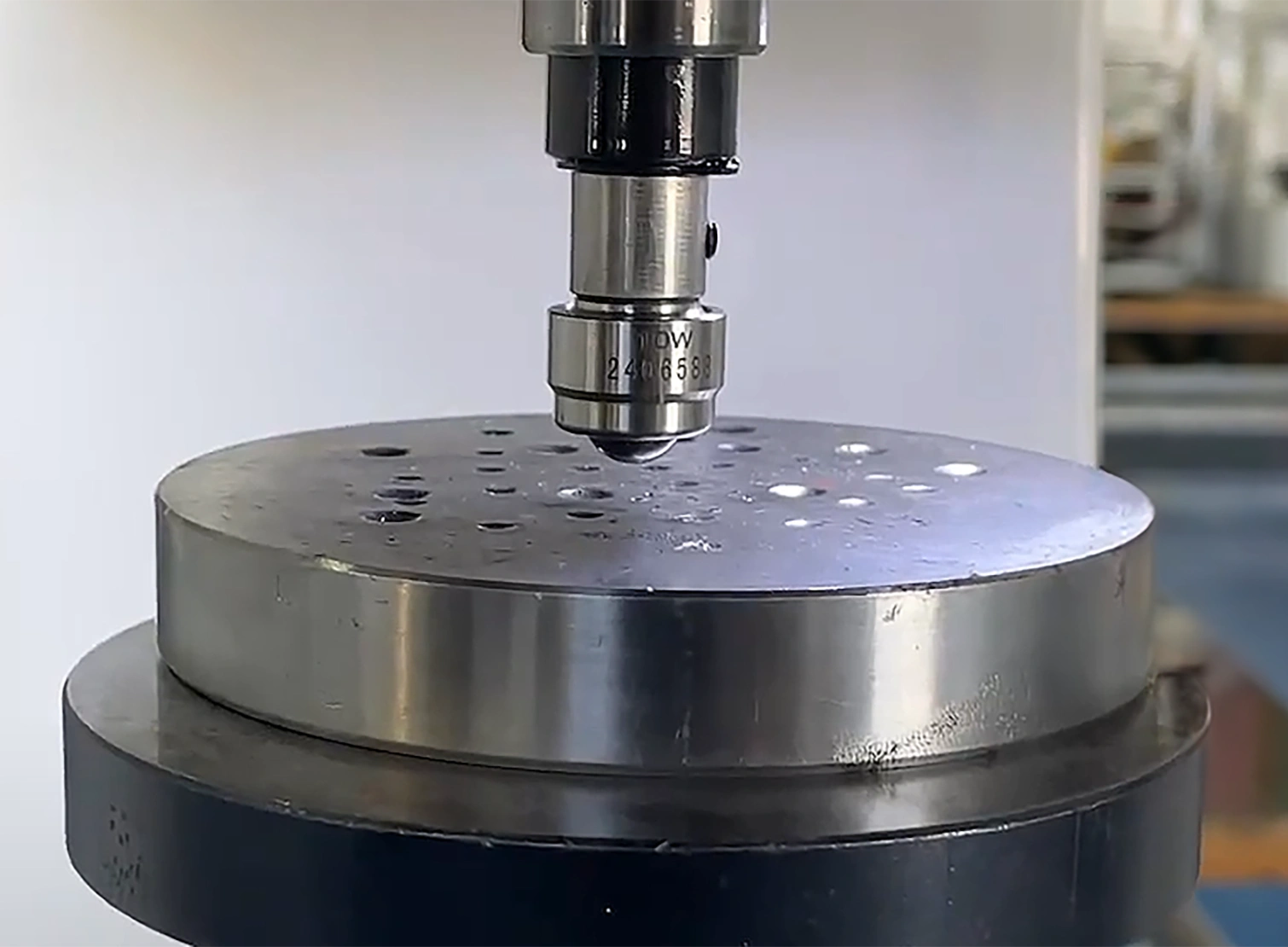

This diameter is then used to calculate the Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) or Brinell Hardness Value (BHV), which gives a reliable indication of the material’s hardness. Larger indentations correspond to softer materials, while smaller ones indicate higher hardness.
Unlike microhardness tests that focus on surface layers, the Brinell method provides a more representative reading of the material’s overall structure. It’s particularly useful for components with uneven surfaces, larger grains, or variable microstructures, such as castings, forgings, and rolled steel plates.
Depending on the application, the indentation can be measured manually using a microscope or automatically through CCD-based optical systems. Both approaches are recognized under international standards like ASTM E10 and ISO 6506.
The Brinell test is valued for its simplicity, repeatability, and suitability for large or rough components that cannot be tested using lighter-load methods. It's a go-to choice for many industries needing reliable hardness data for heavy-duty metal parts.
Our Brinell Hardness Testing Equipment
NextGen offers a complete range of Brinell hardness testing systems to meet the needs of both industrial and laboratory environments. Our products — including high-resolution optical scopes, certified accessories, and fully automated digital testers — are engineered to deliver precise, repeatable, and user-friendly operation for various metals and sample sizes.
BrinGen 3000 Series – Digital & Automatic Brinell Testing System
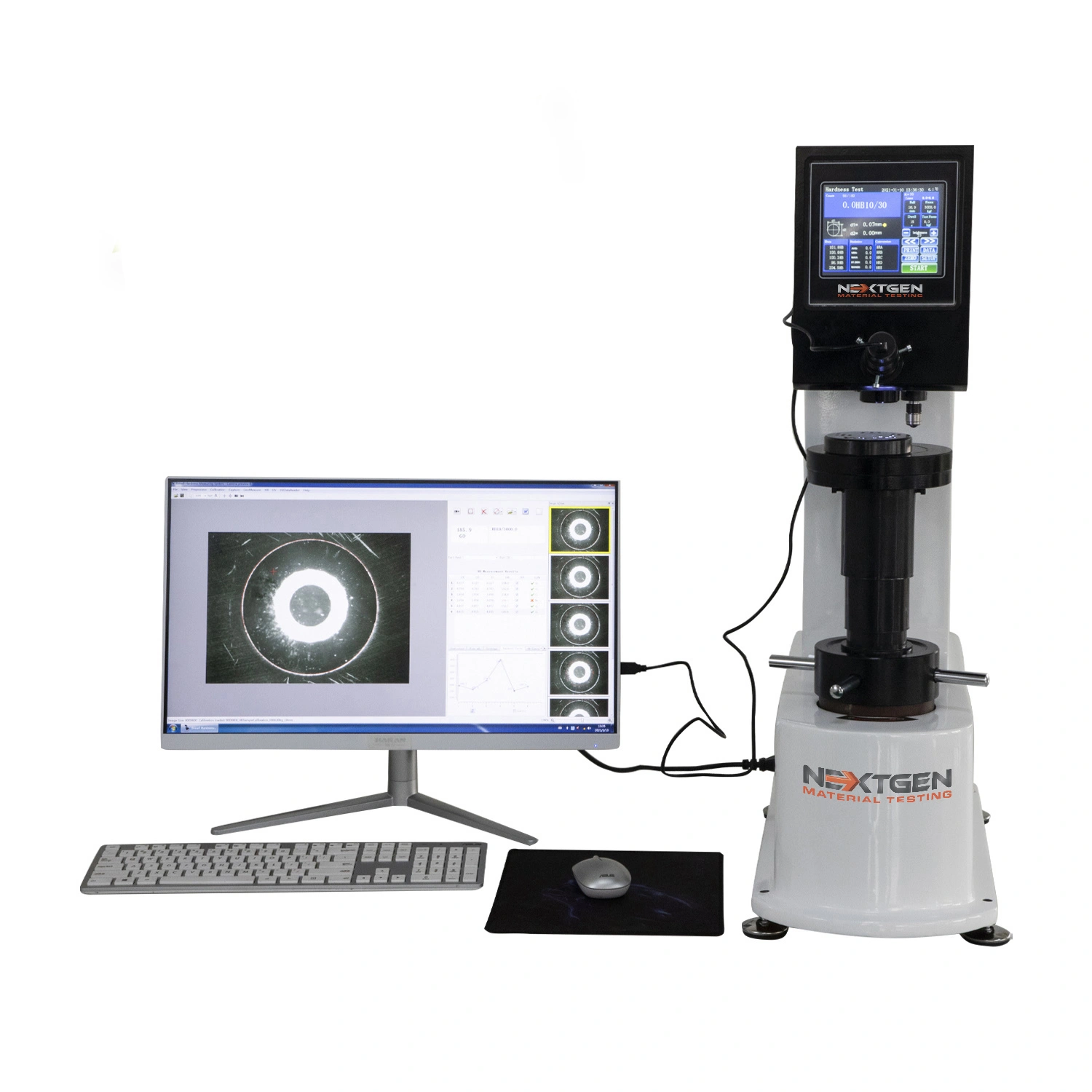 The BrinGen 3000 is a robust digital Brinell tester built for high-force applications ranging from 62.5 kgf to 3000 kgf. Featuring a fully automatic loading sequence and closed-loop control system, it ensures precise and consistent force application as required by ASTM E10. Ideal for production floors and advanced quality control labs, this system supports efficient testing of castings, forgings, and large structural components.
The BrinGen 3000 is a robust digital Brinell tester built for high-force applications ranging from 62.5 kgf to 3000 kgf. Featuring a fully automatic loading sequence and closed-loop control system, it ensures precise and consistent force application as required by ASTM E10. Ideal for production floors and advanced quality control labs, this system supports efficient testing of castings, forgings, and large structural components.
BrinGen Scope – Advanced CCD Optical Measurement System
The BrinGen Scope is a high-performance CCD-based measurement unit designed to automate the reading of Brinell indentations. Compatible with both manual and digital testing setups, it connects directly to your PC or laptop and provides real-time scanning, analysis, and result storage. This optical scope removes subjectivity from measurements and increases speed and accuracy in reporting.
Hardness Test Blocks, Indenters, and Accessories
 We supply a full selection of certified Brinell test blocks, tungsten carbide indenters, and other accessories required for accurate and traceable testing. Each item is manufactured to meet relevant calibration standards and is compatible with NextGen and most third-party testing systems.
We supply a full selection of certified Brinell test blocks, tungsten carbide indenters, and other accessories required for accurate and traceable testing. Each item is manufactured to meet relevant calibration standards and is compatible with NextGen and most third-party testing systems.
Metallography Consumables
 Our line of metallographic consumables includes everything you need for sample preparation before Brinell testing. This includes cutting discs, mounting resins, grinding papers, and polishing cloths—all selected for durability, consistency, and compatibility with major preparation systems.
Our line of metallographic consumables includes everything you need for sample preparation before Brinell testing. This includes cutting discs, mounting resins, grinding papers, and polishing cloths—all selected for durability, consistency, and compatibility with major preparation systems.
Testing Standards We Support
All of NextGen’s Brinell hardness testers are built to meet the requirements of trusted international standards. These standards outline how tests should be performed—from how much force is applied to how results are measured—so that you get consistent, traceable results whether you're working in a production facility or a testing lab.
ASTM E10 – Standard Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
ASTM E10 outlines the procedures for performing Brinell hardness tests using a tungsten carbide ball under various force levels. It includes guidance on test durations, indentation measurements, and acceptable tolerances. This standard is widely used in North America and is considered a benchmark for heavy-load hardness testing of metals like cast iron, steel, and non-ferrous alloys.
ISO 6506 – Brinell Hardness Test for Metallic Materials
ISO 6506 is the international equivalent of ASTM E10 and is used globally in industries that require standardized testing. The standard provides detailed specifications for the indenter, force application, test durations, and how the Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) is calculated based on the diameter of the indentation. It also covers calibration and verification procedures for test machines and reference blocks.
EN ISO 6506 – European Harmonized Standard
EN ISO 6506 mirrors the content of ISO 6506 and is harmonized for use throughout the European Union. This standard is required for CE compliance and supports uniform testing practices across different countries.
GB/T 231 – National Standard for Brinell Hardness Testing
GB/T 231 aligns closely with ASTM E10 and ISO 6506. It provides Brinell testing guidelines widely used in manufacturing systems that follow international material testing practices. This standard is often referenced in OEM and supply chain quality assurance programs.
Industries and Applications for Brinell Hardness Testing
Brinell hardness testing is trusted across industries where large, heavy, or uneven components need to be evaluated for durability and structural integrity. Its ability to deliver stable readings on coarse-grained metals makes it a preferred method in production environments where fine-scale methods may fall short. Here’s how different industries rely on Brinell testing in real-world scenarios:
Heavy Equipment and Automotive
Brinell testing is commonly used to check hardness on steel plates, axles, brake drums, crankshafts, and other heavy-duty parts that undergo high mechanical loads. It helps manufacturers confirm that heat-treated or welded components meet strength specifications before going into service.
Foundries and Metal Casting
In foundries, Brinell testers are used to evaluate cast iron, aluminum, and bronze parts where grain structure and surface roughness make other methods unreliable. The test helps validate batch consistency and supports material certification during final inspection.
Aerospace and Defense
For large aerospace forgings, landing gear housings, and stress-bearing components, Brinell testing offers a dependable way to assess hardness after heat treatment or machining. It supports both process control and documentation required for compliance and traceability.
Energy and Infrastructure
Industries such as power generation and oil and gas rely on Brinell testing to confirm that materials can withstand long-term wear, pressure, and stress. Pipes, pressure vessel components, and structural beams are often tested to confirm hardness levels before deployment.
Rail and Construction
Railway wheels, tracks, and other heavy components undergo Brinell testing to verify resistance to deformation under heavy loads. In construction, it’s used to test the core strength of load-bearing frames, crane arms, and foundation supports.
Quality Control and Materials Labs
In laboratories, Brinell hardness testing is used for material comparisons, R&D, and failure analysis. The method helps researchers study how alloying, heat treatment, or forming methods affect bulk material properties.






 The
The  We supply a full selection of certified
We supply a full selection of certified  Our line of
Our line of