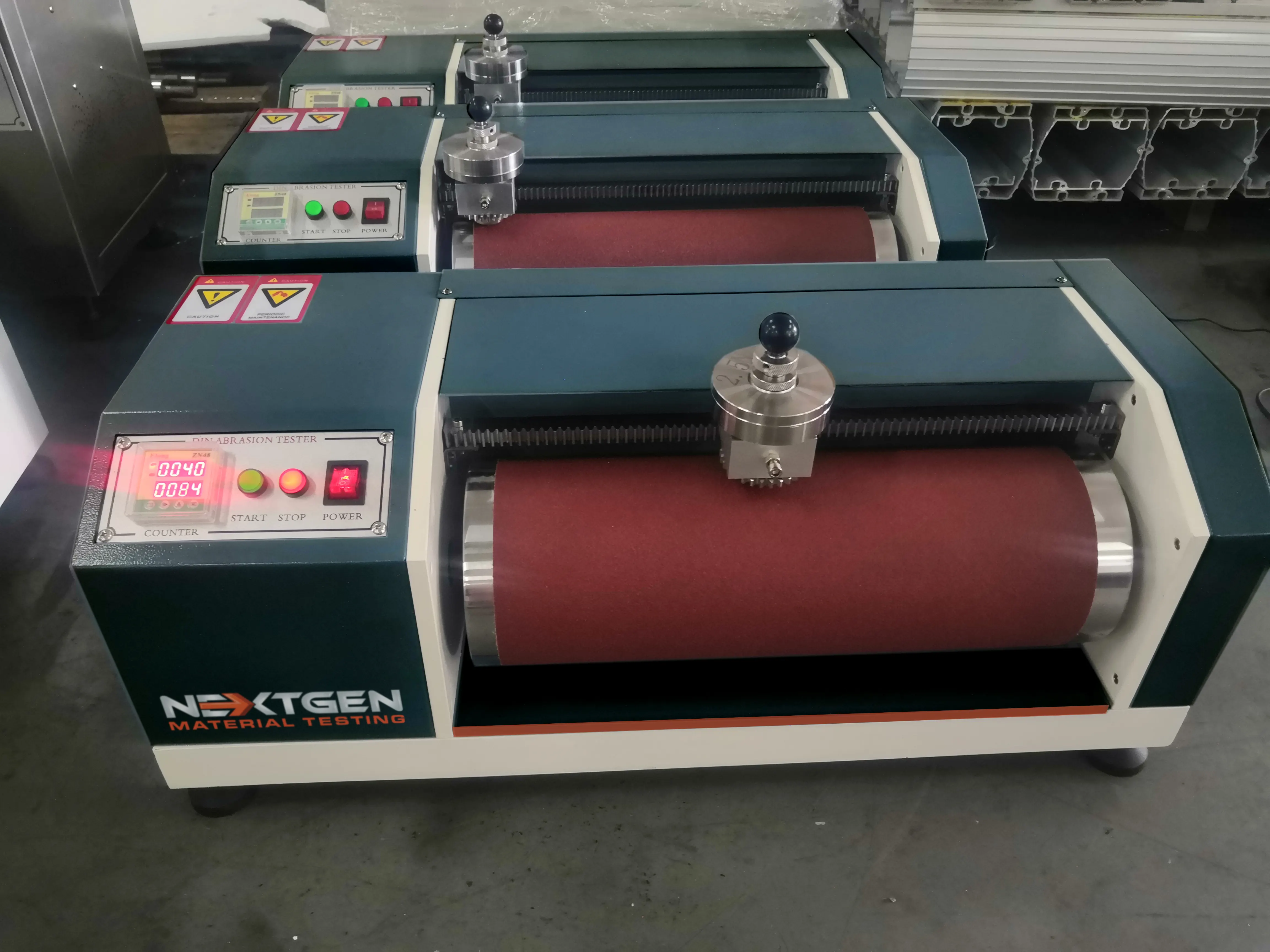

A DIN abrasion tester is a machine that measures the abrasion resistance of rubbers, including thermoplastic elastomers and vulcanized thermoset rubbers.
The abrasion resistance of different types of rubbers is measured in order to quantify how well they resist wear and tear during their actual service. Several test methods are used to simulate long-term wear, including DIN (German Institute for Standardization) abrasion tests.
DIN Abrasion Testing

One method used to quantify the wear resistance of rubber is DIN abrasion testing. The samples used in this test include tires, soles, or any rubber material that undergoes a lot of stress in their actual service.
The DIN abrasion test is also useful in evaluating the wear resistance of rubber material used in making rubber floor coverings and hoses.
A DIN tester is used to ensure that only quality and durable materials are used in manufacturing products that use rubber as a component.
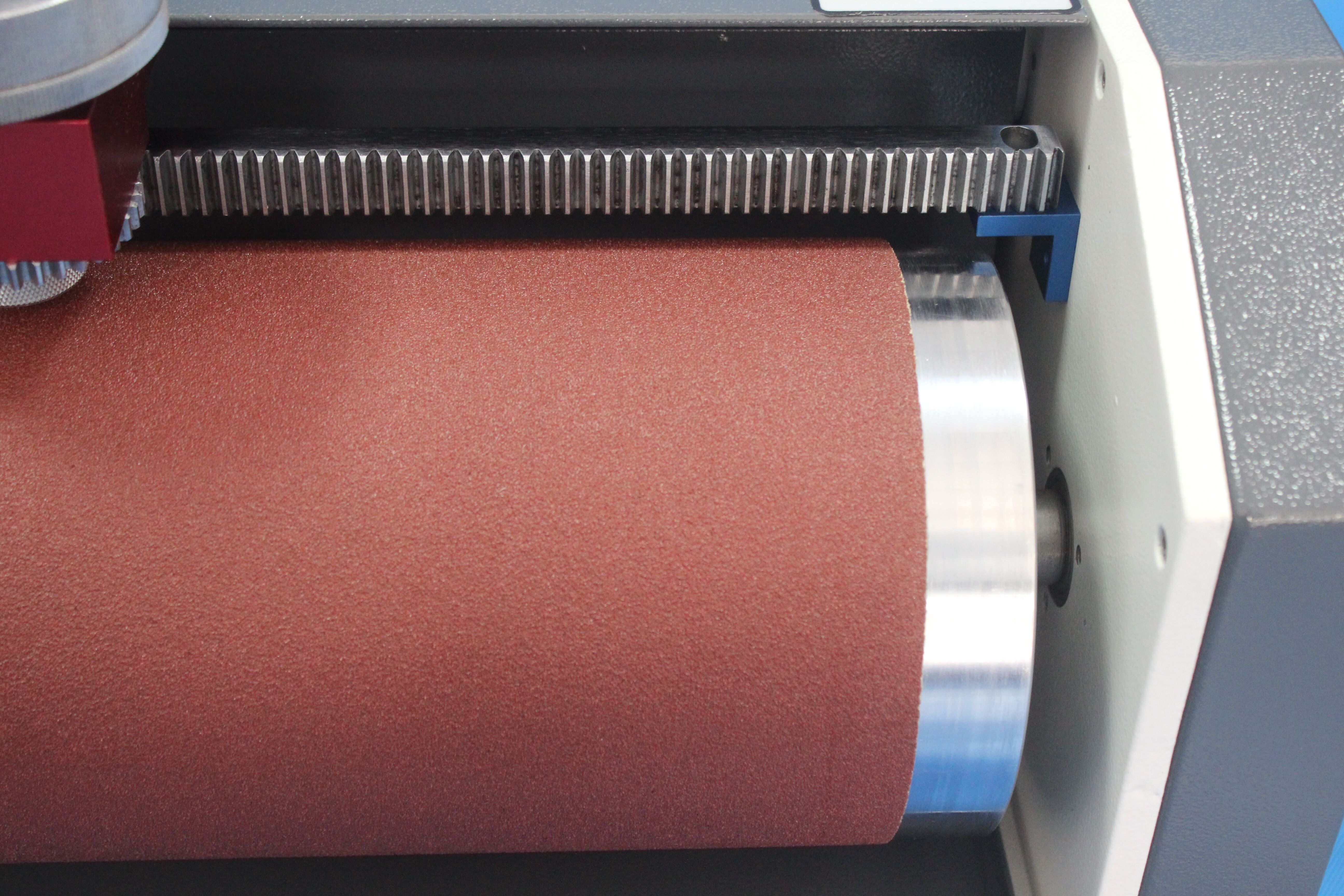
A DIN abrasion test is accomplished by moving a piece of rubber against an abrasive material or sheet mounted on a spinning drum, also called a rotary drum abrader. The amount of material that will be scraped away in the abrasion process is expressed as volume loss in cubic millimeters or as a resistance index expressed in percent.
If the test results in a high amount of volume loss, it denotes that the material is low in quality and durability. Conversely, if the resistance index is high, then the material under testing has a high level of durability.
However, like other material quality assurance tests, the DIN rubber abrasion test does not provide the actual condition of how it will perform in its actual service. At best, the test can only give close estimates.
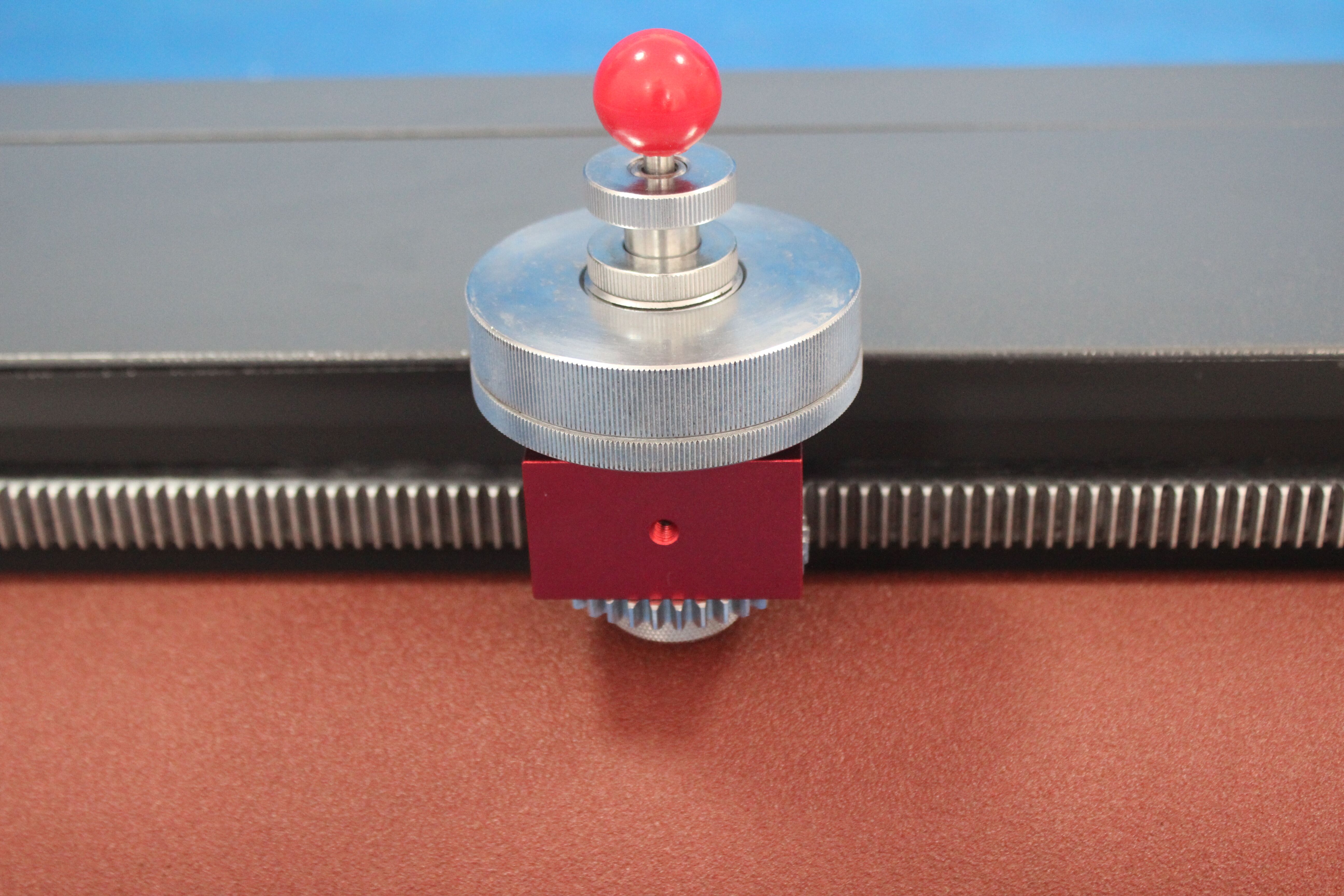
The DIN rubber abrasion testing technique requires only a few steps to complete. Prepare a sample for the testing, preferably around 16 mm in length. Check for the initial weight of your sample.
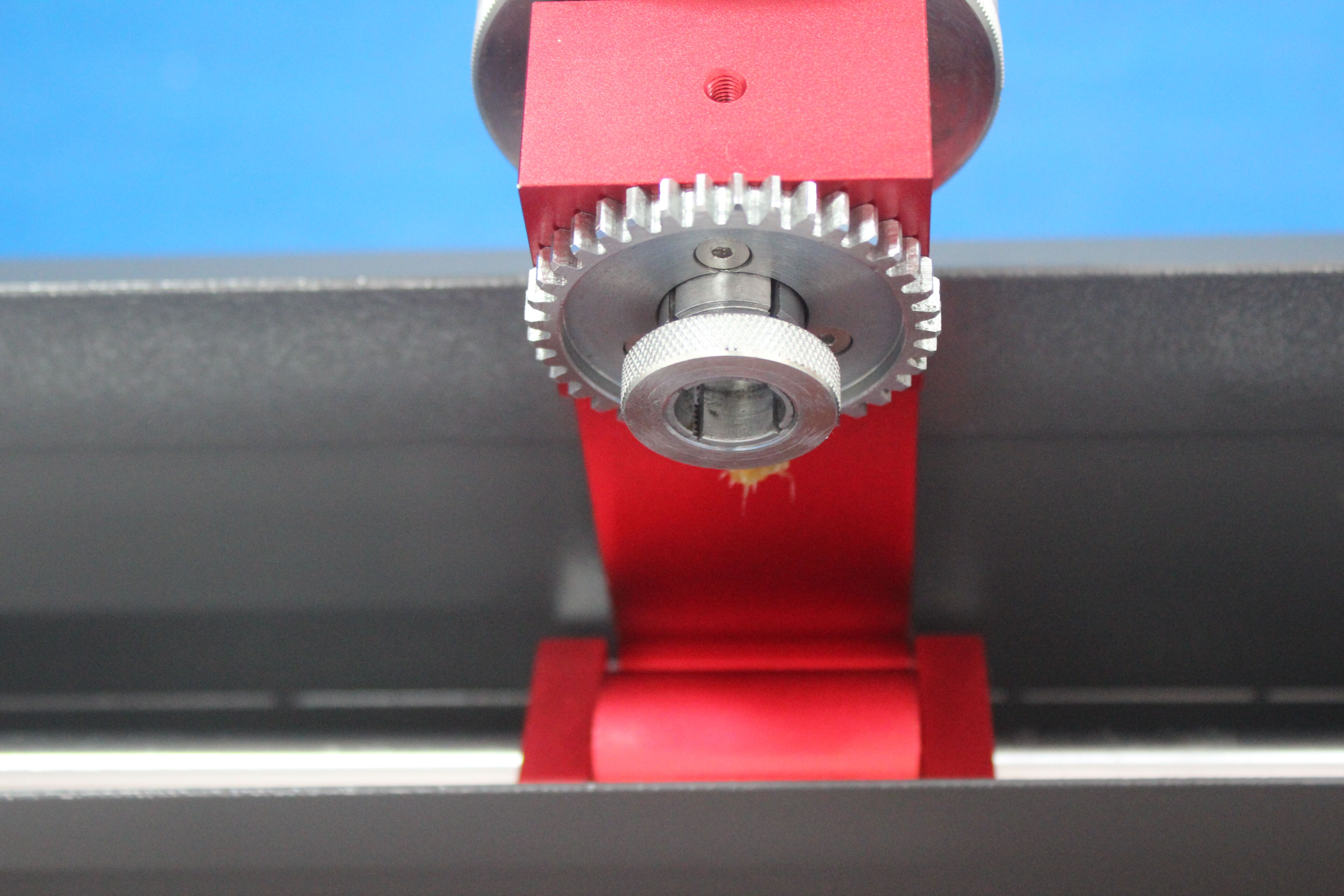
Fit the sample in the tester’s sample holder. Now, switch on the power supply. You will see the sample continuously moving from left to right through a rocker switch that rubs the sample against the revolving drum.
When the test cycle is complete, remove the sample and weigh it again. The difference between the initial and final figures represents the loss in volume achieved through the test.
Rotary Drum
Rotary drum tests are conducted with strict compliance to testing standards ISO 4649 and ASTM D5963. The specimen for testing is moved laterally against a rotating cylinder, and the specimen holder should be firmly fixed in position. This standard guarantees uniform abrasion across the test material.
The technique of using a rotary drum to serve as the abrasive tool is primarily applicable to rubber materials used in polymeric footwear soles and other polymer-based parts or products.
Different Rubber Testing Standards
This section covers different rubber testing standards for different types of rubber materials. Use them as your reference for determining which standard applies best to the rubber material you need to test.
ASTM D5963
A wide range of industries uses the ASTM D5963-04 abrasion standards for testing materials to use in their products. These industries include R&D facilities, aerospace, leather, and textile. Small and large-sized companies use this standard consistently as an essential part of their quality control.
The types of products that often use this standard as a basis for selecting quality materials include:
- Conveyor belts
- Tires
- Hoses
- Automotive Belts
- Footwear
- Flooring
- Suitcases
- Carpets
- Plastic Coating
- Varnish
- Traffic Paint
- Electronic Components
- Dental materials
- Automotive Interiors
- Furniture
- Resins




The tester checks the weight loss of the sample’s outer surface, such as mechanical damage and amount of scraped material.
The test employed is a quick and simple method of measuring wear resistance and offers comparable data. It can provide side-by-side comparisons of different grades of materials, so you can assess the material with a better wear resistance under simulated wear conditions.
ISO 4649
ISO 4649 is a rubber testing standard that identifies two ways of determining wear resistance. The standard also specifies the use of a gyrating cylinder to produce the abrasion effect.
The two different methods involve either a revolving or a non-revolving test piece. In either case, the abrasive action is provided by a specific grade of abrasive panels, and similarly, with the ASTM D5963, the test results are expressed in volume loss or abrasion resistance index.
The ISO 4649 requires that the test piece holder of the testing machine has a cylindrical opening with a diameter that can be adjusted from 15.5 mm to 16.3 mm.
The lateral displacement of the holder must be around 4.20 mm for every revolution of the drum. Appropriate attachments may be used to rotate the test piece preferably at an additional rate of one revolution for every 50 revolutions of the cylindrical abrader.



DIN 53516
The DIN 53516 rubber testing standard also works for the determination of abrasion resistance under a spinning abrasive device. The standard is acceptable in terms of rating various rubber compounds that engineers, operators, and manufacturers use in creating products.
However, the test that can be employed based on this standard may not be that comprehensive, as it does not take into account other important aspects of material testing, such as pressure, turbulence, edge sharpness, rock morphology, and temperature.
In addition, the standard does not also require tests to provide data on material degradation on the account of the difference in tensile strength, elastic modulus, or applied stress.
The machine required for testing must have a machine frame that includes a specimen holder, an electric motor for spinning the cylindrical drum, and a metal housing.
Basically, the methods that conform to ISO 4649 and DIN 53516 are perceived to be the ways of imitating long-term damage and ravages of usage and time.



AS 1683.21
Along with the other standards of rubber testing, the Australian Standard AS 1683.21 lays down the right conditions for abrasive resistance assessments.
The 1683.21 standard specifically notes that rubber material testing is important mainly for products loaded with friction during their use. Examples of these products include covering layers of conveyor belts, tire treads, and tire protectors.
This standard requires that test pieces should be tested with a piece of roller with a diameter of 16 mm and a minimum elevation of 6 mm. The cylindrical abrasive device should also be covered with an abrasive agent, with Alumina grains (Al203) as the standard abrasive agent.
For this standard, it is required that the reference compound should have a weight loss of 180 – 220 mg after completing a rubbing path of 40 mm under a pressure of 10 N.
Before testing, the testing piece is reground, and its weight is measured. Then it is subjected to the rubbing action of the abrasive agent covering the rotating cylindrical drum.
The weight loss is calculated after coverage of a 40-meter path, or you may opt to calculate for the abrasive resistance index instead, depending on your requirements.



Importance of Abrasion Test for Rubber Materials
Abrasion resistance refers to the capacity of materials to resist abrasion. Abrasion is the process through which materials lose volume or mass by way of friction.
The ability to resist abrasion keeps the material’s structure and looks intact.
Highly abrasion-resistant materials are desirable for both fixed and moving parts in a setting where wearing is an issue.
When friction is the predominant cause of deterioration of materials, abrasion wear testing is one of the most effective tests to employ in such situations. It can provide you with valuable data when testing materials of different grades to help you predict the lifespan of your product.
Abrasion tests are appropriate for R&D, compliance testing, quality control, and comparative testing.

Calculating Rubber Abrasion Resistance
Depending on your preference, you can calculate either the volume loss or the resistance index of the material under testing.
For volume loss, the formula is Vloss = Mt x Mconst/ Pt x Mr, where:
Mt = mass loss (in mg)
Mconst = mass loss (based on a standard reference compound)
Pt = density of the rubber material (in mg/cubic millimeter)
Mr = Mass loss of the reference compound
For the resistance index, use the formula ARI = Mr x Pt/Mt x Pr, where:
Mr = mass loss (reference compound, in mg)
Mt = mass loss (test rubber, in mg)
Pr = density (test rubber)
Pt = density (reference compound)
Abrasion Testing Related Definitions
Abrasion resistance – This expression refers to the ability to withstand wear and tear when a material is subjected to friction. Abrasion resistance testing is one of the best ways to test materials usually subjected to repetitive scraping and rubbing.
Relative volume loss – refers to the volume loss of a test rubber piece after having been subjected to abrasion using an abrasive sheet. The abrasion test compares the result to a reference compound with its predefined mass loss under the same test conditions.
Smearing rubber – A rubber material that, when interposed between consecutive tests (for standard rubbers), entails a mass loss higher than 10%.
For any questions or clarifications, get in touch with the technical specialists from NextGen Material Testing, Inc. We are a provider of metal, rubber, and plastic testing equipment and can help you decide the best equipment to use for all your quality control needs.